使用PythonGoogle Sheets 数据存储到 SQLite 数据库中
在本文中,我们将使用Python将谷歌表数据存储到数据库中。第一步是启用 API 并创建凭据,让我们开始吧。
启用 API 并创建凭证
- 转到 Cloud Console 中的 Marketplace。
- 单击启用 API 和服务
- 然后搜索 Google Drive API 并启用它
- 然后转到屏幕左侧导航栏上的凭据选项卡。
- 然后单击创建凭据,然后选择服务帐户密钥
- 然后通过给它一个名称来创建一个新的服务帐户,并将“项目”子字段下的“角色”设置为“编辑器”,并将密钥类型保持为 JSON,然后单击“创建”按钮。安全地保存下载的 JSON。
- 完成所有这些步骤后,您的页面应如下所示。
- 再次转到仪表板并执行相同的步骤。这次搜索 Google Sheets 并启用 API。

启用 API 后,让我们创建谷歌表单。
创建谷歌表单:
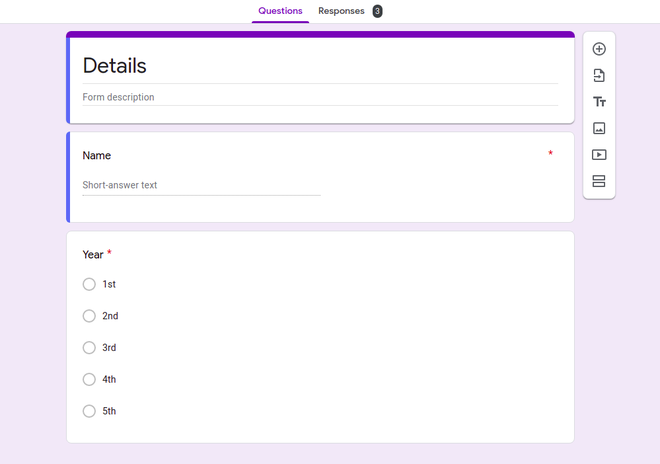
- 创建一个谷歌表单。在这里,我们保留了一个只有两个字段的简单表单。
- 使 Google 表单接受 Google 表格中的回复。
- 然后为字段client_email查找下载的 JSON 文件并复制该电子邮件。
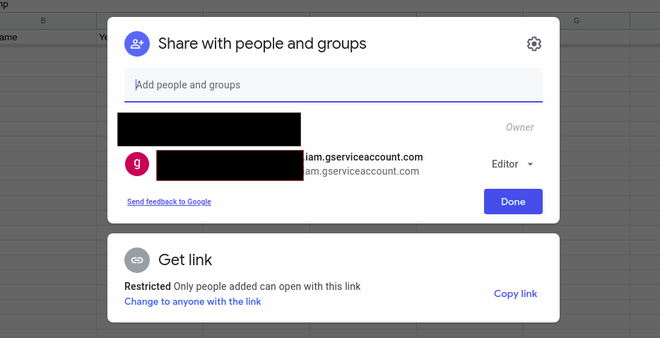
- 打开新创建的电子表格并单击共享选项并在其中键入粘贴client_email 。
在授予对客户端电子邮件的访问权限后,它应该看起来像这样。顶部的电子邮件将是您的个人电子邮件,底部的电子邮件将是client_email
谷歌表格:
这样我们就完成了设置。现在,让我们开始编码。在开始之前,让我们先了解一下流程。
- 我们将根据表单的条目模式创建一个数据库和一个表。
- 通过 API 连接到工作表并获取所有行。
- 执行插入查询将工作表中的行数据插入到数据库中。
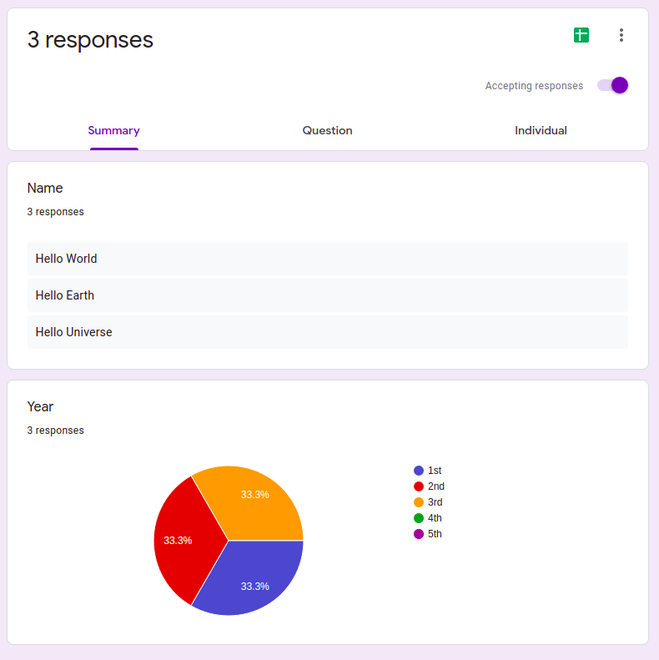
方法:
- 首先,我们从服务帐户 JSON 初始化凭据。
- 然后我们使用这些凭证对象来访问我们从 Google 表单生成的表格。
- 一旦我们可以访问工作表,我们只需一次提取所有行以减少 API 调用次数。
- 现在,我们首先建立与数据库的连接。在这里,为了简单起见,我们使用 sqlite 数据库。您可以使用任何类型的数据库,您需要做的就是传递连接字符串。
- 建立连接后,我们创建表(如果它不存在)
- 一旦表准备好,我们将获取的行传递给表。我们简单地遍历获得的所有行,然后将行中的每一列值传递给数据库。
代码:
Python3
# imports
import sqlite3
from sqlite3 import Error
import gspread
from oauth2client.service_account import ServiceAccountCredentials
def get_from_sheet():
# name of the sheet
# you should replace with the name
# of your sheet
sheet_name = "Details (Responses)"
config = { Your_API
# should contain the service account
# key JSON as dict here
}
# use credentials to create a client to
# interact with the Google Drive API
scope = [
"https://spreadsheets.google.com/feeds",
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive",
]
# credential object for authenticating
creds_obj = ServiceAccountCredentials.from_json_keyfile_dict(config, scope)
# initializing gspread client with the
# credentials object
client = gspread.authorize(creds_obj)
# Find a workbook by name and open the
# first sheet Make sure you use the
# right name here.
sheet = client.open(sheet_name).sheet1
