循环排序是一种就地排序算法,一种不稳定的排序算法,一种比较排序,在理论上,对原始数组的写入总数在比较上是最佳的。
- 就内存写入次数而言,这是最佳的。它最大程度地减少了要排序的内存写操作的数量(每个值要么被写入零次(如果它已经处于其正确位置,要么被写入一次至其正确位置)。)
- 基于这样的思想,可以将要排序的数组划分为多个循环。周期可以显示为图表。如果在排序数组中第i个索引处的元素必须出现在第j个索引处,则我们有n个节点和从节点i指向节点j的边。
以arr [] = {4,5,2,1,5}循环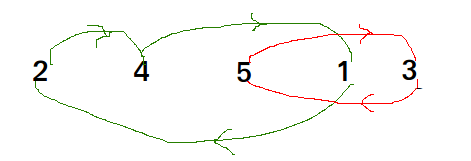
以arr [] = {4,3,2,1}循环
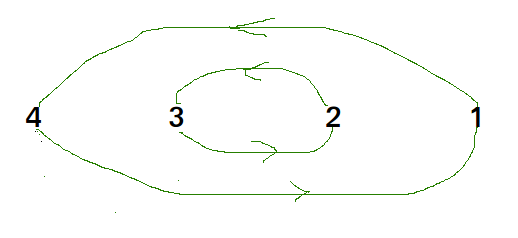
我们一个接一个地考虑所有周期。我们首先考虑包含第一个元素的循环。我们找到第一个元素的正确位置,将其放置在正确的位置,例如j。我们考虑arr [j]的旧值并找到其正确位置,直到当前循环的所有元素都放置在正确位置之前,我们一直这样做,即,我们不回到循环起点。
Java
// Java program to impleament cycle sort
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
class GFG
{
// Function sort the array using Cycle sort
public static void cycleSort (int arr[], int n)
{
// count number of memory writes
int writes = 0;
// traverse array elements and put it to on
// the right place
for (int cycle_start=0; cycle_start<=n-2; cycle_start++)
{
// initialize item as starting point
int item = arr[cycle_start];
// Find position where we put the item. We basically
// count all smaller elements on right side of item.
int pos = cycle_start;
for (int i = cycle_start+1; i
Output:After sort :
1 2 3 4 8 9 10 10
Please refer complete article on Cycle Sort for more details!