给定具有V顶点和E边的无向图G ,任务是检查图是否为2边连接。
A graph is said to be 2-edge connected if, on removing any edge of the graph, it still remains connected, i.e. it contains no Bridges.
例子:
Input: V = 8, E = 10

Output: Yes
Explanation:
Given any vertex in the graph, we can reach any other vertex in the graph. Moreover, removing any edge from the graph does not affect its connectivity. So, the graph is said to be 2-edge connected.
Input: V = 8, E = 9
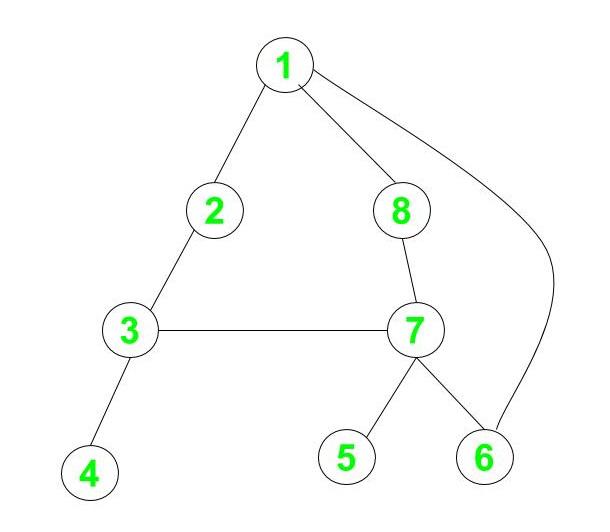
Output: No
Explanation:
On removal of the edge between vertex 3 and vertex 4, the graph is not connected anymore. So, the graph is not 2-edge connected.
幼稚的方法:幼稚的方法是在删除任何边X时检查是否连接了其余图形G –X 。如果在逐个删除每个边时该图保持连接,则它是2边连接图。要实现上述想法,请删除一条边并从任何顶点执行深度优先搜索(DFS)或宽度优先搜索(BFS),并检查是否覆盖了所有顶点。对所有E边重复此过程。如果无法遍历所有顶点的任何边缘,请打印No。否则,打印是。
时间复杂度: O(E *(V + E))
辅助空间: O(1)
高效方法:由于给定图是无向的,因此仅通过计算连接到节点的边数即可解决问题。如果对于任何节点,连接到它的边数为1,则意味着在删除该边时,该节点将断开连接,并且无法从其他任何节点到达,因此该图不是2边连接的。步骤如下:
- 创建一个大小为V的数组noOfEdges [] ,该数组将存储连接到节点的边数。
- 对于每个边(u,v),增加节点u和v的边数。
- 现在,在数组noOfEdges []上进行迭代,并检查是否有任何边缘仅连接了1个边缘。如果是,则该图不是2边连接的。
- 否则,图形是2边连接的。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++14
// C++14 program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Definition of a graph
class Graph {
// No. of vertices
int V;
// To create adjacency list
list* adj;
public:
// Constructor
Graph(int V);
// Function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// Function to check 2-edge
// 2-edge connectivity
void twoEdge(int v);
};
// Initialize the graph
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
// Adding edges to adjacency list
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v - 1].push_back(w - 1);
adj[w - 1].push_back(v - 1);
}
// Function to find if the graph is
// 2 edge connected or not
void Graph::twoEdge(int v)
{
// To store number of edges for
// each node
int noOfEdges[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
noOfEdges[i] = adj[i].size();
}
bool flag = true;
// Check the number of edges
// connected to each node
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
if (noOfEdges[i] < 2) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
// Print the result
if (flag)
cout << "Yes";
else
cout << "No";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Number of nodes and edges
int V = 8;
int E = 10;
// Given Edges
int edges[E][2] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 8 }, { 1, 6 },
{ 2, 3 }, { 2, 4 }, { 3, 7 },
{ 3, 4 }, { 7, 5 }, { 7, 6 },
{ 7, 8 } };
// Initialize the graph
Graph g(V);
// Adding the edges to graph
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
g.addEdge(edges[i][0], edges[i][1]);
}
// Function call
g.twoEdge(V);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class Graph{
// No. of vertices
private int V;
// Array of lists for Adjacency
// List Representation
private LinkedList adj[];
// Constructor
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for(int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v - 1].add(w - 1); // Add w to v's list.
