给定一个二叉树由N个节点和两个整数K和L,任务是在L增加值K节点的一排个级别,使得原树的方向保持不变。
例子:
Input: K = 1, L = 2
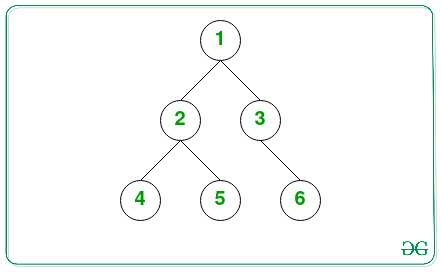
Output:
1
1 1
2 3
4 5 6
Explanation:
Below is the tree after inserting node with value 1 in the K(= 2) th level.
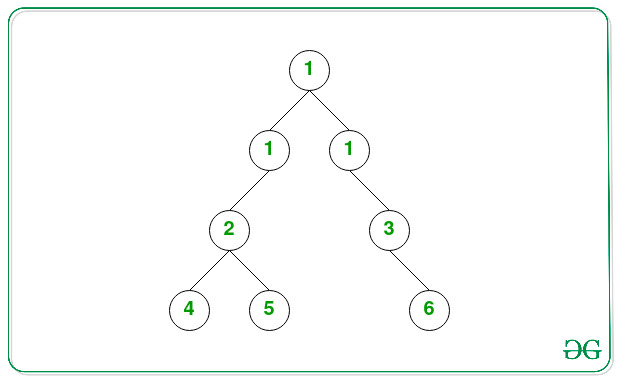
Input: K = 1, L = 1
Output:
1
1
2 3
4 5 6
方法:可以通过使用广度优先搜索遍历树并在级别(L – 1)的节点与其左右子树的根之间添加具有给定值的节点来解决给定的问题。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 如果L为1,则创建值为K的新节点,然后将当前根连接到新节点的左侧,使新节点成为根节点。
- 初始化一个队列,比如说Q ,它用于使用 BFS 遍历树。
- 初始化一个变量,比如CurrLevel ,它存储节点的当前级别。
- 在Q不为空() 且CurrLevel小于(L – 1) 时进行迭代并执行以下步骤:
- 将队列Q的大小存储在一个变量中,比如len 。
- len大于0 时进行迭代,然后弹出队列的最前面元素 并推送Q 中的左右子树。
- 将CurrLevel的值增加1 。
- 现在再次迭代 while Q is not empty() 并执行以下步骤:
- 将Q的前端节点存储在一个变量中,比如temp并弹出前端元素。
- 将临时节点的左子树和右子树存储在变量中,分别是temp1和temp2 。
- 创建一个值为K的新节点,然后通过将节点值分配给temp.left将当前节点连接到节点temp的左侧。
- 再次创建一个值为K的新节点,然后通过将节点值分配给temp.right将当前节点连接到节点temp的右侧。
- 然后将temp1 连接到新节点的左侧,即temp.left.left和temp2到新节点的右侧,即temp.right.right。
- 完成上述步骤后,按层序遍历打印树。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Class of TreeNode
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
// Constructor
TreeNode(int v)
{
val = v;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
// Function to add one row to a
// binary tree
TreeNode *addOneRow(TreeNode *root, int K, int L)
{
// If L is 1
if (L == 1) {
// Store the node having
// the value K
TreeNode *t = new TreeNode(K);
// Join node t with the
// root node
t->left = root;
return t;
}
// Stores the current Level
int currLevel = 1;
// For performing BFS traversal
queue Q;
// Add root node to Queue Q
Q.push(root);
// Traversal while currLevel
// is less than L - 1
while (Q.size() > 0 && currLevel < L - 1)
{
// Stores the count of the
// total nodes at the
// currLevel
int len = Q.size();
// Iterate while len
// is greater than 0
while (len > 0)
{
// Pop the front
// element of Q
TreeNode *node = Q.front();
Q.pop();
// If node.left is
// not NULL
if (node->left != NULL)
Q.push(node->left);
// If node.right is
// not NULL
if (node->right != NULL)
Q.push(node->right);
// Decrement len by 1
len--;
}
// Increment currLevel by 1
currLevel++;
}
// Iterate while Q is
// non empty()
while (Q.size() > 0)
{
// Stores the front node
// of the Q queue
TreeNode *temp = Q.front();
Q.pop();
// Stores its left sub-tree
TreeNode *temp1 = temp->left;
// Create a new Node with
// value K and assign to
// temp.left
temp->left = new TreeNode(K);
// Assign temp1 to the
// temp.left.left
temp->left->left = temp1;
// Store its right subtree
TreeNode *temp2 = temp->right;
// Create a new Node with
// value K and assign to
// temp.right
temp->right = new TreeNode(K);
// Assign temp2 to the
// temp.right.right
temp->right->right = temp2;
}
// Return the updated root
return root;
}
// Function to print the tree in
// the level order traversal
void levelOrder(TreeNode *root)
{
queue Q;
if (root == NULL) {
cout<<("Null")< 0) {
// Stores the total nodes
// at current level
int len = Q.size();
// Iterate while len
// is greater than 0
while (len > 0) {
// Stores the front Node
TreeNode *temp = Q.front();
Q.pop();
// Print the value of
// the current node
cout << temp->val << " ";
// If reference to left
// subtree is not NULL
if (temp->left != NULL)
// Add root of left
// subtree to Q
Q.push(temp->left);
// If reference to right
// subtree is not NULL
if (temp->right != NULL)
// Add root of right
// subtree to Q
Q.push(temp->right);
// Decrement len by 1
