给定一个二叉树,发现它为L argest我ndependent S等(LIS)的大小。如果所有树节点的子集之间没有任何边,则所有树节点的子集都是一个独立集。
例如,考虑下面的二叉树。最大独立集(LIS)为{10,40,60,70,80},LIS的大小为5。
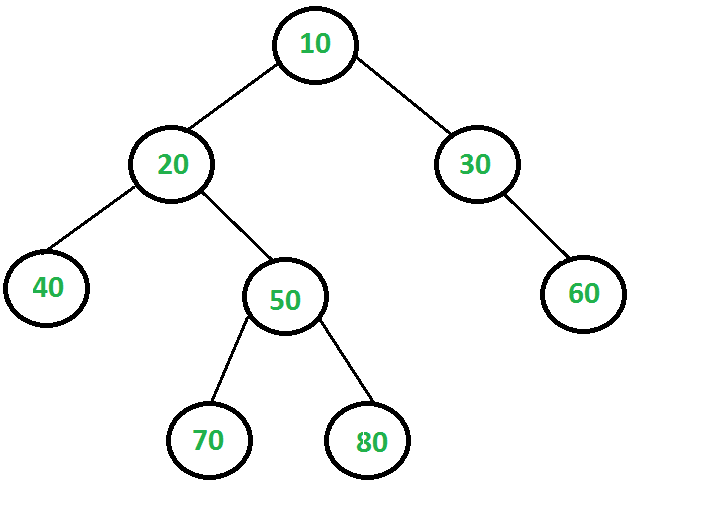
动态编程解决方案使用自下而上的子问题解决方案来解决给定的问题。可以使用子问题的解决方案来解决给定的问题吗?如果是,那么子问题是什么?如果我们知道X的所有后代的LISS,是否可以找到节点X的最大独立集大小(LISS)?如果将节点视为LIS的一部分,则其子节点不能成为LIS的一部分,但其子孙可以。以下是最佳的子结构属性。
1)最佳子结构:
令LISS(X)表示根为X的树的最大独立集的大小。
LISS(X) = MAX { (1 + sum of LISS for all grandchildren of X),
(sum of LISS for all children of X) }
这个想法很简单,每个节点X都有两种可能性,X是集合的成员,或者不是成员。如果X是成员,则LISS(X)的值为1加上所有孙子孙的LISS。如果X不是成员,则该值为所有子项的LISS的总和。
2)重叠子问题
以下是简单地遵循上述递归结构的递归实现。
C++
// A naive recursive implementation of
// Largest Independent Set problem
#include
using namespace std;
// A utility function to find
// max of two integers
int max(int x, int y)
{
return (x > y) ? x : y;
}
/* A binary tree node has data,
pointer to left child and a
pointer to right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
node *left, *right;
};
// The function returns size of the
// largest independent set in a given
// binary tree
int LISS(node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Calculate size excluding the current node
int size_excl = LISS(root->left) +
LISS(root->right);
// Calculate size including the current node
int size_incl = 1;
if (root->left)
size_incl += LISS(root->left->left) +
LISS(root->left->right);
if (root->right)
size_incl += LISS(root->right->left) +
LISS(root->right->right);
// Return the maximum of two sizes
return max(size_incl, size_excl);
}
// A utility function to create a node
node* newNode( int data )
{
node* temp = new node();
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Let us construct the tree
// given in the above diagram
node *root = newNode(20);
root->left = newNode(8);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(12);
root->left->right->left = newNode(10);
root->left->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right = newNode(22);
root->right->right = newNode(25);
cout << "Size of the Largest"
<< " Independent Set is "
<< LISS(root);
return 0;
}
// This is code is contributed
// by rathbhupendra C
// A naive recursive implementation of Largest Independent Set problem
#include
#include
// A utility function to find max of two integers
int max(int x, int y) { return (x > y)? x: y; }
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child and a pointer to
right child */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *left, *right;
};
// The function returns size of the largest independent set in a given
// binary tree
int LISS(struct node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Caculate size excluding the current node
int size_excl = LISS(root->left) + LISS(root->right);
// Calculate size including the current node
int size_incl = 1;
if (root->left)
size_incl += LISS(root->left->left) + LISS(root->left->right);
if (root->right)
size_incl += LISS(root->right->left) + LISS(root->right->right);
// Return the maximum of two sizes
return max(size_incl, size_excl);
}
// A utility function to create a node
struct node* newNode( int data )
{
struct node* temp = (struct node *) malloc( sizeof(struct node) );
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Let us construct the tree given in the above diagram
struct node *root = newNode(20);
root->left = newNode(8);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(12);
root->left->right->left = newNode(10);
root->left->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right = newNode(22);
root->right->right = newNode(25);
printf ("Size of the Largest Independent Set is %d ", LISS(root));
return 0;
} Java
// A naive recursive implementation of
// Largest Independent Set problem
class GFG {
// A utility function to find
// max of two integers
static int max(int x, int y)
{
return (x > y) ? x : y;
}
/* A binary tree node has data,
pointer to left child and a
pointer to right child */
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
};
// The function returns size of the
// largest independent set in a given
// binary tree
static int LISS(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Calculate size excluding the current node
int size_excl = LISS(root.left) +
LISS(root.right);
// Calculate size including the current node
int size_incl = 1;
if (root.left!=null)
size_incl += LISS(root.left.left) +
LISS(root.left.right);
if (root.right!=null)
size_incl += LISS(root.right.left) +
LISS(root.right.right);
// Return the maximum of two sizes
return max(size_incl, size_excl);
}
// A utility function to create a node
