Python中的嵌套if语句
现实生活中会出现一些情况,当我们需要做出一些决定时,我们会根据这些决定决定下一步应该做什么。在编程中也会出现类似的情况,我们需要做出一些决定,并基于这些决定,我们将执行下一个代码块。这是在Python中的决策语句的帮助下完成的。
例子:
# Python program to demonstrate
# decision making
i = 20;
if (i < 15):
print ("i is smaller than 15")
print ("i'm in if Block")
else:
print ("i is greater than 15")
print ("i'm in else Block")
print ("i'm not in if and not in else Block")
输出:
i is greater than 15
i'm in else Block
i'm not in if and not in else Block嵌套 if 语句
我们可以在另一个 if...elif...else 语句中包含一个 if...elif...else 语句。这在计算机编程中称为嵌套。任意数量的这些语句都可以相互嵌套。缩进是确定嵌套级别的唯一方法。这可能会让人感到困惑,所以如果可以的话,必须避免它。
句法:
if (condition1):
# Executes when condition1 is true
if (condition2):
# Executes when condition2 is true
# if Block is end here
# if Block is end here流程图
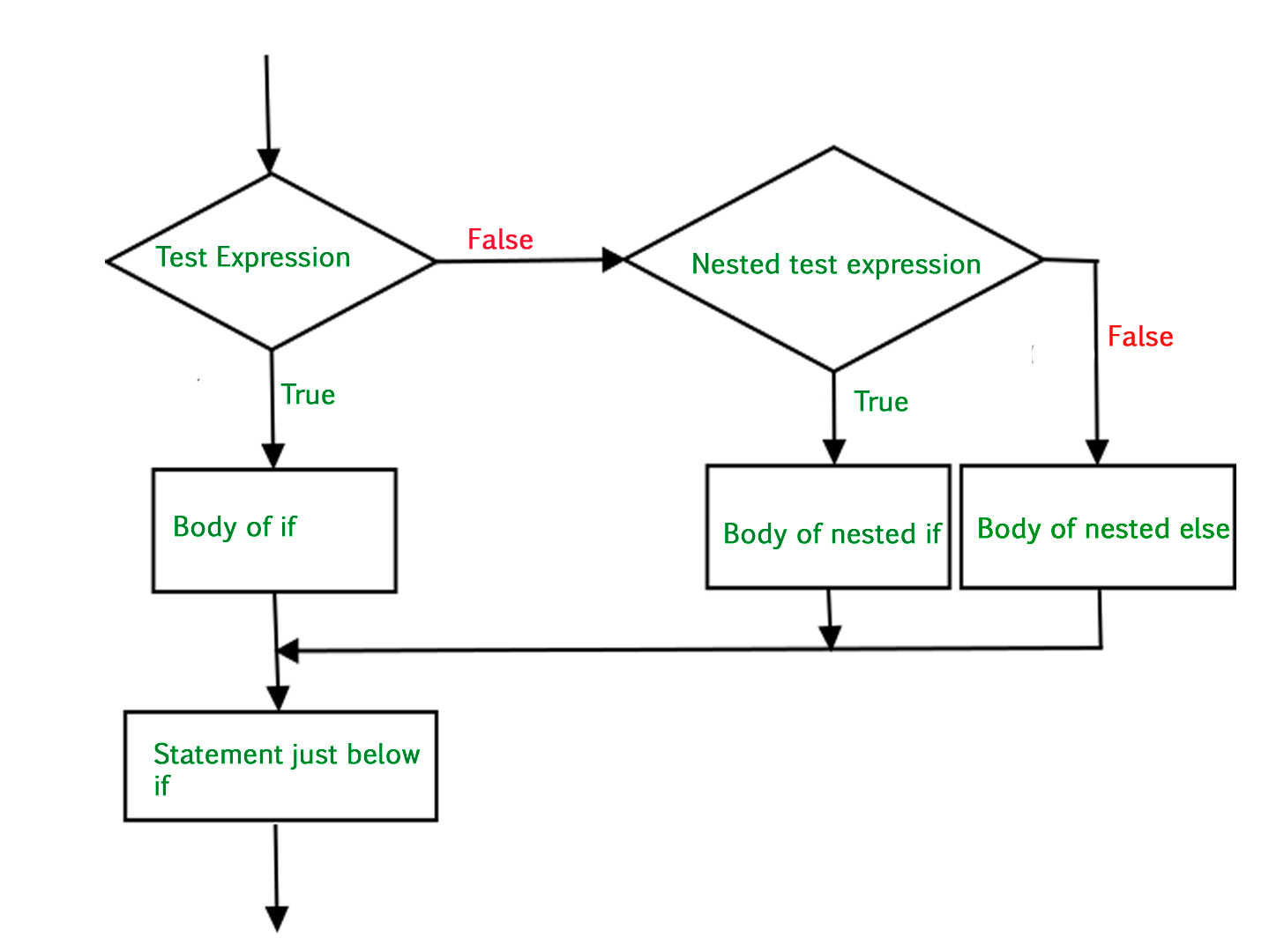
示例 1:
# Python program to demonstrate
# nested if statement
num = 15
if num >= 0:
if num == 0:
print("Zero")
else:
print("Positive number")
else:
print("Negative number")
输出:
Positive number
示例 2:
# Python program to demonstrate
# nested if statement
i = 13
if (i == 13):
# First if statement
if (i < 15):
print ("i is smaller than 15")
# Nested - if statement
# Will only be executed if statement above
# it is true
if (i < 12):
print ("i is smaller than 12 too")
else:
print ("i is greater than 12 and smaller than 15")
输出:
i is smaller than 15
i is greater than 12 and smaller than 15