Wedderburn-Etherington数字序列中的第N个项(从n = 0的数字0开始)计算具有n个叶子的无序根树的数量,其中包括根的所有节点都具有零个或恰好有两个子代。
对于给定的N。任务是找到序列的前N个项。
顺序:
0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 6, 11, 23, 46, 98, 207, 451, 983, 2179, 4850, 10905, 24631, 56011, ….
带有0或2个孩子的树: 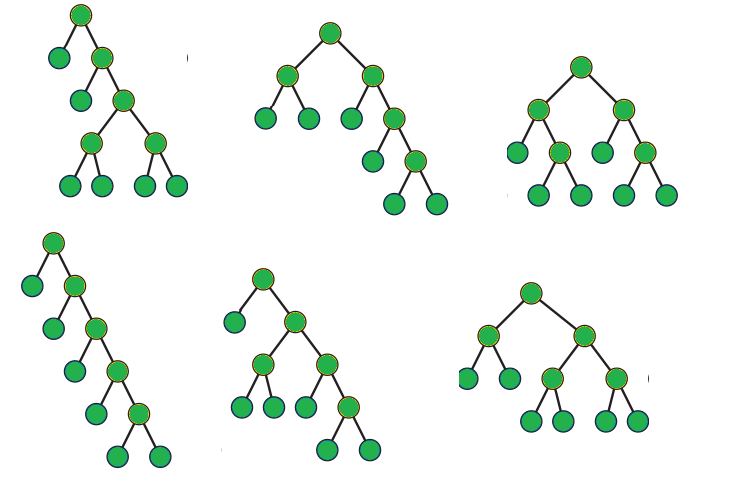
例子:
Input : N = 10
Output : 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 6, 11, 23, 46,
Input : N = 20
Output : 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 6, 11, 23, 46, 98, 207, 451, 983, 2179, 4850, 10905, 24631, 56011, 127912
方法:
查找第N个数字的递归关系为:
- a(2x-1)= a(1)* a(2x-2)+ a(2)* a(2x-3)+…+ a(x-1)* a(x)
- a(2x)= a(1)* a(2x-1)+ a(2)* a(2x-2)+…+ a(x-1)* a(x + 1)+ a(x)* (a(x)+1)/ 2
使用上述关系式,我们可以找到级数的第i个项。我们将从第0个词开始,然后将答案存储在地图中,然后使用地图中的值找到该序列的第i + 1个词。我们还将对第0、1和2nd个元素分别使用0、1、1的基本情况。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// CPP program to find N terms of the sequence
#include
using namespace std;
// Stores the Wedderburn Etherington numbers
map store;
// Function to return the nth
// Wedderburn Etherington numbers
int Wedderburn(int n)
{
// Base case
if (n <= 2)
return store[n];
// If n is even n = 2x
else if (n % 2 == 0)
{
// get x
int x = n / 2, ans = 0;
// a(2x) = a(1)a(2x-1) + a(2)a(2x-2) + ... +
// a(x-1)a(x+1)
for (int i = 1; i < x; i++) {
ans += store[i] * store[n - i];
}
// a(x)(a(x)+1)/2
ans += (store[x] * (store[x] + 1)) / 2;
// Store the ans
store[n] = ans;
// Return the required answer
return ans;
}
else
{
// If n is odd
int x = (n + 1) / 2, ans = 0;
// a(2x-1) = a(1)a(2x-2) + a(2)a(2x-3) + ... +
// a(x-1)a(x),
for (int i = 1; i < x; i++) {
ans += store[i] * store[n - i];
}
// Store the ans
store[n] = ans;
// Return the required answer
return ans;
}
}
// Function to print first N
// Wedderburn Etherington numbers
void Wedderburn_Etherington(int n)
{
// Store first 3 numbers
store[0] = 0;
store[1] = 1;
store[2] = 1;
// Print N terms
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << Wedderburn(i);
if(i!=n-1)
cout << ", ";
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 10;
// function call
Wedderburn_Etherington(n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find N terms of the sequence
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Stores the Wedderburn Etherington numbers
static HashMap store = new HashMap();
// Function to return the nth
// Wedderburn Etherington numbers
static int Wedderburn(int n)
{
// Base case
if (n <= 2)
return store.get(n);
// If n is even n = 2x
else if (n % 2 == 0)
{
// get x
int x = n / 2, ans = 0;
// a(2x) = a(1)a(2x-1) + a(2)a(2x-2) + ... +
// a(x-1)a(x+1)
for (int i = 1; i < x; i++)
{
ans += store.get(i) * store.get(n - i);
}
// a(x)(a(x)+1)/2
ans += (store.get(x) * (store.get(x) + 1)) / 2;
// Store the ans
store. put(n, ans);
// Return the required answer
return ans;
}
else
{
// If n is odd
int x = (n + 1) / 2, ans = 0;
// a(2x-1) = a(1)a(2x-2) + a(2)a(2x-3) + ... +
// a(x-1)a(x),
for (int i = 1; i < x; i++)
{
ans += store.get(i) * store.get(n - i);
}
// Store the ans
store. put(n, ans);
// Return the required answer
return ans;
}
}
// Function to print first N
// Wedderburn Etherington numbers
static void Wedderburn_Etherington(int n)
{
// Store first 3 numbers
store. put(0, 0);
store. put(1, 1);
store. put(2, 1);
// Print N terms
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
System.out.print(Wedderburn(i));
if(i != n - 1)
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 10;
// function call
Wedderburn_Etherington(n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh Python3
# Python3 program to find N terms
# of the sequence
# Stores the Wedderburn Etherington numbers
store = dict()
# Function to return the nth
# Wedderburn Etherington numbers
def Wedderburn(n):
# Base case
if (n <= 2):
return store[n]
# If n is even n = 2x
elif (n % 2 == 0):
# get x
x = n // 2
ans = 0
# a(2x) = a(1)a(2x-1) + a(2)a(2x-2) + ... +
# a(x-1)a(x+1)
for i in range(1, x):
ans += store[i] * store[n - i]
# a(x)(a(x)+1)/2
ans += (store[x] * (store[x] + 1)) // 2
# Store the ans
store[n] = ans
# Return the required answer
return ans
else:
# If n is odd
x = (n + 1) // 2
ans = 0
# a(2x-1) = a(1)a(2x-2) + a(2)a(2x-3) + ... +
# a(x-1)a(x),
for i in range(1, x):
ans += store[i] * store[n - i]
# Store the ans
store[n] = ans
# Return the required answer
return ans
# Function to prfirst N
# Wedderburn Etherington numbers
def Wedderburn_Etherington(n):
# Store first 3 numbers
store[0] = 0
store[1] = 1
store[2] = 1
# PrN terms
for i in range(n):
print(Wedderburn(i), end = "")
if(i != n - 1):
print(end = ", ")
# Driver code
n = 10
# function call
Wedderburn_Etherington(n)
# This code is contributed by Mohit KumarC#
// C# program to find N terms of the sequence
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Stores the Wedderburn Etherington numbers
static Dictionary store = new Dictionary();
// Function to return the nth
// Wedderburn Etherington numbers
static int Wedderburn(int n)
{
// Base case
if (n <= 2)
return store[n];
// If n is even n = 2x
else if (n % 2 == 0)
{
// get x
int x = n / 2, ans = 0;
// a(2x) = a(1)a(2x-1) + a(2)a(2x-2) + ... +
// a(x-1)a(x+1)
for (int i = 1; i < x; i++)
{
ans += store[i] * store[n - i];
}
// a(x)(a(x)+1)/2
ans += (store[x] * (store[x] + 1)) / 2;
// Store the ans
if(store.ContainsKey(n))
{
store.Remove(n);
store.Add(n, ans);
}
else
store.Add(n, ans);
// Return the required answer
return ans;
}
else
{
// If n is odd
int x = (n + 1) / 2, ans = 0;
// a(2x-1) = a(1)a(2x-2) + a(2)a(2x-3) + ... +
// a(x-1)a(x),
for (int i = 1; i < x; i++)
{
ans += store[i] * store[n - i];
}
// Store the ans
if(store.ContainsKey(n))
{
store.Remove(n);
store.Add(n, ans);
}
else
store.Add(n, ans);
// Return the required answer
return ans;
}
}
// Function to print first N
// Wedderburn Etherington numbers
static void Wedderburn_Etherington(int n)
{
// Store first 3 numbers
store.Add(0, 0);
store.Add(1, 1);
store.Add(2, 1);
// Print N terms
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
Console.Write(Wedderburn(i));
if(i != n - 1)
Console.Write(" ");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 10;
// function call
Wedderburn_Etherington(n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 输出:
0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 6, 11, 23, 46