adj[w - 1].add(v - 1);
}
// Function to find if the graph is
// 2 edge connected or not
void twoEdge(int v)
{
// To store number of edges for
// each node
int[] noOfEdges = new int[v];
for(int i = 0; i < v; i++)
{
noOfEdges[i] = adj[i].size();
}
boolean flag = true;
// Check the number of edges
// connected to each node
for(int i = 0; i < v; i++)
{
if (noOfEdges[i] < 2)
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
// Print the result
if (flag)
System.out.print("Yes");
else
System.out.print("No");
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// Number of nodes and edges
int V = 8;
int E = 10;
// Given Edges
int edges[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 8 },
{ 1, 6 }, { 2, 3 },
{ 2, 4 }, { 3, 7 },
{ 3, 4 }, { 7, 5 },
{ 7, 6 }, { 7, 8 } };
Graph g = new Graph(V);
// Adding the edges to graph
for(int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
g.addEdge(edges[i][0], edges[i][1]);
}
// Function call
g.twoEdge(V);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Definition of a graph
class Graph:
# No. of vertices
V = 0
# Array of lists for Adjacency
# List Representation
adj = [[]]
# Constructor
def __init__(self, v):
self.V = v
self.adj = [[] for i in range(v)]
# Function to add an edge into the graph
def addEdge(self, v, w):
self.adj[v - 1].append(w - 1)
# Add w to v's list.
self.adj[w - 1].append(v - 1)
# Function to find if the graph is
# 2 edge connected or not
def twoEdge(self, v):
# To store number of edges for
# each node
noOfEdges = [len(self.adj[i]) for i in range(v)]
flag = True
# Check the number of edges
# connected to each node
for i in range(v):
if (noOfEdges[i] < 2):
flag = False
break
# Print the result
if (flag):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
# Driver code
if __name__=="__main__":
# Number of nodes and edges
V = 8
E = 10
# Given Edges
edges = [ [ 1, 2 ], [ 1, 8 ],
[ 1, 6 ], [ 2, 3 ],
[ 2, 4 ], [ 3, 7 ],
[ 3, 4 ], [ 7, 5 ],
[ 7, 6 ], [ 7, 8 ] ]
g = Graph(V)
# Adding the edges to graph
for i in range(E):
g.addEdge(edges[i][0],
edges[i][1])
# Function call
g.twoEdge(V)
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Graph{
// No. of vertices
private int V;
// Array of lists for Adjacency
// List Representation
private List []adj;
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new List[v];
for(int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new List();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
// Add w to v's list.
adj[v - 1].Add(w - 1);
adj[w - 1].Add(v - 1);
}
// Function to find if the graph is
// 2 edge connected or not
void twoEdge(int v)
{
// To store number of edges for
// each node
int[] noOfEdges = new int[v];
for(int i = 0; i < v; i++)
{
noOfEdges[i] = adj[i].Count;
}
bool flag = true;
// Check the number of edges
// connected to each node
for(int i = 0; i < v; i++)
{
if (noOfEdges[i] < 2)
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
// Print the result
if (flag)
Console.Write("Yes");
else
Console.Write("No");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Number of nodes and edges
int V = 8;
int E = 10;
// Given Edges
int [,]edges = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 8 },
{ 1, 6 }, { 2, 3 },
{ 2, 4 }, { 3, 7 },
{ 3, 4 }, { 7, 5 },
{ 7, 6 }, { 7, 8 } };
Graph g = new Graph(V);
// Adding the edges to graph
for(int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
g.addEdge(edges[i, 0], edges[i, 1]);
}
// Function call
g.twoEdge(V);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar No
时间复杂度: O(V + E)
辅助空间: O(V)