从文件内容创建字符串的Java程序
文件是一种计算机资源,用于存储不同类型的数据,例如文本、图像、视频等。它基本上是绑定到单个实体的数据集合。在使用计算机时,能够处理文件变得至关重要,在本文中,我们将学习从文件中读取数据的各种方法。我们将使用 文件类 广泛用于相同。读取文件内容后,我们会将它们存储在一个字符串中,该字符串通常是一个字符数组。有关 String 类的更多信息,请单击 这里。
在Java中有 4 种方法可以读取文件的内容并将它们转换为字符串。下面提到了这 4 种方法:
- 使用 Files 类的 readString() 方法
- 以字节数组的形式读取文件的内容,然后将其转换为字符串
- 使用 BufferedReader 类逐行读取文件
- 以流的形式存储文件的内容,然后从中生成一个字符串
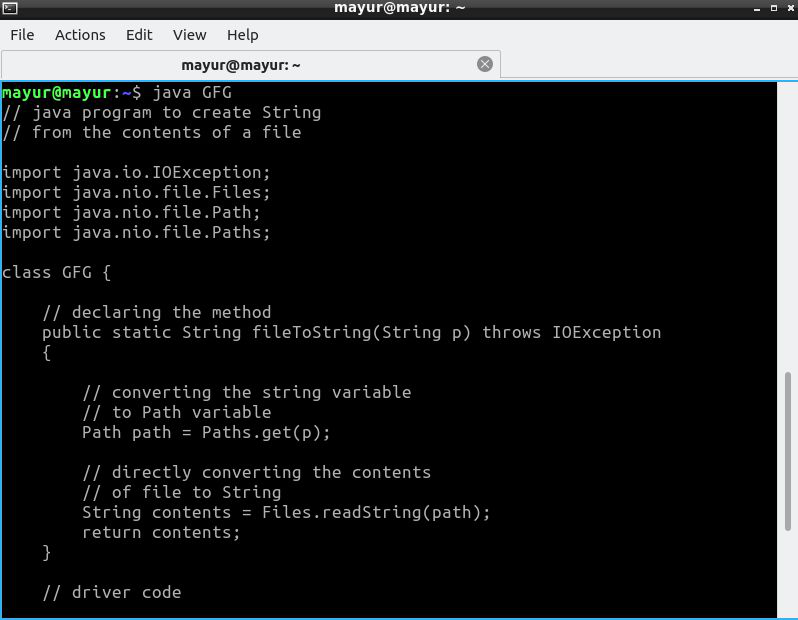
使用这种方法,我们部署了 readString()函数。
算法 :
- 以字符串形式读取文件路径。
- 将字符串转换为 Path 变量。
- 将此 Path 变量作为参数提供给 readString()函数。
- 将字符串返回给主函数。
执行 :
Java
// java program to create String
// from the contents of a file
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
class GFG {
// declaring the method
public static String fileToString(String p) throws IOException
{
// converting the string variable
// to Path variable
Path path = Paths.get(p);
// directly converting the contents
// of file to String
String contents = Files.readString(path);
return contents;
}
// driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
// printing the contents of the string
// by calling the fileToString() method
// parameter would be "C:\\Users\\harshit\\"
// + "Desktop\\text.txt" for Windows User
System.out.print(fileToString("/home/mayur/GFG.java"));
}
}Java
// java program to create a String
// from the contents of a File
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.Files;
class GFG {
public static String fileToString(String p)
{
// converting string variable
// to Path variable
Path path = Paths.get(p);
// initializing an empty byte array
byte[] b = {};
// try block
try {
// storing the bytes in the array
b = Files.readAllBytes(path);
}
// catch block
catch (IOException e) {
// printing the error
e.printStackTrace();
}
// converting the byte array to String
String contents = new String(b);
return contents;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// printing the string returned by the
// fileToString() method
// path would have been "C:\\Users\\"
// + "harshit\\Desktop\\text.txt"
System.out.print(fileToString("/home/mayur/GFG.java"));
}
}Java
// java program to create a String
// from the contents of a file
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
class GFG {
// declaring the method
public static String fileToString(String p)
{
// initializing the variable to
// store the string
String contents = "";
// Instantiating the FileReader class
try (FileReader f = new FileReader(p)) {
// instantiating the BufferedReader class
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(f);
// to store the current line read by the
// readLine () method
String current = "";
// looping till we find the null char
while ((current = br.readLine()) != null)
