给定一个有向图G,它具有N个顶点和M个边。任务是在Graph中找到最长的有向路径的长度。
注意:定向路径的长度是其中的边数。
例子:
Input: N = 4, M = 5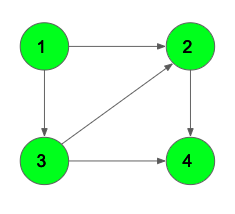
Output: 3
The directed path 1->3->2->4
Input: N = 5, M = 8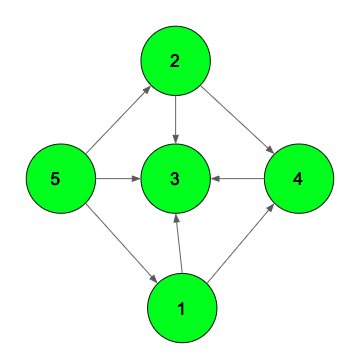
Output: 3
简单方法:天真的方法是使用DFS计算来自每个节点的最长路径的长度。
该方法的时间复杂度为O(N 2 )。
高效的方法:一种有效的方法是将动态编程和DFS一起使用以在图形中找到最长的路径。
令dp [i]为从节点i开始的最长路径的长度。最初dp的所有位置均为0。我们可以从每个节点调用DFS函数,并遍历其所有子节点。递归公式将是:
dp[node] = max(dp[node], 1 + max(dp[child1], dp[child2], dp[child3]..))
最后,检查dp []数组中的最大值,它将是DAG中的最长路径。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to find the longest
// path in the DAG
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to traverse the DAG
// and apply Dynamic Programming
// to find the longest path
void dfs(int node, vector adj[], int dp[], bool vis[])
{
// Mark as visited
vis[node] = true;
// Traverse for all its children
for (int i = 0; i < adj[node].size(); i++) {
// If not visited
if (!vis[adj[node][i]])
dfs(adj[node][i], adj, dp, vis);
// Store the max of the paths
dp[node] = max(dp[node], 1 + dp[adj[node][i]]);
}
}
// Function to add an edge
void addEdge(vector adj[], int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v);
}
// Function that returns the longest path
int findLongestPath(vector adj[], int n)
{
// Dp array
int dp[n + 1];
memset(dp, 0, sizeof dp);
// Visited array to know if the node
// has been visited previously or not
bool vis[n + 1];
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);
// Call DFS for every unvisited vertex
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis[i])
dfs(i, adj, dp, vis);
}
int ans = 0;
// Traverse and find the maximum of all dp[i]
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ans = max(ans, dp[i]);
}
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 5;
vector adj[n + 1];
// Example-1
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 1, 3);
addEdge(adj, 3, 2);
addEdge(adj, 2, 4);
addEdge(adj, 3, 4);
cout << findLongestPath(adj, n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find the longest
// path in the DAG
import java.util.ArrayList;
// graph class
class Graph
{
int vertices;
ArrayList edge[];
Graph(int vertices)
{
this.vertices = vertices;
edge = new ArrayList[vertices+1];
for (int i = 0; i <= vertices; i++)
{
edge[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
void addEdge(int a,int b)
{
edge[a].add(b);
}
void dfs(int node, ArrayList adj[], int dp[],
boolean visited[])
{
// Mark as visited
visited[node] = true;
// Traverse for all its children
for (int i = 0; i < adj[node].size(); i++)
{
// If not visited
if (!visited[adj[node].get(i)])
dfs(adj[node].get(i), adj, dp, visited);
// Store the max of the paths
dp[node] = Math.max(dp[node], 1 + dp[adj[node].get(i)]);
}
}
// Function that returns the longest path
int findLongestPath( int n)
{
ArrayList adj[] = edge;
// Dp array
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
// Visited array to know if the node
// has been visited previously or not
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n + 1];
// Call DFS for every unvisited vertex
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (!visited[i])
dfs(i, adj, dp, visited);
}
int ans = 0;
// Traverse and find the maximum of all dp[i]
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i]);
}
return ans;
}
}
public class Main
{
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
Graph graph = new Graph(n);
// Example-1
graph.addEdge( 1, 2);
graph.addEdge( 1, 3);
graph.addEdge( 3, 2);
graph.addEdge( 2, 4);
graph.addEdge( 3, 4);
graph.findLongestPath(n);
System.out.println( graph.findLongestPath( n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by SumanSaurav Python3
# Python3 program to find the
# longest path in the DAG
# Function to traverse the DAG
# and apply Dynamic Programming
# to find the longest path
def dfs(node, adj, dp, vis):
# Mark as visited
vis[node] = True
# Traverse for all its children
for i in range(0, len(adj[node])):
# If not visited
if not vis[adj[node][i]]:
dfs(adj[node][i], adj, dp, vis)
# Store the max of the paths
dp[node] = max(dp[node], 1 + dp[adj[node][i]])
# Function to add an edge
def addEdge(adj, u, v):
adj[u].append(v)
# Function that returns the longest path
def findLongestPath(adj, n):
# Dp array
dp = [0] * (n + 1)
# Visited array to know if the node
# has been visited previously or not
vis = [False] * (n + 1)
# Call DFS for every unvisited vertex
for i in range(1, n + 1):
if not vis[i]:
dfs(i, adj, dp, vis)
ans = 0
# Traverse and find the maximum of all dp[i]
for i in range(1, n + 1):
ans = max(ans, dp[i])
return ans
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 5
adj = [[] for i in range(n + 1)]
# Example-1
addEdge(adj, 1, 2)
addEdge(adj, 1, 3)
addEdge(adj, 3, 2)
addEdge(adj, 2, 4)
addEdge(adj, 3, 4)
print(findLongestPath(adj, n))
# This code is contributed by Rituraj JainC#
// C# program to find the longest
// path in the DAG
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// graph class
class Graph
{
public int vertices;
public List []edge;
public Graph(int vertices)
{
this.vertices = vertices;
edge = new List[vertices + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= vertices; i++)
{
edge[i] = new List();
}
}
public void addEdge(int a, int b)
{
edge[a].Add(b);
}
public void dfs(int node, List []adj,
int []dp, Boolean []visited)
{
// Mark as visited
visited[node] = true;
// Traverse for all its children
for (int i = 0; i < adj[node].Count; i++)
{
// If not visited
if (!visited[adj[node][i]])
dfs(adj[node][i], adj, dp, visited);
// Store the max of the paths
dp[node] = Math.Max(dp[node], 1 +
dp[adj[node][i]]);
}
}
// Function that returns the longest path
public int findLongestPath( int n)
{
List []adj = edge;
// Dp array
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
// Visited array to know if the node
// has been visited previously or not
Boolean[] visited = new Boolean[n + 1];
// Call DFS for every unvisited vertex
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (!visited[i])
dfs(i, adj, dp, visited);
}
int ans = 0;
// Traverse and find the maximum of all dp[i]
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
ans = Math.Max(ans, dp[i]);
}
return ans;
}
}
class GFG
{
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
Graph graph = new Graph(n);
// Example-1
graph.addEdge( 1, 2);
graph.addEdge( 1, 3);
graph.addEdge( 3, 2);
graph.addEdge( 2, 4);
graph.addEdge( 3, 4);
graph.findLongestPath(n);
Console.WriteLine(graph.findLongestPath(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh 输出:
3
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)