具有最大节点数的级别
找到具有最大节点数的二叉树中的级别。根在级别 0。
例子:
Input: 
Output : 2
Explanation: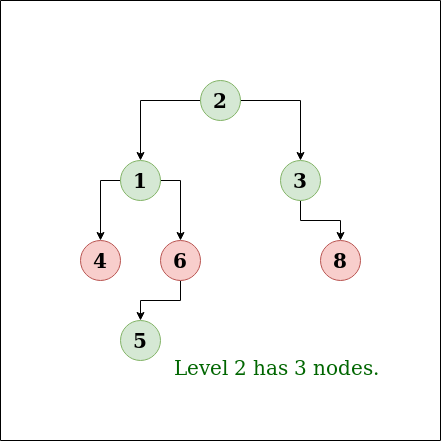
Input: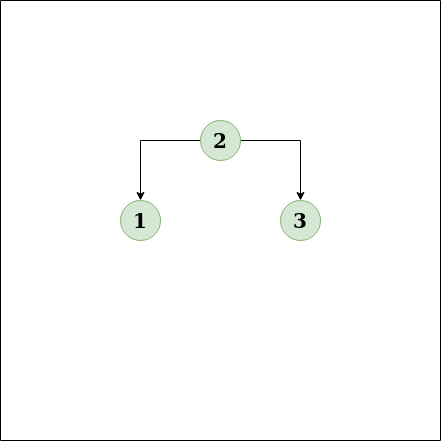
Output:1
Explanation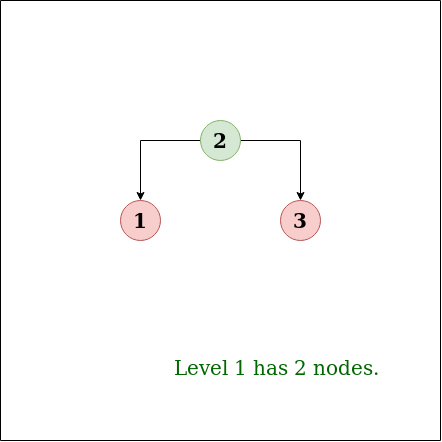
方法:众所周知,在带队列的二叉树的级别顺序遍历中,任何时候我们的队列都包含特定级别的所有元素。所以找到队列中最大节点数的级别。
BFS 遍历是一种用于遍历或搜索树或图的算法。它从树根开始,并在移动到下一个深度级别的节点之前探索当前深度的所有邻居节点。
所以在任何时候,BFS 的队列都将包含相邻层的元素。所以这使得该算法非常适合这个问题。
算法:
- 创建树,一个队列来存储节点并将根插入队列中。创建变量 level=0,count =0 和 level_no=-1
- 实现会略有不同,同一级别的所有元素将在一次迭代中删除。
- 当队列的大小大于 0 时运行一个循环。获取队列的大小 ( size ) 并存储它。如果 size 大于 count 则更新 count = size 和 level_no = level。
- 现在运行一个循环大小的时间,并从队列中弹出一个节点并插入其子节点(如果存在)。
- 递增级别。
执行:
C++
// C++ implementation to find the level
// having maximum number of Nodes
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree Node has data, pointer
to left child and a pointer to right
child */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
// function to find the level
// having maximum number of Nodes
int maxNodeLevel(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return -1;
queue q;
q.push(root);
// Current level
int level = 0;
// Maximum Nodes at same level
int max = INT_MIN;
// Level having maximum Nodes
int level_no = 0;
while (1)
{
// Count Nodes in a level
int NodeCount = q.size();
if (NodeCount == 0)
break;
// If it is maximum till now
// Update level_no to current level
if (NodeCount > max)
{
max = NodeCount;
level_no = level;
}
// Pop complete current level
while (NodeCount > 0)
{
Node *Node = q.front();
q.pop();
if (Node->left != NULL)
q.push(Node->left);
if (Node->right != NULL)
q.push(Node->right);
NodeCount--;
}
// Increment for next level
level++;
}
return level_no;
}
// Driver program to test above
int main()
{
// binary tree formation
struct Node *root = newNode(2); /* 2 */
root->left = newNode(1); /* / \ */
root->right = newNode(3); /* 1 3 */
root->left->left = newNode(4); /* / \ \ */
root->left->right = newNode(6); /* 4 6 8 */
root->right->right = newNode(8); /* / */
root->left->right->left = newNode(5);/* 5 */
printf("Level having maximum number of Nodes : %d",
maxNodeLevel(root));
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation to find the level
// having maximum number of Nodes
import java.util.*;
class GfG {
/* A binary tree Node has data, pointer
to left child and a pointer to right
child */
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = null;
node.right = null;
return(node);
}
// function to find the level
// having maximum number of Nodes
static int maxNodeLevel(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return -1;
Queue q = new LinkedList ();
q.add(root);
// Current level
int level = 0;
// Maximum Nodes at same level
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// Level having maximum Nodes
int level_no = 0;
while (true)
{
// Count Nodes in a level
int NodeCount = q.size();
if (NodeCount == 0)
break;
// If it is maximum till now
// Update level_no to current level
if (NodeCount > max)
{
max = NodeCount;
level_no = level;
}
// Pop complete current level
while (NodeCount > 0)
{
Node Node = q.peek();
q.remove();
if (Node.left != null)
q.add(Node.left);
if (Node.right != null)
q.add(Node.right);
NodeCount--;
}
// Increment for next level
level++;
}
return level_no;
}
// Driver program to test above
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// binary tree formation
Node root = newNode(2); /* 2 */
root.left = newNode(1); /* / \ */
root.right = newNode(3); /* 1 3 */
root.left.left = newNode(4); /* / \ \ */
root.left.right = newNode(6); /* 4 6 8 */
root.right.right = newNode(8); /* / */
