Playfair密码是第一个实用的有向图替换密码。该方案由查尔斯·惠斯通(Charles Wheatstone)于1854年发明,但以促进密码使用的普勒费尔勋爵(Lord Playfair)命名。在与传统密码不同的游戏公平密码中,我们对一对字母(图)进行加密,而不是对单个字母进行加密。
它在第二次布尔战争和第一次世界大战中被英国军队用于战术目的,在第二次世界大战期间被澳大利亚人用于相同目的。这是因为Playfair的使用速度相当快,并且不需要任何特殊设备。
加密技术
对于加密过程,让我们考虑以下示例:

Playfair密码加密算法:
该算法包括2个步骤:
- 生成密钥Square(5×5):
- 密钥方块是一个5×5的字母网格,用作加密明文的密钥。 25个字母中的每个字母必须唯一,并且表中省略了一个字母(通常为J)(因为表只能容纳25个字母)。如果明文包含J,则将其替换为I。
- 按键方块中的初始字母是按键的唯一字母,按照它们出现的顺序排列,然后依次排列其余字母。
例如:
The key is "monarchy" Thus the initial entires are 'm', 'o', 'n', 'a', 'r', 'c', 'h', 'y' followed by remaining characters of a-z(except 'j') in that order.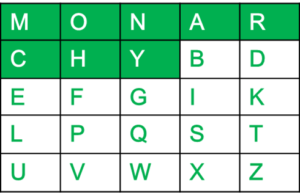
- 加密纯文本的算法:将纯文本分为两个字母(图)组成的对。如果字母的数量为奇数,则将Z添加到最后一个字母。
例如:
PlainText: "instruments" After Split: 'in' 'st' 'ru' 'me' 'nt' 'sz'加密规则:
- 如果两个字母都在同一列中:取每个字母下方的字母(如果位于底部,则返回顶部)。
例如:
Diagraph: "me" Encrypted Text: cl Encryption: m -> c e -> l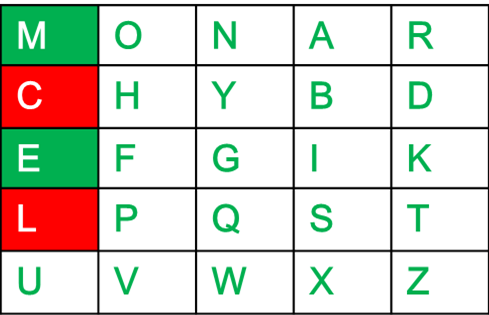
- 如果两个字母都在同一行中:取每个字母右边的字母(如果位于最右边,则返回最左边)。
例如:
Diagraph: "st" Encrypted Text: tl Encryption: s -> t t -> l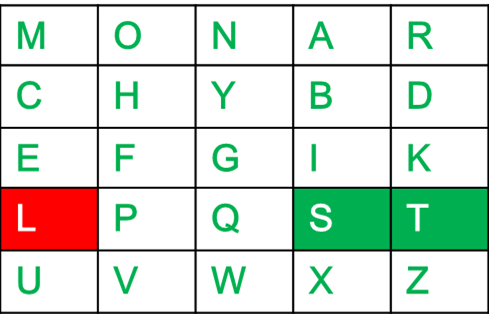
- 如果以上规则都不成立:用两个字母组成一个矩形,并在矩形的水平相对角上取字母。
例如:
Diagraph: "nt" Encrypted Text: rq Encryption: n -> r t -> q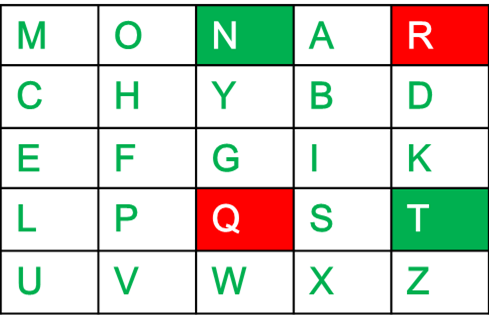
- 如果两个字母都在同一列中:取每个字母下方的字母(如果位于底部,则返回顶部)。
例如:
Plain Text: "instrumentsz"
Encrypted Text: gatlmzclrqtx
Encryption:
i -> g
n -> a
s -> t
t -> l
r -> m
u -> z
m -> c
e -> l
n -> r
t -> q
s -> t
z -> x
以下是Playfair Cipher在C语言中的实现:
// C program to implement Playfair Cipher
#include
#include
#include
#define SIZE 30
// Function to convert the string to lowercase
void toLowerCase(char plain[], int ps)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < ps; i++) {
if (plain[i] > 64 && plain[i] < 91)
plain[i] += 32;
}
}
// Function to remove all spaces in a string
int removeSpaces(char* plain, int ps)
{
int i, count = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps; i++)
if (plain[i] != ' ')
plain[count++] = plain[i];
plain[count] = '\0';
return count;
}
// Function to generate the 5x5 key square
void generateKeyTable(char key[], int ks, char keyT[5][5])
{
int i, j, k, flag = 0, *dicty;
// a 26 character hashmap
// to store count of the alphabet
dicty = (int*)calloc(26, sizeof(int));
for (i = 0; i < ks; i++) {
if (key[i] != 'j')
dicty[key[i] - 97] = 2;
}
dicty['j' - 97] = 1;
i = 0;
j = 0;
for (k = 0; k < ks; k++) {
if (dicty[key[k] - 97] == 2) {
dicty[key[k] - 97] -= 1;
keyT[i][j] = key[k];
