亲核加成反应
醛和酮是具有羰基 (>C= O) 的化学分子。因此,它们被称为羰基化合物。由于羰基在醛类和酮类中很常见,它们的合成方法和特性非常相似。
羰基分子天然存在于植物和动物的核酸碳水化合物和蛋白质中。它们在维持生命的新陈代谢过程中起着至关重要的作用。它们为大自然带来香味和风味,也存在于各种药物和纺织品中。杏仁(苯甲醛)、肉桂(肉桂醛)、香草豆(香草醛)、樟脑(来自樟树)、香茅油(香茅醛)、维生素 K 和许多其他天然成分,包括必需的羰基化合物。
碳原子通过羰基中的双键与氧相连,而剩余的两个化合价由氢原子或烷基满足。羰基碳与醛中的一个氢原子和一个联合基团相连,但与酮中的两个不同的烷基相连。羰基碳与甲醛中的两个氢原子相连。结构的差异会影响特性,例如醛在亲核加成过程中如何比酮更具反应性以及醛氧化的速度。羰基碳原子与羧酸中的烷基和 (-OH) 基团相连。羰基存在于下列化学物质中。
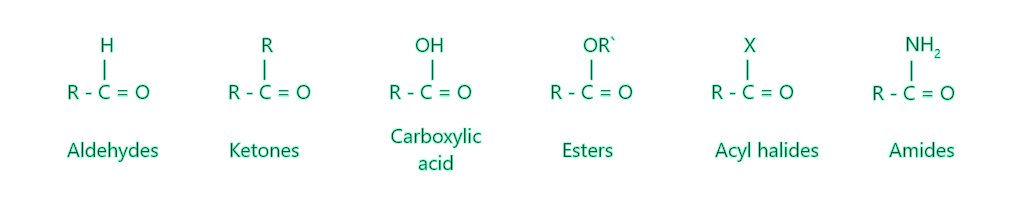
羰基官能团的结构
羰基的碳是 sp 2杂化并与醛和酮中的三个额外原子结合。碳原子产生三个键角为 120° 的 sigma (σ) 键,它们都在同一平面上。一个σ键与氧原子建立,另外两个与氢和/或碳原子建立。为了产生 pi (π) 键,剩余的未杂化 2p 轨道碳与氧的 2p 轨道重合。结果,碳和氧通过双键连接。氧原子携带两个孤对电子。