# returns all the data in the entire sheet
return sheet.get_all_values()
class SQLite:
# change this to your sqlite file path
# if you keep then, then it will create
# a sqlite database in your current working
# directory
DB_NAME = "db.sqlite"
def __init__(self):
self.conn = self.create_connection()
self._get_or_create_table()
@classmethod
def create_connection(cls):
"""
create a database connection to the SQLite database specified by db_name
:return: Connection object or None
"""
conn = None
try:
# connects or creates a sqlite3 file
conn = sqlite3.connect(cls.DB_NAME)
return conn
except Error as e:
print(e)
# returns the connection object
return conn
def _get_or_create_table(self):
"""Creates the table if it does not exists"""
# sql query to create a details table
create_table_sql = """CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS details (
timestamp varchar(20) PRIMARY KEY,
name varchar(30) NOT NULL,
year varchar(3) NOT NULL
)"""
try:
# initializing the query cursor
c = self.conn.cursor()
# executes the create table query
c.execute(create_table_sql)
except Error as e:
# prints the exception if any errors
# occurs during runtime
print(e)
def add_data_to_table(self, rows: list):
"""Inserts the data from sheets to the table"""
# initializing sql cursor
c = self.conn.cursor()
# excluding the first row because it
# contains the headers
insert_table_sql = """INSERT INTO details (timestamp, name, year)
VALUES (?, ?, ?);"""
for row in rows[1:]:
# inserts the data into the table
# NOTE: the data needs to be in the order
# which the values are provided into the
# sql statement
c.execute(insert_table_sql, tuple(row))
# committing all the changes to the database
self.conn.commit()
# closing the connection to the database
c.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# fetches data from the sheets
data = get_from_sheet()
sqlite_util = SQLite()
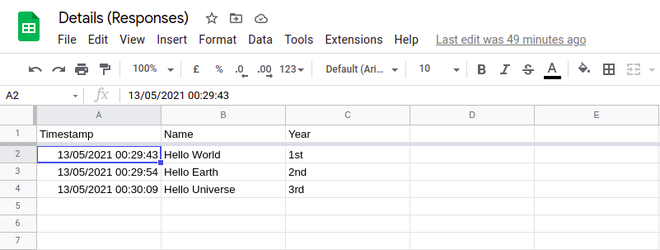
sqlite_util.add_data_to_table(data)输出:
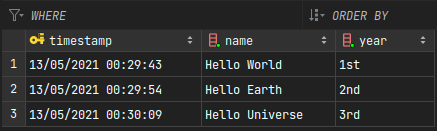
如您所见,我们现在成功地在我们的数据库中拥有了数据。