j++;
if (j == 5) {
i++;
j = 0;
}
}
}
for (k = 0; k < 26; k++) {
if (dicty[k] == 0) {
keyT[i][j] = (char)(k + 97);
j++;
if (j == 5) {
i++;
j = 0;
}
}
}
}
// Function to search for the characters of a digraph
// in the key square and return their position
void search(char keyT[5][5], char a, char b, int arr[])
{
int i, j;
if (a == 'j')
a = 'i';
else if (b == 'j')
b = 'i';
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (keyT[i][j] == a) {
arr[0] = i;
arr[1] = j;
}
else if (keyT[i][j] == b) {
arr[2] = i;
arr[3] = j;
}
}
}
}
// Function to find the modulus with 5
int mod5(int a)
{
return (a % 5);
}
// Function to make the plain text length to be even
int prepare(char str[], int ptrs)
{
if (ptrs % 2 != 0) {
str[ptrs++] = 'z';
str[ptrs] = '\0';
}
return ptrs;
}
// Function for performing the encryption
void encrypt(char str[], char keyT[5][5], int ps)
{
int i, a[4];
for (i = 0; i < ps; i += 2) {
search(keyT, str[i], str[i + 1], a);
if (a[0] == a[2]) {
str[i] = keyT[a[0]][mod5(a[1] + 1)];
str[i + 1] = keyT[a[0]][mod5(a[3] + 1)];
}
else if (a[1] == a[3]) {
str[i] = keyT[mod5(a[0] + 1)][a[1]];
str[i + 1] = keyT[mod5(a[2] + 1)][a[1]];
}
else {
str[i] = keyT[a[0]][a[3]];
str[i + 1] = keyT[a[2]][a[1]];
}
}
}
// Function to encrypt using Playfair Cipher
void encryptByPlayfairCipher(char str[], char key[])
{
char ps, ks, keyT[5][5];
// Key
ks = strlen(key);
ks = removeSpaces(key, ks);
toLowerCase(key, ks);
// Plaintext
ps = strlen(str);
toLowerCase(str, ps);
ps = removeSpaces(str, ps);
ps = prepare(str, ps);
generateKeyTable(key, ks, keyT);
encrypt(str, keyT, ps);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
char str[SIZE], key[SIZE];
// Key to be encrypted
strcpy(key, "Monarchy");
printf("Key text: %s\n", key);
// Plaintext to be encrypted
strcpy(str, "instruments");
printf("Plain text: %s\n", str);
// encrypt using Playfair Cipher
encryptByPlayfairCipher(str, key);
printf("Cipher text: %s\n", str);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by AbhayBhat
输出:
Key text: Monarchy
Plain text: instruments
Cipher text: gatlmzclrqtx
解密技术
解密Playfair密码与执行相反的过程一样简单。接收者具有相同的密钥,可以创建相同的密钥表,然后解密使用该密钥发出的任何消息。

Playfair密码解密算法:
该算法包括2个步骤:
- 在接收方的末端生成密钥Square(5×5):
- 密钥方块是一个5×5的字母网格,用作加密明文的密钥。 25个字母中的每个字母必须唯一,并且表中省略了一个字母(通常为J)(因为表只能容纳25个字母)。如果明文包含J,则将其替换为I。
- 按键方块中的初始字母是按键的唯一字母,按照它们出现的顺序排列,然后依次排列其余字母。
Note: For both encryption and decryption, the same key is to be used.
