在本文中,讨论了检查数字是否为质数的试算法。给定数字N,任务是检查数字是否为质数。
例子:
Input: N = 433
Output: Prime
Explanation:
The only factors of 433 are 1 and 433. Therefore, it is a prime.
Input: N = 1263
Output: Composite
Explanation:
The factors of 1263 are 1, 3, 421, 1263. Therefore, it is a composite number.
天真的方法:根据定义,素数是大于1的整数,只能被1及其自身整除。因此,我们初始化一个从2到N – 1的循环,并检查可除性。以下是该方法的伪代码:
N <- input
initialise: i <- 2
while(i ≤ N - 1):
if(N % i == 0):
return "Composite"
return "Prime"
时间复杂度分析:
- 对于任何给定的数字N ,while循环运行N – 2次。因此,while循环的时间复杂度为O(N) 。
- 可除性检查是在固定时间内完成的。因此,while循环中if条件的时间复杂度为O(1) 。
- 因此,上述方法的总时间复杂度为O(N) 。
审判分割法:通过审判分割法的概念可以更有效地执行素数检查。当处理整数分解时,Trial Division方法是关键但最简单的分解技术之一。
观察:上述方法适用于观察到任何数字N的最大因数始终小于或等于平方根(N)。该结论可以通过以下方式得出:
- 从学校算法来看,众所周知的事实是,任何复合数都是由两个或多个质数构成的。
- 令N的因子为n1,n2,依此类推。仅当数量N存在两个因子n1和n2时,这些因子才最大。
- 因此,假设n1和n2是数量N的两个最大因子。仅当n1和n2相等时,这些数字n1和n2才能最大。
- 令n1 = n2 = n 。因此, N = n * n 。因此,N的最大可能因数是平方根(N) 。
方法:根据以上观察,该算法的方法很简单。这个想法不是检查直到N – 1的一个因数,我们只检查直到平方根(N) 。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// CPP implementation of
// Trial Division Algorithm
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to check if a number is
// a prime number or not
int TrialDivision(int N){
// Initializing with the value 2
// from where the number is checked
int i = 2;
// Computing the square root of
// the number N
int k = ceil(sqrt(N));
// While loop till the
// square root of N
while(i<= k){
// If any of the numbers between
// [2, sqrt(N)] is a factor of N
// Then the number is composite
if(N % i == 0)
return 0;
i += 1;
}
// If none of the numbers is a factor,
// then it is a prime number
return 1;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int N = 49;
int p = TrialDivision(N);
// To check if a number is a prime or not
if(p)
cout << ("Prime");
else
cout << ("Composite");
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29 Java
// Java implementation of
// Trial Division Algorithm
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to check if a number is
// a prime number or not
static int TrialDivision(int N){
// Initializing with the value 2
// from where the number is checked
int i = 2;
// Computing the square root of
// the number N
int k =(int) Math.ceil(Math.sqrt(N));
// While loop till the
// square root of N
while(i<= k){
// If any of the numbers between
// [2, sqrt(N)] is a factor of N
// Then the number is composite
if(N % i == 0)
return 0;
i += 1;
}
// If none of the numbers is a factor,
// then it is a prime number
return 1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 49;
int p = TrialDivision(N);
// To check if a number is a prime or not
if(p != 0)
System.out.print("Prime");
else
System.out.print("Composite");
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110Python3
# Python3 implementation of
# Trial Division Algorithm
# Function to check if a number is
# a prime number or not
def TrialDivision(N):
# Initializing with the value 2
# from where the number is checked
i = 2
# Computing the square root of
# the number N
k = int(N ** 0.5)
# While loop till the
# square root of N
while(i<= k):
# If any of the numbers between
# [2, sqrt(N)] is a factor of N
# Then the number is composite
if(N % i == 0):
return 0
i += 1
# If none of the numbers is a factor,
# then it is a prime number
return 1
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 49
p = TrialDivision(N)
# To check if a number is a prime or not
if(p):
print("Prime")
else:
print("Composite")C#
// C# implementation of
// Trial Division Algorithm
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to check if a number is
// a prime number or not
static int TrialDivision(int N){
// Initializing with the value 2
// from where the number is checked
int i = 2;
// Computing the square root of
// the number N
int k =(int) Math.Ceiling(Math.Sqrt(N));
// While loop till the
// square root of N
while(i<= k){
// If any of the numbers between
// [2, sqrt(N)] is a factor of N
// Then the number is composite
if(N % i == 0)
return 0;
i += 1;
}
// If none of the numbers is a factor,
// then it is a prime number
return 1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int N = 49;
int p = TrialDivision(N);
// To check if a number is a prime or not
if(p != 0)
Console.Write("Prime");
else
Console.Write("Composite");
}
}
// This codee is contributed by AbhiThakurComposite
时间复杂度分析:
- while循环最多执行平方根(N)次。因此,while循环的时间复杂度为O(sqrt(N)) 。
- 所有if条件的运行时间都是恒定的。因此,if语句的时间复杂度为O(1) 。
- 因此,总体时间复杂度为O(sqrt(N)) 。
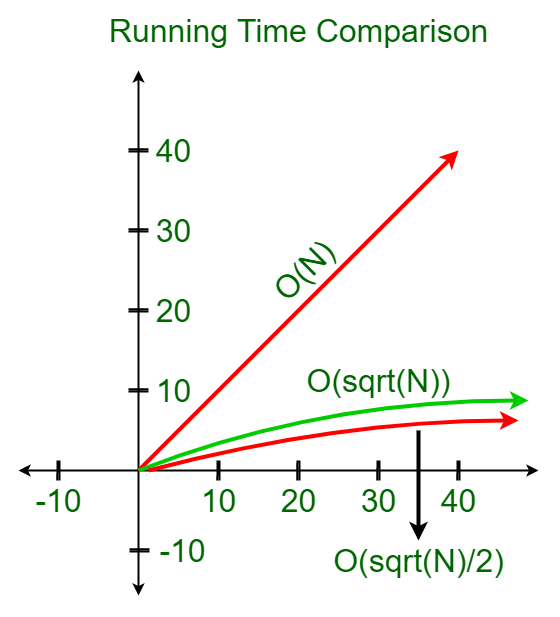
优化的试验划分方法:可以通过消除范围[2,K]中的所有偶数来进一步优化上述试验划分方法,其中K =平方根(N),因为2是唯一的偶数素数。总体复杂度仍然保持不变,但是执行次数减少了一半。
注意:在Trial Division方法中进行的优化可能看起来很小,因为除了迭代次数外,该方法与Naive Approach几乎相似。但是,这极大地减少了较高N值的计算数量。这可以通过以下图表相对于算法的相应运行时间来绘制来说明: