我们在下面的文章中介绍了Branch和Bound,并讨论了0/1背包问题。
- 分界线|套装1(带0/1背包的简介)
- 分界线|第2组(0/1背包的实施)
在这个难题解决方案中,讨论了8个难题。
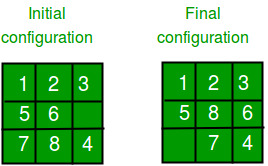
给定一个具有8个图块的3×3板(每个图块都有一个1到8的数字)和一个空白空间。目的是将数字放置在图块上,以使用空白空间匹配最终配置。我们可以将四个相邻的(左,右,上方和下方)磁贴滑动到空白区域。
例如,
1. DFS(蛮力)
我们可以在状态空间(给定问题的所有配置,即可以从初始状态到达的所有状态的集合)上进行深度优先搜索。
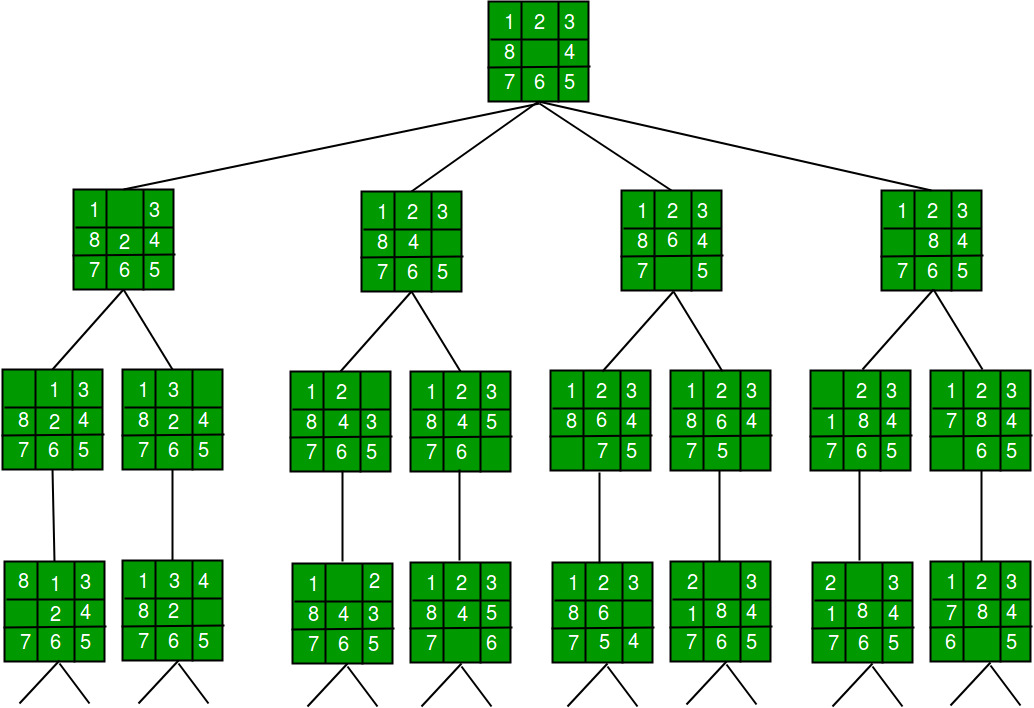
在这种解决方案中,连续的动作可以使我们远离目标,而不是使我们离目标更近。无论初始状态如何,对状态空间树的搜索都遵循从根到最左边的路径。在这种方法中可能永远找不到答案节点。
2. BFS(蛮力)
我们可以在状态空间树上执行广度优先搜索。这总是找到最接近根的目标状态。但是,无论初始状态是什么,该算法都会尝试像DFS一样的顺序移动。
3.分支定界
通常可以通过使用“智能”排名函数(也称为近似成本函数)来加快对答案节点的搜索,以避免在不包含答案节点的子树中进行搜索。它类似于回溯技术,但使用类似BFS的搜索。
分支和绑定基本上涉及三种类型的节点
1.活动节点是已生成但尚未生成其子节点的节点。
2.电子节点是一个活动节点,当前正在探索其子节点。换句话说,E节点是当前正在扩展的节点。
3.死节点是生成的节点,将不再扩展或探索。死节点的所有子节点均已扩展。
成本函数:
搜索树中的每个节点X与一个成本相关联。成本函数对于确定下一个电子节点很有用。下一个电子节点是成本最低的电子节点。成本函数定义为
C(X) = g(X) + h(X) where
g(X) = cost of reaching the current node
from the root
h(X) = cost of reaching an answer node from X. 8难题算法的理想成本函数:
我们假设在任何方向上移动一个图块的成本为1。请记住,我们为8难题算法定义了一个成本函数,如下所示:
c(x) = f(x) + h(x) where
f(x) is the length of the path from root to x
(the number of moves so far) and
h(x) is the number of non-blank tiles not in
their goal position (the number of mis-
-placed tiles). There are at least h(x)
moves to transform state x to a goal state有一种算法可用于获取h(x)的近似值,该近似值是未知值。
完整算法:
/* Algorithm LCSearch uses c(x) to find an answer node
* LCSearch uses Least() and Add() to maintain the list
of live nodes
* Least() finds a live node with least c(x), deletes
it from the list and returns it
* Add(x) adds x to the list of live nodes
* Implement list of live nodes as a min-heap */
struct list_node
{
list_node *next;
// Helps in tracing path when answer is found
list_node *parent;
float cost;
}
algorithm LCSearch(list_node *t)
{
// Search t for an answer node
// Input: Root node of tree t
// Output: Path from answer node to root
if (*t is an answer node)
{
print(*t);
return;
}
E = t; // E-node
Initialize the list of live nodes to be empty;
while (true)
{
for each child x of E
{
if x is an answer node
{
print the path from x to t;
return;
}
Add (x); // Add x to list of live nodes;
x->parent = E; // Pointer for path to root
}
if there are no more live nodes
{
print ("No answer node");
return;
}
// Find a live node with least estimated cost
E = Least();
// The found node is deleted from the list of
// live nodes
}
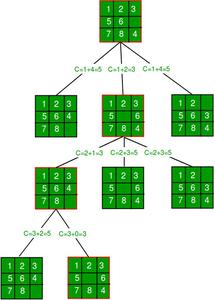
}下图显示了上述算法从8拼图的给定初始配置到达最终配置所遵循的路径。注意,仅具有最小成本函数值的节点被扩展。
C++14
// Program to print path from root node to destination node
// for N*N -1 puzzle algorithm using Branch and Bound
// The solution assumes that instance of puzzle is solvable
#include
using namespace std;
#define N 3
// state space tree nodes
struct Node
{
// stores the parent node of the current node
// helps in tracing path when the answer is found
Node* parent;
// stores matrix
int mat[N][N];
// stores blank tile coordinates
int x, y;
// stores the number of misplaced tiles
int cost;
// stores the number of moves so far
int level;
};
// Function to print N x N matrix
int printMatrix(int mat[N][N])
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
printf("%d ", mat[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
// Function to allocate a new node
Node* newNode(int mat[N][N], int x, int y, int newX,
int newY, int level, Node* parent)
{
Node* node = new Node;
// set pointer for path to root
node->parent = parent;
// copy data from parent node to current node
memcpy(node->mat, mat, sizeof node->mat);
// move tile by 1 position
swap(node->mat[x][y], node->mat[newX][newY]);
// set number of misplaced tiles
node->cost = INT_MAX;
// set number of moves so far
node->level = level;
// update new blank tile cordinates
node->x = newX;
node->y = newY;
return node;
}
// bottom, left, top, right
int row[] = { 1, 0, -1, 0 };
int col[] = { 0, -1, 0, 1 };
// Function to calculate the number of misplaced tiles
// ie. number of non-blank tiles not in their goal position
int calculateCost(int initial[N][N], int final[N][N])
{
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
if (initial[i][j] && initial[i][j] != final[i][j])
count++;
return count;
}
// Function to check if (x, y) is a valid matrix cordinate
int isSafe(int x, int y)
{
return (x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < N);
}
// print path from root node to destination node
void printPath(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
printPath(root->parent);
printMatrix(root->mat);
printf("\n");
}
// Comparison object to be used to order the heap
struct comp
{
bool operator()(const Node* lhs, const Node* rhs) const
{
return (lhs->cost + lhs->level) > (rhs->cost + rhs->level);
}
};
// Function to solve N*N - 1 puzzle algorithm using
// Branch and Bound. x and y are blank tile coordinates
// in initial state
void solve(int initial[N][N], int x, int y,
int final[N][N])
{
// Create a priority queue to store live nodes of
// search tree;
priority_queue, comp> pq;
// create a root node and calculate its cost
Node* root = newNode(initial, x, y, x, y, 0, NULL);
root->cost = calculateCost(initial, final);
// Add root to list of live nodes;
pq.push(root);
// Finds a live node with least cost,
// add its childrens to list of live nodes and
// finally deletes it from the list.
while (!pq.empty())
{
// Find a live node with least estimated cost
Node* min = pq.top();
// The found node is deleted from the list of
// live nodes
pq.pop();
// if min is an answer node
if (min->cost == 0)
{
// print the path from root to destination;
printPath(min);
return;
}
// do for each child of min
// max 4 children for a node
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
if (isSafe(min->x + row[i], min->y + col[i]))
{
// create a child node and calculate
// its cost
Node* child = newNode(min->mat, min->x,
min->y, min->x + row[i],
min->y + col[i],
min->level + 1, min);
child->cost = calculateCost(child->mat, final);
// Add child to list of live nodes
pq.push(child);
}
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Initial configuration
// Value 0 is used for empty space
int initial[N][N] =
{
{1, 2, 3},
{5, 6, 0},
{7, 8, 4}
};
// Solvable Final configuration
// Value 0 is used for empty space
int final[N][N] =
{
{1, 2, 3},
{5, 8, 6},
{0, 7, 4}
};
// Blank tile coordinates in initial
// configuration
int x = 1, y = 2;
solve(initial, x, y, final);
return 0;
} 输出 :
1 2 3
5 6 0
7 8 4
1 2 3
5 0 6
7 8 4
1 2 3
5 8 6
7 0 4
1 2 3
5 8 6
0 7 4