root.left.right.left = newNode(5);/* 5 */
System.out.println("Level having maximum number of Nodes : " + maxNodeLevel(root));
}
} Python3
# Python3 implementation to find the
# level having Maximum number of Nodes
# Importing Queue
from queue import Queue
# Helper class that allocates a new
# node with the given data and None
# left and right pointers.
class newNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# function to find the level
# having Maximum number of Nodes
def maxNodeLevel(root):
if (root == None):
return -1
q = Queue()
q.put(root)
# Current level
level = 0
# Maximum Nodes at same level
Max = -999999999999
# Level having Maximum Nodes
level_no = 0
while (1):
# Count Nodes in a level
NodeCount = q.qsize()
if (NodeCount == 0):
break
# If it is Maximum till now
# Update level_no to current level
if (NodeCount > Max):
Max = NodeCount
level_no = level
# Pop complete current level
while (NodeCount > 0):
Node = q.queue[0]
q.get()
if (Node.left != None):
q.put(Node.left)
if (Node.right != None):
q.put(Node.right)
NodeCount -= 1
# Increment for next level
level += 1
return level_no
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# binary tree formation
root = newNode(2) # 2
root.left = newNode(1) # / \
root.right = newNode(3) # 1 3
root.left.left = newNode(4) # / \ \
root.left.right = newNode(6) # 4 6 8
root.right.right = newNode(8) # /
root.left.right.left = newNode(5)# 5
print("Level having Maximum number of Nodes : ",
maxNodeLevel(root))
# This code is contributed by PranchalkC#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// C# implementation to find the level
// having maximum number of Nodes
public class GfG
{
/* A binary tree Node has data, pointer
to left child and a pointer to right
child */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left;
public Node right;
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
public static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node node = new Node();
node.data = data;
node.left = null;
node.right = null;
return (node);
}
// function to find the level
// having maximum number of Nodes
public static int maxNodeLevel(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
{
return -1;
}
LinkedList q = new LinkedList ();
q.AddLast(root);
// Current level
int level = 0;
// Maximum Nodes at same level
int max = int.MinValue;
// Level having maximum Nodes
int level_no = 0;
while (true)
{
// Count Nodes in a level
int NodeCount = q.Count;
if (NodeCount == 0)
{
break;
}
// If it is maximum till now
// Update level_no to current level
if (NodeCount > max)
{
max = NodeCount;
level_no = level;
}
// Pop complete current level
while (NodeCount > 0)
{
Node Node = q.First.Value;
q.RemoveFirst();
if (Node.left != null)
{
q.AddLast(Node.left);
}
if (Node.right != null)
{
q.AddLast(Node.right);
}
NodeCount--;
}
// Increment for next level
level++;
}
return level_no;
}
// Driver program to test above
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// binary tree formation
Node root = newNode(2); // 2
root.left = newNode(1); // / \
root.right = newNode(3); // 1 3
root.left.left = newNode(4); // / \ \
root.left.right = newNode(6); // 4 6 8
root.right.right = newNode(8); // /
root.left.right.left = newNode(5); // 5
Console.WriteLine("Level having maximum number of Nodes : " + maxNodeLevel(root));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13 Javascript
输出:
Level having maximum number of nodes : 2 复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
在 BFS 遍历中,每个节点只被访问一次,所以时间复杂度是 O(n)。 - 空间复杂度: O(n)。
需要空间来将节点存储在队列中。