Python中的字符串切片
Python切片是关于通过从头到尾分别切片来从给定字符串中获取子字符串。
Python切片可以通过两种方式完成。
- slice() 构造函数
- 扩展索引
slice() 构造函数
slice()构造函数创建一个切片对象,表示由 range(start, stop, step) 指定的索引集。
Syntax:
- slice(stop)
- slice(start, stop, step)
Parameters:
start: Starting index where the slicing of object starts.
stop: Ending index where the slicing of object stops.
step: It is an optional argument that determines the increment between each index for slicing.
Return Type: Returns a sliced object containing elements in the given range only.
正负索引的索引跟踪器:
反向跟踪字符串时会考虑负数。
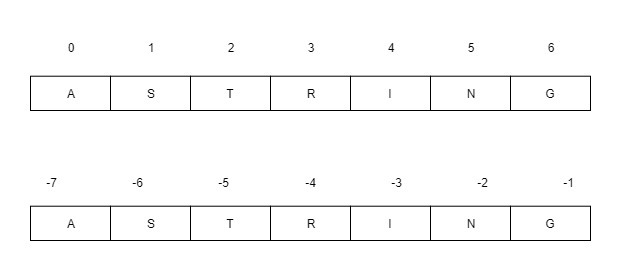
例子
# Python program to demonstrate
# string slicing
# String slicing
String ='ASTRING'
# Using slice constructor
s1 = slice(3)
s2 = slice(1, 5, 2)
s3 = slice(-1, -12, -2)
print("String slicing")
print(String[s1])
print(String[s2])
print(String[s3])
输出:
String slicing
AST
SR
GITA
扩展索引
在Python中,索引语法可以用作切片对象的替代品。这是一种在语法方面和执行方面对字符串进行切片的简单方便的方法。
句法
string[start:end:step] start、end 和 step 与slice()构造函数具有相同的机制。
例子
# Python program to demonstrate
# string slicing
# String slicing
String ='ASTRING'
# Using indexing sequence
print(String[:3])
print(String[1:5:2])
print(String[-1:-12:-2])
# Prints string in reverse
print("\nReverse String")
print(String[::-1])
输出:
AST
SR
GITA
Reverse String
GNIRTSA
注意:要了解有关字符串的更多信息,请单击此处。