羰基的结构
羰基键更强大。与烯烃中的双键相比,该键更短且极化程度更高。因为氧比碳更负电,所以羰基的双键是极性的并且具有偶极矩。极化增加了醛和酮的反应性。
醛和酮的亲核加成反应
Mechanism
Oxygen has a greater electronegativity than carbon, because of that, the C = O bond in aldehydes and ketones is polarised.
Electrons are highly attracted to oxygen. The oxygen atom receives a partial negative charge (δ–), whereas the carbon atom receives a partial positive charge (δ+).
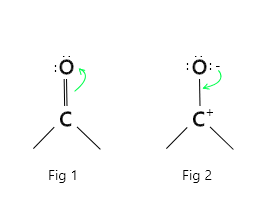
This high polarity of carbonyl group is explained on the basis of resonance involving a neutral [Fig 1] and Dipolar [Fig 2] structures.
Nucleophilic addition reactions occur between aldehydes and ketones. A nucleophile, Nu–, approaches the plane of the carbonyl group from an angle of about 75° degrees along the C = O bond and attaches to an electrophilic carbonyl carbon atom. The hybridised state of the carbonyl carbon atom shifts from sp2 to sp3 during this process. The electron pair in the C=O bond changes to carbonyl oxygen, resulting in the formation of a tetrahedral alkoxide ion intermediate. To produce the final product, this tetrahedral intermediate is protonated. As a result, the net result of the addition of Nu– and H+ across the C = O bond is [refer to below image
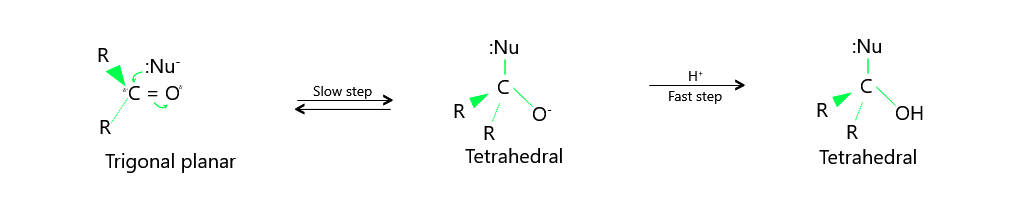
Mechanism of nucleophilic addition reactioon
Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones in nucleophilic addition processes for both steric and electrical reasons. Because aldehyde has just one bulky substituent, a nucleophile can reach the carbonyl carbon more easily than ketones, which have two bulky substituents. The carbonyl carbon in aldehyde is more electrophilic than the carbonyl carbon in ketones. This is due to the +I effect of two bulky substituents in ketones reducing the electrophilicity of carbonyl carbon.
The result of aldehyde attack is less inhibited than the product of ketone attack, especially with a bulky mucleophile (sterric effects). Aromatic aldehydes are less reactive in nucleophilic addition processes than aliphatic aldehydes. This is due to the aromatic ring’s electron-donating resonance effect, which renders carbonyl carbon less electrophilic.
- 添加氰化物
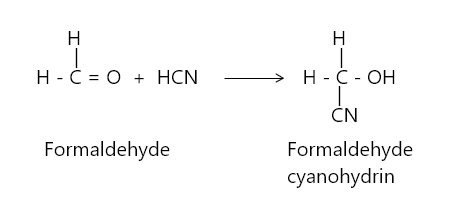
Aldehydes and ketones add hydrogen cyanide to give corresponding cyanohydrins. The reaction is reversible and occurs slowly when pure hydrogen cyanide is used but rapidly when a small amount of base is used to generate the nucleophile CN–
![]()
The mechanism of addition of nucleophile CN– is given below,
Step 1: A strong nucleophile adds to the carbonyl group (>C = O) to form an intermediate alkoxide.
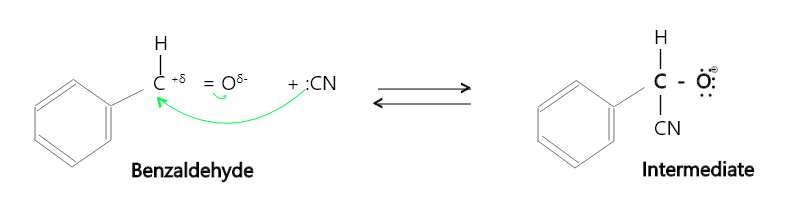
Step 2: The alkoxide ion formed is protonated by a weak acid to give the addition product.

[Note: The cyanohydrin formation is reversible. The order of reactivity is Formaldehyde > other aldehydes > Ketones]
For Examples:
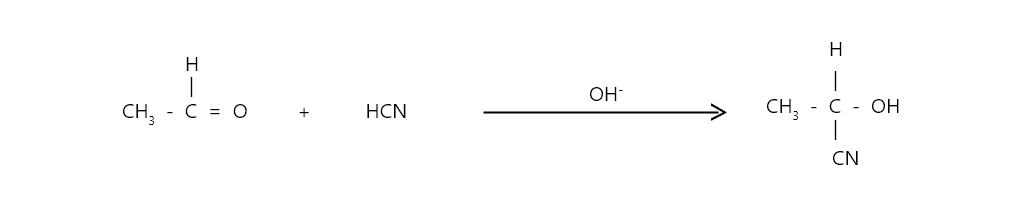
Acetaldehyde reacts with Hydrogen cyanide to give acetal cyanohydrin
- 添加硫酸氢钠
Aldehydes and ketones when treated with saturated aqueous solution of sodium bisulphate give addition products

They are water soluble crystalline solids that are hydroxy sulphonic acid salts. By treating them with weak mineral acids or alkali, they may be readily hydrolyzed back to aldehydes and ketones. As a result, this process is used to separate and purify aldehydes or ketones from other organic molecules.
- 添加格氏试剂
An aldehyde or a ketone undergoes nucleophilic addition of grignard reagent in presence of dry ether to form a complex which on acid hydrolysis gives alcohol

Methanal reacts with methyl magnesium iodide in presence of dry ether to give complex which on acid hydrolysis gives ethanol.

