晶格和晶胞
在结晶固体中,它们的组成颗粒在三个维度上具有确定的排列。这些粒子在晶体中的相对位置通常用点来表示。这些无法忍受的点集的分布称为空间格。晶格中原子、离子或分子所占据的位置是领晶格点或晶格点。本文将介绍空间点阵、二维点阵、三维点阵的基本理解。让我们一个一个开始。
二维点阵
二维晶格是构成粒子(原子、离子或分子)在平面中的静止分布。二维点阵有五种类型。这些是正方形矩形,平行四边形,菱形和六边形格子。它们在点排列的对称性上有所不同。六边形格子的点排列最对称,而平行四边形格子的点排列对称性最小。
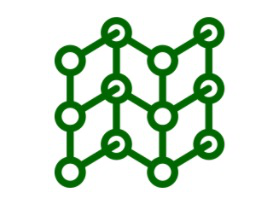
二维点阵
由于二维点阵中点的规则重复排列,因此需要描述点阵的一小部分以完全指定它。例如,在二维点阵中选取四个点,将它们连接起来形成一个平行四边形。这个最小的部分称为晶胞。理想晶格可以通过将晶胞沿其边缘方向重复旋转与晶胞边缘相等的距离来产生。
一个晶胞给出了整个晶格的形状。然而,可以注意到对于任何给定的晶格,可以以许多不同的方式选择单位单元。这是因为晶格包含非常多的原子,并且可以找到许多相同的点。
具有内部点的单元称为聚焦晶胞。那些没有任何内部点的晶胞称为原始晶胞。
Thus, a two-dimensional lattice can be described as specifying the unit cell by the lengths of the edges and the angles between them. Thus, the five two-dimensional lattices are:
- Square lattice
- Rectangular lattice
- Parallelogram lattice
- Rhombic Lattice
- Hexagonal Lattice
三维晶格
结晶固体中的组成粒子(原子、离子或分子)具有明确的三维排列。如果晶体中组成粒子的三维排列通过逐点描绘每个粒子来图解表示,则该排列称为晶格或空间点阵。晶格是晶体固体的组成粒子在三维空间中的有序排列。
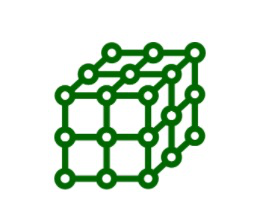
三维晶格
三维晶格类似于二维晶格。通过仔细分析晶格可以找到晶格中重复的晶格点的集合。这种下突的Ingeminate图案称为晶胞。晶胞可以定义为空间晶格中最小的三维重复部分,当它在不同方向重复时会产生完整的晶格。
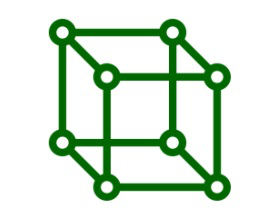
单元格
这个最小的融合图案代表了整个水晶的大小。一个完整的晶格可以通过从与晶胞边缘相等的距离沿其边缘方向反复旋转晶胞来产生。晶体可以被认为是由无数个晶胞组成。
水晶格子
A regular three-dimensional arrangement of points (ions, atoms, etc.) in space is called a crystal lattice. There are 14 possible three-dimensional lattices. These are called Bravais lattices.
晶格的特性
- 晶格中的每个点称为一个晶格点或晶格点。
- 晶格中的每个点代表一个构成粒子,可以是一个原子、一个分子(一组原子)或一个离子。
- 表示晶格的晶格点的三维分布。
- 格点由直线连接,以显示格的几何形状。
单元格
The unit cell is the smallest part of the crystal lattice, which when repeated in different directions produces the entire lattice, e.g. Primitive unit cells and concentrated unit cells.
单元格的类型——单元格可以大致分为两类,
- 原始晶胞——在原始晶胞中,组成粒子仅存在于晶胞的拐角位置,而在浓缩晶胞中,一个或多个组成粒子存在于拐角以外的位置。
- 中心晶胞 中心晶胞分为体心晶胞 (bcc)、面心晶胞 (fcc)、端心晶胞 (ecc)。
单元格的参数
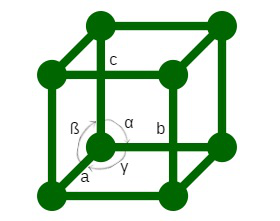
单位细胞的特征是-
- 它的尺寸(长度)是具有三个边缘的 a、b 和 c 形式。这些边缘可能相互垂直,也可能不相互垂直。
- 一对边之间的角度 α、ß 和 γ。角度 α 在边 b 和 c 之间,角度 ß 在边 c 和 a 之间,角度 γ 在边 a 和 b 之间。因此,晶胞的特征在于六个参数,a、b、c、α、ß 和 γ。通过在所有三个方向上扩展晶胞可以获得完整的晶格。
示例问题
问题1:这个晶胞有什么特点。
回答:
The most convenient cell is the smallest unit cell that has perfect lattice symmetry.
- For square, rectangular, and parallelogram lattice, the unit cells chosen are square, rectangle, and parallelogram respectively.
- For a hexagonal lattice, the unit cell is a rhombus with an angle of 60°.
- For a rhombus lattice, a rectangular unit cell with one interior point is usually chosen.
问题 2:哪种网络固体是极好的电导体?
回答:
Graphite, a network solid, is a good conductor of electricity.
问题 3. 晶胞和空间晶格有什么关系?
回答:
The space lattice is obtained by repeating the unit cell in three dimensions. The spatial arrangement, stump, and density of the unit cell and space lattice are equivalent.
问题 3:从以下集合中选出奇数:硫磺、氩气、固体 Co 2 、金刚石、SIC、石英、BaO、石墨
回答:
Diamond because all other molecular solids and BaO because all are covalent solids.
问题4:玻璃和石英的区别是什么,都是SiO 4 ,四面体?石英在什么条件下可以转化为玻璃?
回答:
Glass is an amorphous solid whereas quartz is a crystalline solid. When quartz melts and then rapidly cools, quartz turns into glass.
问题 5:如果你打破一块立方体,你希望看到玻璃和氯化钠的行为有什么不同?
回答:
Glass (an amorphous solid) will break irregularly, usually in a curved shape because its constituent molecules are not arranged in an ordered pattern. As a substitute, sodium chloride (tan ionic solid) will break all plane surfaces parallel to the faces of the cube because the planes of its constituent ions are parallel to the faces of the crystalline cube.