static Node newNode( int data )
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Let us construct the tree
// given in the above diagram
Node root = newNode(20);
root.left = newNode(8);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(12);
root.left.right.left = newNode(10);
root.left.right.right = newNode(14);
root.right = newNode(22);
root.right.right = newNode(25);
System.out.println("Size of the Largest"
+ " Independent Set is "
+ LISS(root));
}
}
// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# A naive recursive implementation of
# Largest Independent Set problem
# A utility function to find
# max of two integers
def max(x, y):
if(x > y):
return x
else:
return y
# A binary tree node has data,
#pointer to left child and a
#pointer to right child
class node :
def __init__(self):
self.data = 0
self.left = self.right = None
# The function returns size of the
# largest independent set in a given
# binary tree
def LISS(root):
if (root == None) :
return 0
# Calculate size excluding the current node
size_excl = LISS(root.left) + LISS(root.right)
# Calculate size including the current node
size_incl = 1
if (root.left != None):
size_incl += LISS(root.left.left) + \
LISS(root.left.right)
if (root.right != None):
size_incl += LISS(root.right.left) + \
LISS(root.right.right)
# Return the maximum of two sizes
return max(size_incl, size_excl)
# A utility function to create a node
def newNode( data ) :
temp = node()
temp.data = data
temp.left = temp.right = None
return temp
# Driver Code
# Let us construct the tree
# given in the above diagram
root = newNode(20)
root.left = newNode(8)
root.left.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right = newNode(12)
root.left.right.left = newNode(10)
root.left.right.right = newNode(14)
root.right = newNode(22)
root.right.right = newNode(25)
print( "Size of the Largest"
, " Independent Set is "
, LISS(root) )
# This code is contributed by Arnab KunduC#
// C# program for calculating LISS
// using dynamic programming
using System;
class LisTree
{
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer
to left child and a pointer to right
child */
public class node
{
public int data, liss;
public node left, right;
public node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.liss = 0;
}
}
// A memoization function returns size
// of the largest independent set in
// a given binary tree
static int liss(node root)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
if (root.liss != 0)
return root.liss;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return root.liss = 1;
// Calculate size excluding the
// current node
int liss_excl = liss(root.left) + liss(root.right);
// Calculate size including the
// current node
int liss_incl = 1;
if (root.left != null)
{
liss_incl += (liss(root.left.left) +
liss(root.left.right));
}
if (root.right != null)
{
liss_incl += (liss(root.right.left) +
liss(root.right.right));
}
// Maximum of two sizes is LISS,
// store it for future uses.
return root.liss = Math.Max(liss_excl, liss_incl);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Let us construct the tree given
// in the above diagram
node root = new node(20);
root.left = new node(8);
root.left.left = new node(4);
root.left.right = new node(12);
root.left.right.left = new node(10);
root.left.right.right = new node(14);
root.right = new node(22);
root.right.right = new node(25);
Console.WriteLine("Size of the Largest Independent Set is " + liss(root));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi SinghC++
/* Dynamic programming based program
for Largest Independent Set problem */
#include
using namespace std;
// A utility function to find max of two integers
int max(int x, int y) { return (x > y)? x: y; }
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer
to left child and a pointer to
right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
int liss;
node *left, *right;
};
// A memoization function returns size
// of the largest independent set in
// a given binary tree
int LISS(node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->liss)
return root->liss;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return (root->liss = 1);
// Calculate size excluding the current node
int liss_excl = LISS(root->left) + LISS(root->right);
// Calculate size including the current node
int liss_incl = 1;
if (root->left)
liss_incl += LISS(root->left->left) + LISS(root->left->right);
if (root->right)
liss_incl += LISS(root->right->left) + LISS(root->right->right);
// Maximum of two sizes is LISS, store it for future uses.