Note: Methanal produces primary alcohols containing one more carbon than in grignard reagant.
- 添加醇类
Aldehydes and Ketones react with alcohols to form branched acetal and cyclic acetal.
- Branched acetal
Two molecules of alcohol are added to carbonyl group to form acetal by elimination of one water molecule

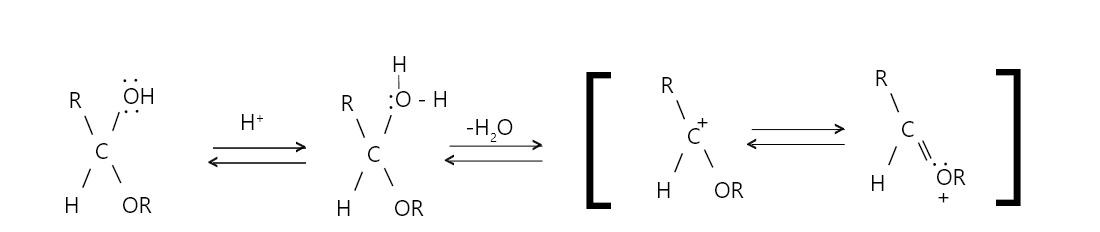
Step 1: Acid catalysed addition of an alcohol to the carbonyl group n presence of dry hydrogen chloride, to form hemiacetal.

Step 2: In the second half of the mechanism the hemiacetal gets converted to more stable acetal

- Cyclic acetal
Acetal is a geminal dialkoxy comp[und (an ether). Aldehydes and Ketones react with one equivalent of 1,2 or 1,3 -diols in presence of dry hydrogen chloride to give cyclic acetal.

Acetal and Ketals are rapidy hydrolysed back into aldehydes and Ketones, by the action of dilute mineral acids even at room temperature
- 添加氨及其衍生物
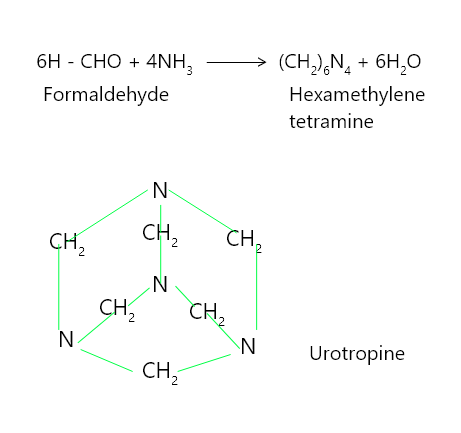
Urotropine is formed when formaldehyde interacts with an excess of ammonia to form hexamethylene tetramine. Urotropine is used as an antiseptic for the urinary tract, as well as to treat rheumatism and gout. It is also utilised in the manufacture of polymers and pharmaceuticals. When nitrated, it produces cyclonite, a powerful explosive.
6HCNO + 4NH3 ⟶ (CH2)6N4 + 6H2O
Hexamethylene tetramine has a cage-like structure composed of three six-membered rings, each in chair conformation.
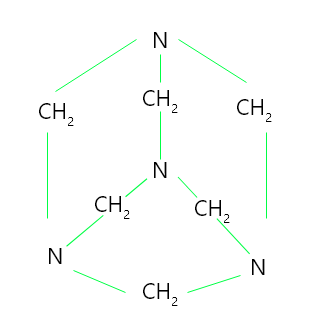
Structure of hexamethylene tetramine
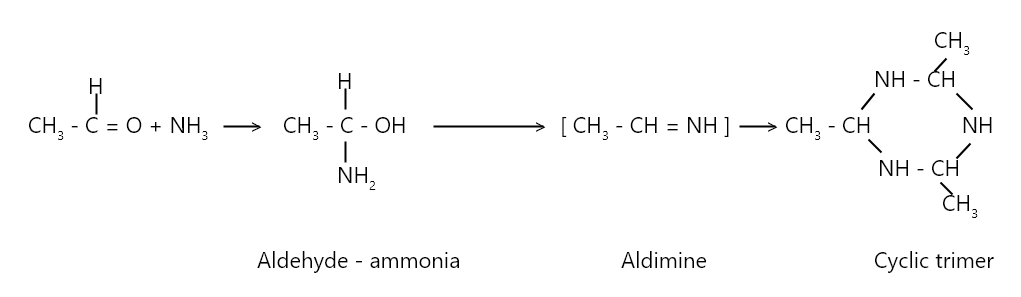
Acetaldehyde dissolved in ether reacts with ammonia gas to form solid acetaldehyde ammonía. It loses a water molecule to give an imine which further trimerises to give a heterocyclic compound.
When acetone is boiled with ammonia in slightly acidic medium for long time, diacetone amine is formed. The reactions take place in two steps as follows.