例如:
The key is "monarchy" Thus the initial entires are 'm', 'o', 'n', 'a', 'r', 'c', 'h', 'y' followed by remaining characters of a-z(except 'j') in that order.
- 解密密文的算法:密文分成两个字母(图)的对。
Note: The ciphertext always have even number of characters.
例如:
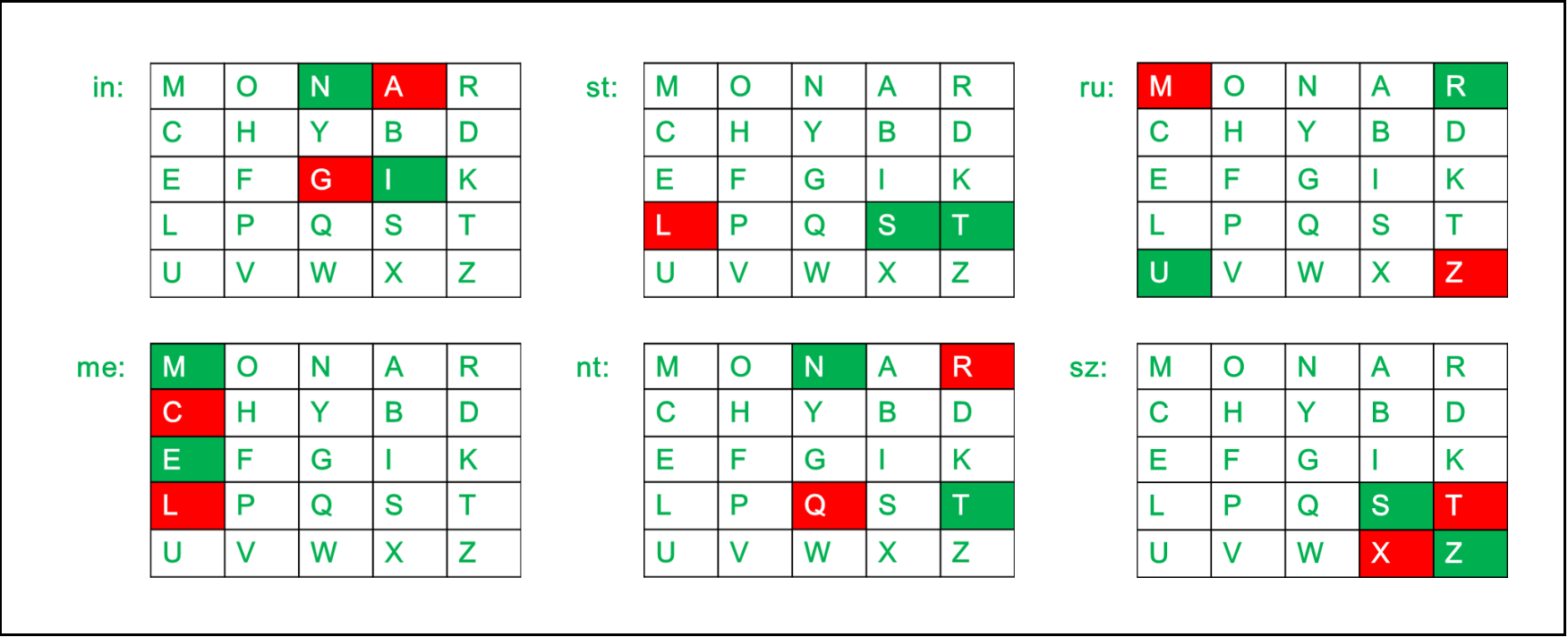
CipherText: "gatlmzclrqtx" After Split: 'ga' 'tl' 'mz' 'cl' 'rq' 'tx'解密规则:
- 如果两个字母都在同一列中:将每个字母上方(如果回到顶部,则返回底部)。
例如:
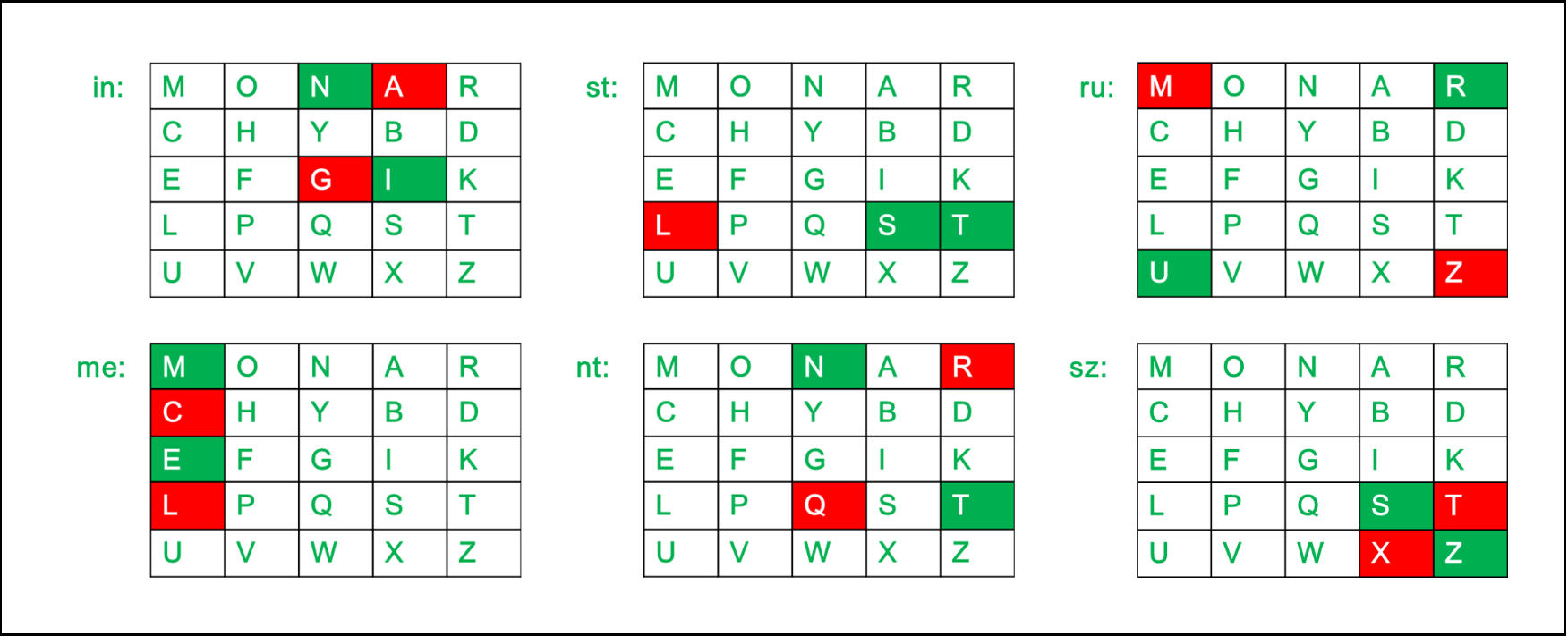
Diagraph: "cl" Decrypted Text: me Decryption: c -> m l -> e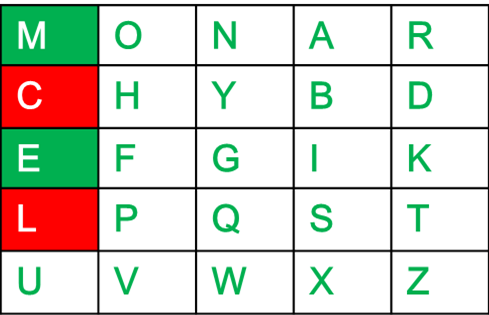
- 如果两个字母都在同一行中:将每个字母都放在左边(如果在最左边,则返回最右边)。
例如:
Diagraph: "tl" Decrypted Text: st Decryption: t -> s l -> t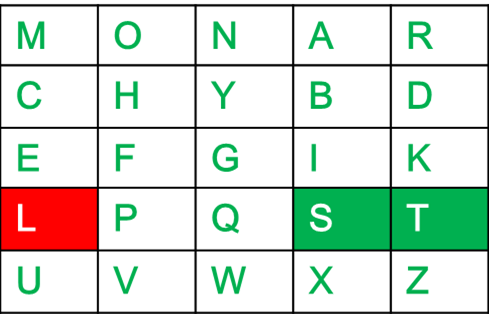
- 如果以上规则都不成立:用两个字母组成一个矩形,并在矩形的水平相对角上取字母。
例如:
Diagraph: "rq" Decrypted Text: nt Decryption: r -> n q -> t
- 如果两个字母都在同一列中:将每个字母上方(如果回到顶部,则返回底部)。
例如:
Plain Text: "gatlmzclrqtx"
Decrypted Text: instrumentsz
Decryption:
(red)-> (green)
ga -> in
tl -> st
mz -> ru
cl -> me
rq -> nt
tx -> sz
以下是C语言中Playfair密码解密的实现:
#include
#include
#include
#define SIZE 30
// Convert all the characters
// of a string to lowercase
void toLowerCase(char plain[], int ps)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < ps; i++) {
if (plain[i] > 64 && plain[i] < 91)
plain[i] += 32;
}
}
// Remove all spaces in a string
// can be extended to remove punctuation