root->liss = max(liss_incl, liss_excl);
return root->liss;
}
// A utility function to create a node
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* temp = new node();
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
temp->liss = 0;
return temp;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Let us construct the tree
// given in the above diagram
node *root = newNode(20);
root->left = newNode(8);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(12);
root->left->right->left = newNode(10);
root->left->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right = newNode(22);
root->right->right = newNode(25);
cout << "Size of the Largest Independent Set is " << LISS(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra C
/* Dynamic programming based program for Largest Independent Set problem */
#include
#include
// A utility function to find max of two integers
int max(int x, int y) { return (x > y)? x: y; }
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child and a pointer to
right child */
struct node
{
int data;
int liss;
struct node *left, *right;
};
// A memoization function returns size of the largest independent set in
// a given binary tree
int LISS(struct node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->liss)
return root->liss;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return (root->liss = 1);
// Calculate size excluding the current node
int liss_excl = LISS(root->left) + LISS(root->right);
// Calculate size including the current node
int liss_incl = 1;
if (root->left)
liss_incl += LISS(root->left->left) + LISS(root->left->right);
if (root->right)
liss_incl += LISS(root->right->left) + LISS(root->right->right);
// Maximum of two sizes is LISS, store it for future uses.
root->liss = max(liss_incl, liss_excl);
return root->liss;
}
// A utility function to create a node
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* temp = (struct node *) malloc( sizeof(struct node) );
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
temp->liss = 0;
return temp;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Let us construct the tree given in the above diagram
struct node *root = newNode(20);
root->left = newNode(8);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(12);
root->left->right->left = newNode(10);
root->left->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right = newNode(22);
root->right->right = newNode(25);
printf ("Size of the Largest Independent Set is %d ", LISS(root));
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for calculating LISS
// using dynamic programming
public class LisTree
{
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer
to left child and a pointer to right
child */
static class node
{
int data, liss;
node left, right;
public node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.liss = 0;
}
}
// A memoization function returns size
// of the largest independent set in
// a given binary tree
static int liss(node root)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
if (root.liss != 0)
return root.liss;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return root.liss = 1;
// Calculate size excluding the
// current node
int liss_excl = liss(root.left) + liss(root.right);
// Calculate size including the
// current node
int liss_incl = 1;
if (root.left != null)
{
liss_incl += (liss(root.left.left) + liss(root.left.right));
}
if (root.right != null)
{
liss_incl += (liss(root.right.left) + liss(root.right.right));
}
// Maximum of two sizes is LISS,
// store it for future uses.
return root.liss = Math.max(liss_excl, liss_incl);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Let us construct the tree given
// in the above diagram
node root = new node(20);
root.left = new node(8);
root.left.left = new node(4);
root.left.right = new node(12);
root.left.right.left = new node(10);
root.left.right.right = new node(14);
root.right = new node(22);
root.right.right = new node(25);
System.out.println("Size of the Largest Independent Set is " + liss(root));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rishabh MahrseePython3
# Python3 program for calculating LISS
# using dynamic programming
# A binary tree node has data,
# pointer to left child and a
# pointer to right child
class node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = self.right = None
self.liss = 0
# A memoization function returns size
# of the largest independent set in
# a given binary tree
def liss(root):
if root == None:
return 0
if root.liss != 0:
return root.liss
if (root.left == None and
root.right == None):
root.liss = 1
return root.liss
# Calculate size excluding the
# current node
liss_excl = (liss(root.left) +
liss(root.right))
# Calculate size including the
# current node
liss_incl = 1
if root.left != None:
liss_incl += (liss(root.left.left) +
liss(root.left.right))
if root.right != None:
liss_incl += (liss(root.right.left) +
liss(root.right.right))