len--;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
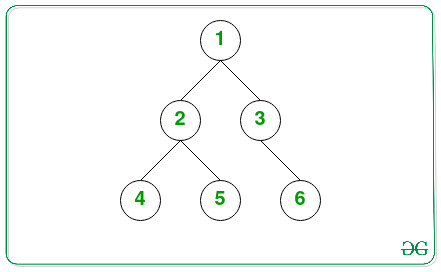
// Given Tree
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(1);
root->left = new TreeNode(2);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(4);
root->left->right = new TreeNode(5);
root->right = new TreeNode(3);
root->right->right = new TreeNode(6);
int L = 2;
int K = 1;
levelOrder(addOneRow(root, K, L));
}
// This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29. Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Class of TreeNode
public static class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
// Constructor
TreeNode(int val)
{
this.val = val;
}
}
// Function to add one row to a
// binary tree
public static TreeNode addOneRow(
TreeNode root, int K, int L)
{
// If L is 1
if (L == 1) {
// Store the node having
// the value K
TreeNode t = new TreeNode(K);
// Join node t with the
// root node
t.left = root;
return t;
}
// Stores the current Level
int currLevel = 1;
// For performing BFS traversal
Queue Q
= new LinkedList();
// Add root node to Queue Q
Q.add(root);
// Traversal while currLevel
// is less than L - 1
while (!Q.isEmpty()
&& currLevel < L - 1) {
// Stores the count of the
// total nodes at the
// currLevel
int len = Q.size();
// Iterate while len
// is greater than 0
while (len > 0) {
// Pop the front
// element of Q
TreeNode node = Q.poll();
// If node.left is
// not null
if (node.left != null)
Q.add(node.left);
// If node.right is
// not null
if (node.right != null)
Q.add(node.right);
// Decrement len by 1
len--;
}
// Increment currLevel by 1
currLevel++;
}
// Iterate while Q is
// non empty()
while (!Q.isEmpty()) {
// Stores the front node
// of the Q queue
TreeNode temp = Q.poll();
// Stores its left sub-tree
TreeNode temp1 = temp.left;
// Create a new Node with
// value K and assign to
// temp.left
temp.left = new TreeNode(K);
// Assign temp1 to the
// temp.left.left
temp.left.left = temp1;
// Store its right subtree
TreeNode temp2 = temp.right;
// Create a new Node with
// value K and assign to
// temp.right
temp.right = new TreeNode(K);
// Assign temp2 to the
// temp.right.right
temp.right.right = temp2;
}
// Return the updated root
return root;
}
// Function to print the tree in
// the level order traversal
public static void levelOrder(
TreeNode root)
{
Queue Q
= new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) {
System.out.println("Null");
return;
}
// Add root node to Q
Q.add(root);
while (!Q.isEmpty()) {
// Stores the total nodes
// at current level
int len = Q.size();
// Iterate while len
// is greater than 0
while (len > 0) {
// Stores the front Node
TreeNode temp = Q.poll();
// Print the value of
// the current node
System.out.print(
temp.val + " ");
// If reference to left
// subtree is not null
if (temp.left != null)
// Add root of left
// subtree to Q
Q.add(temp.left);
// If reference to right
// subtree is not null
if (temp.right != null)
// Add root of right
// subtree to Q
Q.add(temp.right);
// Decrement len by 1
len--;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given Tree
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);
root.left = new TreeNode(2);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(5);
root.right = new TreeNode(3);
root.right.right = new TreeNode(6);
int L = 2;
int K = 1;
levelOrder(addOneRow(root, K, L));
}
} 输出:
1
1 1
2 3
4 5 6时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live