理想的二叉树是一种二叉树,其中每个内部节点恰好有两个子节点,而所有叶节点都处于同一级别。
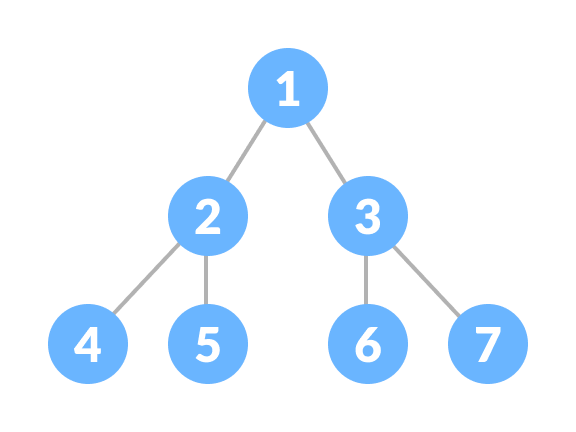
所有内部节点的度数均为2。
递归地,可以将完美的二叉树定义为:
- 如果单个节点没有子节点,则它是高度为
h = 0的理想二叉树, - 如果节点的
h > 0,则如果其两个子树的高度均为h - 1且不重叠,则它是理想的二叉树。
Python,Java和C / C++示例
以下代码用于检查树是否是完美的二叉树。
Python
爪哇
C
C++
# Checking if a binary tree is a perfect binary tree in Python
class newNode:
def __init__(self, k):
self.key = k
self.right = self.left = None
# Calculate the depth
def calculateDepth(node):
d = 0
while (node is not None):
d += 1
node = node.left
return d
# Check if the tree is perfect binary tree
def is_perfect(root, d, level=0):
# Check if the tree is empty
if (root is None):
return True
# Check the presence of trees
if (root.left is None and root.right is None):
return (d == level + 1)
if (root.left is None or root.right is None):
return False
return (is_perfect(root.left, d, level + 1) and
is_perfect(root.right, d, level + 1))
root = None
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right = newNode(5)
if (is_perfect(root, calculateDepth(root))):
print("The tree is a perfect binary tree")
else:
print("The tree is not a perfect binary tree")// Checking if a binary tree is a perfect binary tree in Java
class PerfectBinaryTree {
static class Node {
int key;
Node left, right;
}
// Calculate the depth
static int depth(Node node) {
int d = 0;
while (node != null) {
d++;
node = node.left;
}
return d;
}
// Check if the tree is perfect binary tree
static boolean is_perfect(Node root, int d, int level) {
// Check if the tree is empty
if (root == null)
return true;
// If for children
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return (d == level + 1);
if (root.left == null || root.right == null)
return false;
return is_perfect(root.left, d, level + 1) && is_perfect(root.right, d, level + 1);
}
// Wrapper function
static boolean is_Perfect(Node root) {
int d = depth(root);
return is_perfect(root, d, 0);
}
// Create a new node
static Node newNode(int k) {
Node node = new Node();
node.key = k;
node.right = null;
node.left = null;
return node;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Node root = null;
root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
if (is_Perfect(root) == true)
System.out.println("The tree is a perfect binary tree");
else
System.out.println("The tree is not a perfect binary tree");
}
}// Checking if a binary tree is a perfect binary tree in C
#include
#include
#include
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
};
// Creating a new node
struct node *newnode(int data) {
struct node *node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
// Calculate the depth
int depth(struct node *node) {
int d = 0;
while (node != NULL) {
d++;
node = node->left;
}
return d;
}
// Check if the tree is perfect
bool is_perfect(struct node *root, int d, int level) {
// Check if the tree is empty
if (root == NULL)
return true;
// Check the presence of children
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return (d == level + 1);
if (root->left == NULL || root->right == NULL)
return false;
return is_perfect(root->left, d, level + 1) &&
is_perfect(root->right, d, level + 1);
}
// Wrapper function
bool is_Perfect(struct node *root) {
int d = depth(root);
return is_perfect(root, d, 0);
}
int main() {
struct node *root = NULL;
root = newnode(1);
root->left = newnode(2);
root->right = newnode(3);
root->left->left = newnode(4);
root->left->right = newnode(5);
root->right->left = newnode(6);
if (is_Perfect(root))
printf("The tree is a perfect binary tree\n");
else
printf("The tree is not a perfect binary tree\n");
} // Checking if a binary tree is a perfect binary tree in C++
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
int depth(Node *node) {
int d = 0;
while (node != NULL) {
d++;
node = node->left;
}
return d;
}
bool isPerfectR(struct Node *root, int d, int level = 0) {
if (root == NULL)
return true;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return (d == level + 1);
if (root->left == NULL || root->right == NULL)
return false;
return isPerfectR(root->left, d, level + 1) &&
isPerfectR(root->right, d, level + 1);
}
bool isPerfect(Node *root) {
int d = depth(root);
return isPerfectR(root, d);
}
struct Node *newNode(int k) {
struct Node *node = new Node;
node->key = k;
node->right = node->left = NULL;
return node;
}
int main() {
struct Node *root = NULL;
root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
if (isPerfect(root))
cout << "The tree is a perfect binary tree\n";
else
cout << "The tree is not a perfect binary tree\n";
} 完美二叉树定理
- 高度为h的理想二叉树具有
2 h + 1 – 1节点。 - 具有n个节点的理想二叉树的高度为
log(n + 1) – 1 = Θ(ln(n))。 - 高度为h的理想二叉树具有
2 h叶节点。 - 理想二叉树中节点的平均深度为
Θ(ln(n))。