Several ammonia derivatives of the H2N-Z type react with aldehydes or ketones to form an addition product that loses a water molecule to form imines. The process is reversible and catalysed by acid. Carbonyl oxygen is protonated, making carbonyl carbon more vulnerable to attack by the nucleophile H2NZ. However, in sufficiently acidic media, the nitrogen atom of the ammonia derivative H2NZ gets protonated, resulting in the ion H I N+-Z, which is no longer a nucleophile. As a result, the process is aided by low acidity.
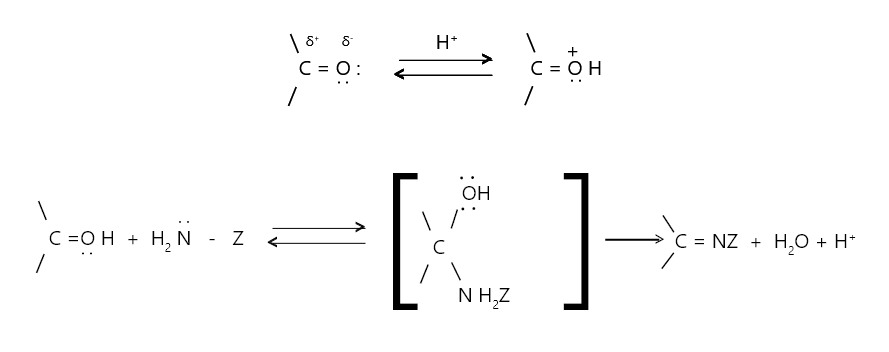
Here Z is -R, -Ar, -OH, -NH2, -NHC6H5 etc. The C = O group is transformed into the C = N – Z group. The majority of imines can be hydrolyzed back to aldehydes, ketones, and amines. A Schiff base is a substituted imine. Because these imine derivatives are frequently solids with high melting temperatures, they are employed for the characterization and identification of aldehydes and ketones.
Note: Carboxylic acid has a carbonyl group but does not undergo nucleophilic addition as do aldehyde and ketone. The partial positive charge on the carbonyl carbon atom is lowered as a result of resonance.
示例问题
问题1:什么是醛和酮?酮类是如何分类的?
回答:
Aldehydes are the carbonyl compounds, in which carbonyl group is attached with at-least one -H atom.
Ketones are the first oxidation products of secondary alcohols. They contain > C = O functional group.
Classification of Ketones
- Simple ketone (similar alkyl groups)
- Mixed ketone (different alkyl groups)
问题2:解释醛和酮发生亲核反应而羧酸不发生?
回答:
In carbonyl group (C=O)), oxygen being more electronegative, electrons get slightly shifted towards the oxygen atom. Due to this, the carbon-atom develops a partial positive charge (electron deficient)

Hence the carbon atom in the carbonyl group is readily attacked by a nucleophilic addition reaction.
On the other hand, Carboxylic acid possesses a carbonyl group but, unlike aldehyde and ketone, does not undergo nucleophilic addition. As a result of resonance, the partial positive charge on the carbonyl carbon atom is reduced.
问题3:下列试剂对甲醛的作用是什么
- 氢氰酸
- 硫酸钠3
回答:
- HCN
Action of HCN on formaldehyde: Fmaldehyde wen reacted with hydroge cyanid gives formaldehyde cyanohydrin
- NaHSO3
Formaldehyde when reacted with sodium bisulphite gives formaldehyde sodium bisulphite.

问题4:为什么醛比酮更容易发生亲核加成反应?
回答:
The electron-releasing group (+I effect) of the alkyl radicals linked to the carbonyl carbon in ketone makes the carbonyl carbon less positive. This reduces the proclivity of carbonyl carbon to accept the nucleophile. As a result, aldehydes are more easily nucleophilic than ketones.
问题 5:您将如何使用醛制备六亚甲基四胺,并绘制其结构?
回答:
Using Formaldehyde we can prepare hexamethylene tetramine
Formaldehyde, when reacted with ammonia (NH3) in ether solution gives hexamethylene tetramine, i.e., urotropine
问题6:CH 3 - MgI对乙醛的作用是什么,产生反应?
回答:
Acetaldehyde when reacted with CH3 – MgI in the presence of dry ether, gives Mg – complex, which on hydrolysis with dil. acid gives iso – propyl alcohol

问题 7:写出羰基化合物和铵衍生物的结构,它们结合起来得到以下亚胺。
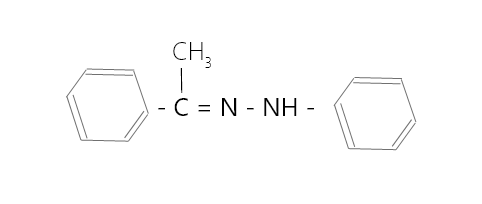
回答:
Carbonyl compound is,
Ammonium derivative is,