// storing the contents in string
contents += current + "\n";
}
// catch block
catch (IOException e) {
// printing the error
e.printStackTrace();
}
// returning the string
return contents;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// printing the string
// parameter would have been "C:\\Users\\"
// + "harshit\\Desktop\\text.txt"
// for Windows users
System.out.print(
fileToString("/home/mayur/GFG.java"));
}
}Java
// java program to create a string
// from the contents of a File
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.charset.*;
import java.util.stream.*;
class GFG {
// declaring the method
public static String fileToString(String p)
{
// converting string to path
// variable
Path path = Paths.get(p);
// initializing the StringBuffer class
StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer();
// initializing the final variable
String contents = "";
// storing the contents in a Stream
try (Stream str
= Files.lines(path, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) {
// converting stream to string array
String[] arr
= str.toArray(size -> new String[size]);
// iterating through the String array
for (String string : arr) {
contents += string + "\n";
}
}
// catch block
catch (IOException e) {
// printing the error
e.printStackTrace();
}
return contents;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// printing the string
// parameter would be "C:\\Users\\harshit"
// + "\\Desktop\\text.txt" for Windows Users
System.out.print(
fileToString("/home/mayur/GFG.java"));
}
} 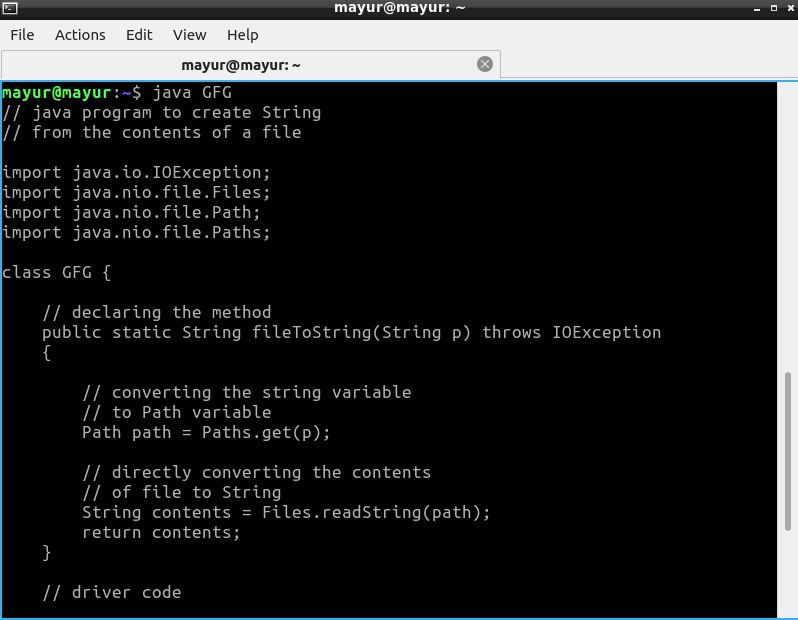
方法二:
使用这种方法,我们首先读取文件的内容并将它们存储为字节数组。最后,我们将其转换为字符串。
算法 :
- 首先,将路径作为字符串变量传递给函数。
- 接下来,将其转换为路径变量。
- 将此变量作为参数传递给 Files 类的 readAllBytes()函数。
- 接下来,将此数组转换为字符串。
执行 :
Java
// java program to create a String
// from the contents of a File
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.Files;
class GFG {
public static String fileToString(String p)
{
// converting string variable
// to Path variable
Path path = Paths.get(p);
// initializing an empty byte array
byte[] b = {};
// try block
try {
// storing the bytes in the array
b = Files.readAllBytes(path);
}
// catch block
catch (IOException e) {
// printing the error
e.printStackTrace();
}
// converting the byte array to String
String contents = new String(b);
return contents;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// printing the string returned by the
// fileToString() method
// path would have been "C:\\Users\\"
// + "harshit\\Desktop\\text.txt"
System.out.print(fileToString("/home/mayur/GFG.java"));
}
}
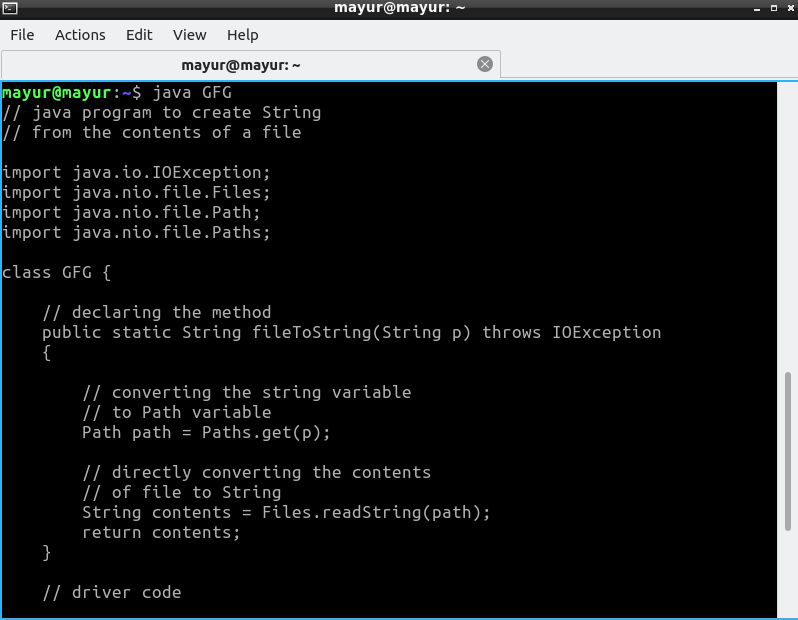
方法三:
使用这种方法,我们一次一行地读取文件的内容,直到我们使用 BufferedReader 类的 readLine()函数找到一个空字符。