# Maximum of two sizes is LISS,
# store it for future uses.
root.liss = max(liss_excl, liss_incl)
return root.liss
# Driver Code
# Let us construct the tree given
# in the above diagram
root = node(20)
root.left = node(8)
root.left.left = node(4)
root.left.right = node(12)
root.left.right.left = node(10)
root.left.right.right = node(14)
root.right = node(22)
root.right.right = node(25)
print("Size of the Largest Independent "\
"Set is ", liss(root))
# This code is contributed by nishthagoel712C#
// C# program for calculating LISS
// using dynamic programming
using System;
public class LisTree
{
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer
to left child and a pointer to right
child */
public class node
{
public int data, liss;
public node left, right;
public node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.liss = 0;
}
}
// A memoization function returns size
// of the largest independent set in
// a given binary tree
static int liss(node root)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
if (root.liss != 0)
return root.liss;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return root.liss = 1;
// Calculate size excluding the
// current node
int liss_excl = liss(root.left) + liss(root.right);
// Calculate size including the
// current node
int liss_incl = 1;
if (root.left != null)
{
liss_incl += (liss(root.left.left) + liss(root.left.right));
}
if (root.right != null)
{
liss_incl += (liss(root.right.left) + liss(root.right.right));
}
// Maximum of two sizes is LISS,
// store it for future uses.
return root.liss = Math.Max(liss_excl, liss_incl);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Let us construct the tree given
// in the above diagram
node root = new node(20);
root.left = new node(8);
root.left.left = new node(4);
root.left.right = new node(12);
root.left.right.left = new node(10);
root.left.right.right = new node(14);
root.right = new node(22);
root.right.right = new node(25);
Console.WriteLine("Size of the Largest Independent Set is " + liss(root));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */输出:
Size of the Largest Independent Set is 5上述幼稚递归方法的时间复杂度是指数的。应该注意的是,上述函数一次又一次地计算相同的子问题。例如,对于值为10和20的节点,将评估值为50的节点的LISS,因为50是10的孙子和20的子孙。
由于再次调用了相同的问题,因此此问题具有“重叠子问题”属性。因此,LISS问题具有动态编程问题的两个属性(请参阅此内容)。像其他典型的动态规划(DP)问题一样,可以通过存储子问题的解决方案并以自下而上的方式解决问题,从而避免相同子问题的重新计算。
以下是基于动态编程的解决方案的实现。在以下解决方案中,附加字段“ liss”被添加到树节点。所有节点的’liss’初始值均设置为0。递归函数LISS()仅当尚未设置节点时才计算“ liss”。
C++
/* Dynamic programming based program
for Largest Independent Set problem */
#include
using namespace std;
// A utility function to find max of two integers
int max(int x, int y) { return (x > y)? x: y; }
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer
to left child and a pointer to
right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
int liss;
node *left, *right;
};
// A memoization function returns size
// of the largest independent set in
// a given binary tree
int LISS(node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->liss)
return root->liss;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return (root->liss = 1);
// Calculate size excluding the current node
int liss_excl = LISS(root->left) + LISS(root->right);
// Calculate size including the current node
int liss_incl = 1;
if (root->left)
liss_incl += LISS(root->left->left) + LISS(root->left->right);
if (root->right)
liss_incl += LISS(root->right->left) + LISS(root->right->right);
// Maximum of two sizes is LISS, store it for future uses.
root->liss = max(liss_incl, liss_excl);
return root->liss;
}
// A utility function to create a node
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* temp = new node();
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
temp->liss = 0;
return temp;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Let us construct the tree
// given in the above diagram
node *root = newNode(20);
root->left = newNode(8);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(12);
root->left->right->left = newNode(10);
root->left->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right = newNode(22);
root->right->right = newNode(25);
cout << "Size of the Largest Independent Set is " << LISS(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
/* Dynamic programming based program for Largest Independent Set problem */
#include
#include
// A utility function to find max of two integers
int max(int x, int y) { return (x > y)? x: y; }
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child and a pointer to
right child */
struct node
{
int data;
int liss;
struct node *left, *right;
};
// A memoization function returns size of the largest independent set in
// a given binary tree
int LISS(struct node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->liss)
return root->liss;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return (root->liss = 1);
// Calculate size excluding the current node
int liss_excl = LISS(root->left) + LISS(root->right);
// Calculate size including the current node
int liss_incl = 1;
if (root->left)
liss_incl += LISS(root->left->left) + LISS(root->left->right);
if (root->right)
liss_incl += LISS(root->right->left) + LISS(root->right->right);
// Maximum of two sizes is LISS, store it for future uses.