int removeSpaces(char* plain, int ps)
{
int i, count = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps; i++)
if (plain[i] != ' ')
plain[count++] = plain[i];
plain[count] = '\0';
return count;
}
// generates the 5x5 key square
void generateKeyTable(char key[], int ks,
char keyT[5][5])
{
int i, j, k, flag = 0, *dicty;
// a 26 character hashmap
// to store count of the alphabet
dicty = (int*)calloc(26, sizeof(int));
for (i = 0; i < ks; i++) {
if (key[i] != 'j')
dicty[key[i] - 97] = 2;
}
dicty['j' - 97] = 1;
i = 0;
j = 0;
for (k = 0; k < ks; k++) {
if (dicty[key[k] - 97] == 2) {
dicty[key[k] - 97] -= 1;
keyT[i][j] = key[k];
j++;
if (j == 5) {
i++;
j = 0;
}
}
}
for (k = 0; k < 26; k++) {
if (dicty[k] == 0) {
keyT[i][j] = (char)(k + 97);
j++;
if (j == 5) {
i++;
j = 0;
}
}
}
}
// Search for the characters of a digraph
// in the key square and return their position
void search(char keyT[5][5], char a,
char b, int arr[])
{
int i, j;
if (a == 'j')
a = 'i';
else if (b == 'j')
b = 'i';
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (keyT[i][j] == a) {
arr[0] = i;
arr[1] = j;
}
else if (keyT[i][j] == b) {
arr[2] = i;
arr[3] = j;
}
}
}
}
// Function to find the modulus with 5
int mod5(int a)
{
return (a % 5);
}
// Function to decrypt
void decrypt(char str[], char keyT[5][5], int ps)
{
int i, a[4];
for (i = 0; i < ps; i += 2) {
search(keyT, str[i], str[i + 1], a);
