从文件中打印与给定模式匹配的所有字符串的Java程序
找出打印文件中与给定模式匹配的所有字符串的方法。为了更接近目标,文件的概念应该非常清晰,以便在实现相同的 to 达到最终目标时想出一种打印字符串的方法。所以在处理字符串之前,紧迫的是要讨论出文件的概念。一旦掌握了文件概念,就会进行字符串处理。从头开始,目录中没有文件。
思考过程:文件概念 + 字符串
- 第一步:创建文件。
- 第2步
- 写入同一个文件。
- 条件检查消息是否成功写入。
- 在上面编写的文件中沉迷于字符串的概念。
- 如果与上述文件中的给定模式匹配,则显示所有字符串。
文件概念
第 1 步:创建一个新文件
File 是一个抽象的路径,它没有物理存在。只有在“使用”该文件时,才会命中底层物理存储。当文件被间接创建时,抽象路径被创建。该文件是一种方式,其中数据将根据需要存储。
主要,为了创建一个新文件,使用了内置文件和函数,这些文件和函数肯定会在这里抛出异常,以确保安全。所以为了处理它,我们将使用异常处理技术。在这里,我们将使用其中一种已知的 as-try-catch 块技术。
其次,额外的工作只是我们将导入我们将为其导入文件类的文件类。
语法:导入文件库或类
import java.util.File ;
语法:创建一个新文件
File object_name = new File(Directory);
语法:指定目录 在不同的操作系统中是不同的(假设Java文件在桌面上创建的名为'Folder'的文件夹中)
在 Linux 和 Mac 中
/Users/mayanksolanki/Desttop/Folder/
在 Windows 中:使用 '\\' 代替 '/' 来转义 '\'字符。所以访问相同的目录
\\Users\\mayanksolanki\\Desktop\\Folder\\
有两种标准方法可以直接在 File 类的帮助下创建新文件,或者通过在这两种方法中创建文件对象来间接在 FileOutputStream 的帮助下创建新文件。
- 通过使用文件类
- 通过使用 FileOutputStream 类
File Class | FileOutputStreamClass |
|---|---|
| It is a class which is just a handle for | It is an output stream that can be written to FileOutputStream JavaDoc |
| Method: File.createNewFile() | Method: FileOutputStream Example: echo > myFile.txt |
| It is used for those objects which are not having physical existence | It is used for those objects which are already existing |
这两个类都提供了一些主要用于对文件进行操作的方法。例如,创建、写入、比较两个路径名、检查特定文件是否存在等等。要理解这个主题,首先,考虑两种方法的一个例子。
- Terminal Command used to compile any java code on the machine
- Terminal Command used to Run any java code on the machine
- javac class_name.java // For Compilation
- java class_name // For Execution
Terminal of Mac operating system will be used for implementation and providing an output of accessing the directory
Directory Used : /Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/
第 2 步:写入文件:现在第一步结束。现在进入下一个 fie 将被写入
为此,需要导入一个名为“ FileWriter ”的类
语法:用于导入类编写
import java.io.FileWriter; // Class imported to write over a file
语法:覆盖哪个文件
FileWriter myWriter = new FileWriter("filename.txt");
语法:写入文件
myWriter.write("Insert the string here which later is supposed to be checked present or not");
第 3 步:打印文件中的字符串:
为此,需要导入一个名为“ Util.regex ”的类,并且该方法使用此类的“ Patternname.matcher() ”方法仅用于匹配文件中存在的字符串。
Pattern pattern_name = Pattern.compile("[A-Za-z][a-z]+");
因此现在提出名为“test.txt”的演示类的方法
方法:
- 读取文件。
- 定义要搜索的模式。
- 在文件的每一行中查找模式。
考虑一个通过实施来讨论上述内容的示例,以检查内部工作:
Java
// Java Program to print all the
// Strings that match a given
// Pattern from a File
// Importing Classes/Files
import java.io.*;
// Importing Special Class
// for matching patterns
import java.util.regex.*;
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
// Try block for detecting exception
try {
// Creating a file
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("test.txt");
// Writing in file
writer.write("Writing in the test file!");
writer.close();
// Success Message
System.out.println(
"Successfully wrote to the file.\n");
}
// Catch block to handle exception
catch (IOException e) {
// Catching any error
System.out.println("An error occurred.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
// FileReader
BufferedReader read = new BufferedReader(
new FileReader("test.txt"));
// The regex pattern
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("[A-Za-z][a-z]+");
System.out.println("Matched Content:");
// For each line of input, try matching the pattern
String line;
while ((line = read.readLine()) != null) {
// For each match in the
// line, extract and print it
Matcher match = pattern.matcher(line);
while (match.find()) {
// One method:
// System.out.println(match.group(0));
// Another method:
// Get the starting position of the text
int start = match.start(0);
// Get ending position
int end = match.end(0);
// Print whatever matched.
System.out.println(
line.substring(start, end));
}
}
}
}输出:
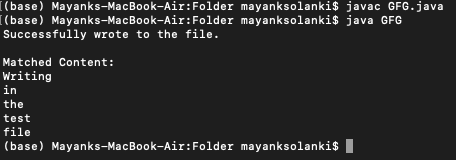
上述输入是在 mac 终端上运行的硬编码输入,其中:
- 第一行 'javac file_name. Java' 编译文件名为GFG的目录下的文件
- 第2行' Java file_name'代表上面的代码被执行
- 直到最后的第三行是在创建的类“test.txt”中匹配的字符串的硬编码输出,作为上述代码的示例类