算法 :
- 在调用 fileToString() 方法时传递包含文件路径的 String 变量
- 使用路径变量作为参数初始化 FileReader 对象。
- 使用 BufferedReader 类读取文件的内容。
- 当您看到空字符时停止。
- 将内容存储在字符串中,同时在接受的每一行后追加新行字符。
执行 :
Java
// java program to create a String
// from the contents of a file
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
class GFG {
// declaring the method
public static String fileToString(String p)
{
// initializing the variable to
// store the string
String contents = "";
// Instantiating the FileReader class
try (FileReader f = new FileReader(p)) {
// instantiating the BufferedReader class
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(f);
// to store the current line read by the
// readLine () method
String current = "";
// looping till we find the null char
while ((current = br.readLine()) != null)
// storing the contents in string
contents += current + "\n";
}
// catch block
catch (IOException e) {
// printing the error
e.printStackTrace();
}
// returning the string
return contents;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// printing the string
// parameter would have been "C:\\Users\\"
// + "harshit\\Desktop\\text.txt"
// for Windows users
System.out.print(
fileToString("/home/mayur/GFG.java"));
}
}
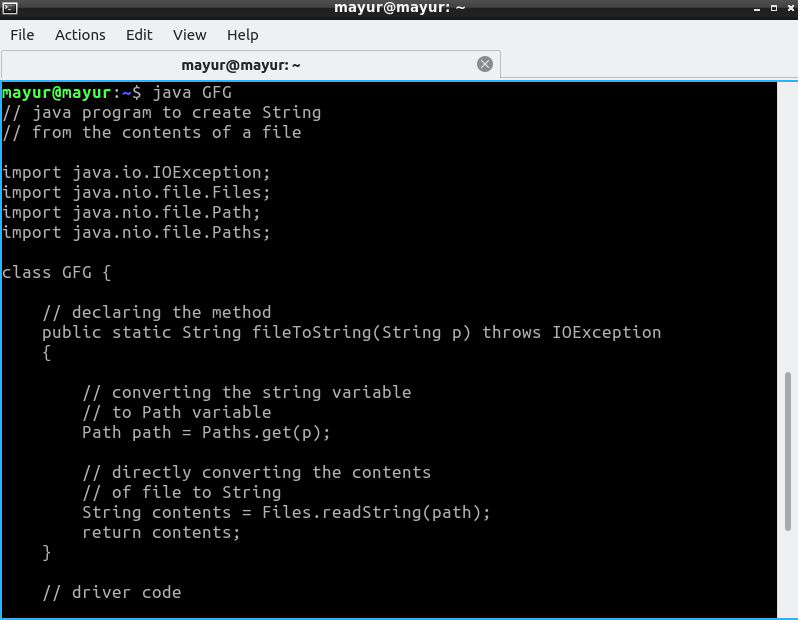
方法四:
使用这种方法,我们读取文件的内容并将它们存储在 Stream of String 中。接下来,我们将此 Stream 转换为 String 数组并对其进行迭代。我们将所有字符串存储在由 StringBuffer 类创建的单个字符串中。
算法 :
- 将字符串路径传递给函数fileToString()。
- 将此字符串转换为 Path 变量。
- 初始化 StringBuffer 对象以存储最终字符串。
- 读取内容并将它们存储在字符串流中。
- 将此字符串流转换为字符串数组。
- 遍历此数组并将所有字符串存储在 StringBuffer 对象中。
- 返回最终字符串。
执行 :
Java
// java program to create a string
// from the contents of a File
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.charset.*;
import java.util.stream.*;
class GFG {
// declaring the method
public static String fileToString(String p)
{
// converting string to path
// variable
Path path = Paths.get(p);
// initializing the StringBuffer class
StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer();
// initializing the final variable
String contents = "";
// storing the contents in a Stream
try (Stream str
= Files.lines(path, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) {
// converting stream to string array
String[] arr
= str.toArray(size -> new String[size]);
// iterating through the String array
for (String string : arr) {
contents += string + "\n";
}
}
// catch block
catch (IOException e) {
// printing the error
e.printStackTrace();
}
return contents;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// printing the string
// parameter would be "C:\\Users\\harshit"
// + "\\Desktop\\text.txt" for Windows Users
System.out.print(
fileToString("/home/mayur/GFG.java"));
}
}