if (a[0] == a[2]) {
str[i] = keyT[a[0]][mod5(a[1] - 1)];
str[i + 1] = keyT[a[0]][mod5(a[3] - 1)];
}
else if (a[1] == a[3]) {
str[i] = keyT[mod5(a[0] - 1)][a[1]];
str[i + 1] = keyT[mod5(a[2] - 1)][a[1]];
}
else {
str[i] = keyT[a[0]][a[3]];
str[i + 1] = keyT[a[2]][a[1]];
}
}
}
// Function to call decrypt
void decryptByPlayfairCipher(char str[], char key[])
{
char ps, ks, keyT[5][5];
// Key
ks = strlen(key);
ks = removeSpaces(key, ks);
toLowerCase(key, ks);
// ciphertext
ps = strlen(str);
toLowerCase(str, ps);
ps = removeSpaces(str, ps);
generateKeyTable(key, ks, keyT);
decrypt(str, keyT, ps);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
char str[SIZE], key[SIZE];
// Key to be encrypted
strcpy(key, "Monarchy");
printf("Key text: %s\n", key);
// Ciphertext to be decrypted
strcpy(str, "gatlmzclrqtx");
printf("Plain text: %s\n", str);
// encrypt using Playfair Cipher
decryptByPlayfairCipher(str, key);
printf("Deciphered text: %s\n", str);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by AbhayBhat
输出:
Key text: Monarchy
Plain text: gatlmzclrqtx
Deciphered text: inskrumentsz
的优点和缺点
- 好处:
- 很难破解,因为用于破解简单替换密码的频率分析技术很困难,但仍可用于(25 * 25)= 625个有向图,而不是很难的25个专论。
- 因此,频率分析需要更多的密文才能破解加密。
- 缺点:
- 一个有趣的弱点是,密文(AB)和反向文(BA)中的有向图将具有相应的明文,例如UR和RU(并且密文UR和RU将对应于明文AB和BA,即替换是自-逆)。如果知道明文的语言,则可以借助频率分析轻松地利用这一点。
- 另一个缺点是游戏公平密码是对称密码,因此相同的密钥用于加密和解密。