root->liss = max(liss_incl, liss_excl);
return root->liss;
}
// A utility function to create a node
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* temp = (struct node *) malloc( sizeof(struct node) );
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
temp->liss = 0;
return temp;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Let us construct the tree given in the above diagram
struct node *root = newNode(20);
root->left = newNode(8);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(12);
root->left->right->left = newNode(10);
root->left->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right = newNode(22);
root->right->right = newNode(25);
printf ("Size of the Largest Independent Set is %d ", LISS(root));
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for calculating LISS
// using dynamic programming
public class LisTree
{
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer
to left child and a pointer to right
child */
static class node
{
int data, liss;
node left, right;
public node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.liss = 0;
}
}
// A memoization function returns size
// of the largest independent set in
// a given binary tree
static int liss(node root)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
if (root.liss != 0)
return root.liss;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return root.liss = 1;
// Calculate size excluding the
// current node
int liss_excl = liss(root.left) + liss(root.right);
// Calculate size including the
// current node
int liss_incl = 1;
if (root.left != null)
{
liss_incl += (liss(root.left.left) + liss(root.left.right));
}
if (root.right != null)
{
liss_incl += (liss(root.right.left) + liss(root.right.right));
}
// Maximum of two sizes is LISS,
// store it for future uses.
return root.liss = Math.max(liss_excl, liss_incl);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Let us construct the tree given
// in the above diagram
node root = new node(20);
root.left = new node(8);
root.left.left = new node(4);
root.left.right = new node(12);
root.left.right.left = new node(10);
root.left.right.right = new node(14);
root.right = new node(22);
root.right.right = new node(25);
System.out.println("Size of the Largest Independent Set is " + liss(root));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rishabh Mahrsee
Python3
# Python3 program for calculating LISS
# using dynamic programming
# A binary tree node has data,
# pointer to left child and a
# pointer to right child
class node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = self.right = None
self.liss = 0
# A memoization function returns size
# of the largest independent set in
# a given binary tree
def liss(root):
if root == None:
return 0
if root.liss != 0:
return root.liss
if (root.left == None and
root.right == None):
root.liss = 1
return root.liss
# Calculate size excluding the
# current node
liss_excl = (liss(root.left) +
liss(root.right))
# Calculate size including the
# current node
liss_incl = 1
if root.left != None:
liss_incl += (liss(root.left.left) +
liss(root.left.right))
if root.right != None:
liss_incl += (liss(root.right.left) +
liss(root.right.right))
# Maximum of two sizes is LISS,
# store it for future uses.
root.liss = max(liss_excl, liss_incl)
return root.liss
# Driver Code
# Let us construct the tree given
# in the above diagram
root = node(20)
root.left = node(8)
root.left.left = node(4)
root.left.right = node(12)
root.left.right.left = node(10)
root.left.right.right = node(14)
root.right = node(22)
root.right.right = node(25)
print("Size of the Largest Independent "\
"Set is ", liss(root))
# This code is contributed by nishthagoel712
C#
// C# program for calculating LISS
// using dynamic programming
using System;
public class LisTree
{
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer
to left child and a pointer to right
child */
public class node
{
public int data, liss;
public node left, right;
public node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.liss = 0;
}
}
// A memoization function returns size
// of the largest independent set in
// a given binary tree
static int liss(node root)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
if (root.liss != 0)
return root.liss;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return root.liss = 1;
// Calculate size excluding the
// current node
int liss_excl = liss(root.left) + liss(root.right);
// Calculate size including the
// current node
int liss_incl = 1;
if (root.left != null)
{
liss_incl += (liss(root.left.left) + liss(root.left.right));
}
if (root.right != null)
{
liss_incl += (liss(root.right.left) + liss(root.right.right));
}
// Maximum of two sizes is LISS,
// store it for future uses.
return root.liss = Math.Max(liss_excl, liss_incl);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Let us construct the tree given
// in the above diagram
node root = new node(20);
root.left = new node(8);
root.left.left = new node(4);
root.left.right = new node(12);
root.left.right.left = new node(10);
root.left.right.right = new node(14);
root.right = new node(22);
root.right.right = new node(25);
Console.WriteLine("Size of the Largest Independent Set is " + liss(root));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
输出:
Size of the Largest Independent Set is 5
时间复杂度: O(n),其中n是给定二叉树中的节点数。
可以尝试对上述解决方案进行以下扩展。
1)将以上解决方案扩展到n元树。
2)上面的解决方案通过向树节点添加额外的字段“ liss”来修改给定的树结构。扩展解决方案,使其不修改树结构。
3)上述解决方案仅返回LIS的大小,而不打印LIS的元素。扩展解决方案以打印属于LIS的所有节点。