本文已讨论了深度优先搜索(DFS),该视图使用邻接表进行图形表示。在本文中,邻接矩阵将用于表示图。
邻接矩阵表示:在图的邻接矩阵表示中,大小为n * n(其中n是顶点数量)的矩阵mat [] []将表示图的边缘,其中mat [i] [j] = 1表示在顶点i和j之间存在边,而mat [i] [i] = 0表示在顶点i和j之间没有边。
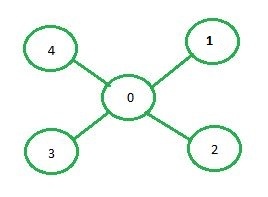
以下是上图中显示的图的邻接矩阵表示:
0 1 2 3 4
0 0 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 0 0 0
2 1 0 0 0 0
3 1 0 0 0 0
4 1 0 0 0 0
例子:
输入: source = 0  输出: 0 1 3 2输入:源= 0
输出: 0 1 3 2输入:源= 0  输出: 0 1 2 3 4
输出: 0 1 2 3 4
方法:
- 创建一个大小为n * n的矩阵,其中每个元素均为0,表示图中没有边。
- 现在,对于顶点i和j之间的图的每个边,设置mat [i] [j] = 1。
- 创建并填充邻接矩阵后,为源调用递归函数,即顶点0,它将为与其相邻的所有顶点递归调用相同的函数。
- 另外,保留一个数组以跟踪访问的顶点,即,visited [i] = true表示顶点i之前已被访问过,并且不需要调用某些已访问过的节点的DFS函数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
class Graph {
// Number of vertex
int v;
// Number of edges
int e;
// Adjacency matrix
int** adj;
public:
// To create the initial adjacency matrix
Graph(int v, int e);
// Function to insert a new edge
void addEdge(int start, int e);
// Function to display the DFS traversal
void DFS(int start, vector& visited);
};
// Function to fill the empty adjacency matrix
Graph::Graph(int v, int e)
{
this->v = v;
this->e = e;
adj = new int*[v];
for (int row = 0; row < v; row++) {
adj[row] = new int[v];
for (int column = 0; column < v; column++) {
adj[row][column] = 0;
}
}
}
// Function to add an edge to the graph
void Graph::addEdge(int start, int e)
{
// Considering a bidirectional edge
adj[start][e] = 1;
adj[e][start] = 1;
}
// Function to perform DFS on the graph
void Graph::DFS(int start, vector& visited)
{
// Print the current node
cout << start << " ";
// Set current node as visited
visited[start] = true;
// For every node of the graph
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
// If some node is adjacent to the current node
// and it has not already been visited
if (adj[start][i] == 1 && (!visited[i])) {
DFS(i, visited);
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int v = 5, e = 4;
// Create the graph
Graph G(v, e);
G.addEdge(0, 1);
G.addEdge(0, 2);
G.addEdge(0, 3);
G.addEdge(0, 4);
// Visited vector to so that
// a vertex is not visited more than once
// Initializing the vector to false as no
// vertex is visited at the beginning
vector visited(v, false);
// Perform DFS
G.DFS(0, visited);
} Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
class Graph:
adj = []
# Function to fill empty adjacency matrix
def __init__(self, v, e):
self.v = v
self.e = e
Graph.adj = [[0 for i in range(v)]
for j in range(v)]
# Function to add an edge to the graph
def addEdge(self, start, e):
# Considering a bidirectional edge
Graph.adj[start][e] = 1
Graph.adj[e][start] = 1
# Function to perform DFS on the graph
def DFS(self, start, visited):
# Print current node
print(start, end = ' ')
# Set current node as visited
visited[start] = True
# For every node of the graph
for i in range(self.v):
# If some node is adjacent to the
# current node and it has not
# already been visited
if (Graph.adj[start][i] == 1 and
(not visited[i])):
self.DFS(i, visited)
# Driver code
v, e = 5, 4
# Create the graph
G = Graph(v, e)
G.addEdge(0, 1)
G.addEdge(0, 2)
G.addEdge(0, 3)
G.addEdge(0, 4)
# Visited vector to so that a vertex
# is not visited more than once
# Initializing the vector to false as no
# vertex is visited at the beginning
visited = [False] * v
# Perform DFS
G.DFS(0, visited);
# This code is contributed by ng24_7输出:
0 1 2 3 4