锈病——矢量
Vector是 Rust 中的一个模块,它提供容器空间来存储值。它是一个连续的可调整大小的数组类型,具有堆分配的内容。它由Vec
一个简单的解释向量的方式是,它是一个像数组一样存储值的容器,但它比数组数据结构有更多的优势。它可以在运行时动态增加大小。它由标准库提供,可以存储任何数据类型的值。向量的数据分配在堆上。它的长度定义了向量中存在的元素数量。它的容量定义了这个向量的堆上实际分配的空间,形式为 2^n。
句法:
Vec
Where T denotes type of data. 在 Rust 中创建一个向量:
要创建 Vector,只需遵循下面列出的方法。
1. 使用 Vec::new() 方法:
let v : Vec = Vec::new(); 这里v是将包含 64 位整数数据类型的初始化向量。它在Vec::new() 方法的帮助下初始化。
Rust
fn main() {
let v : Vec = Vec::new();
// printing the size of vector
println!("{ }",v.len());
} Rust
fn main() {
let v = vec!['G','E','E','K','S'];
// printing the size of vector
println!("{ }",v.len());
}Rust
fn main() {
let v = vec!['G','E','E','K','S'];
// here index is the non negative value which is smaller than the size of the vector
let index: usize = 3;
//getting value at given index value
let ch: char = v[index];
print!("{ }\n",ch);
}Rust
// Method to print the get value
fn value(n:Option<&char>)
{
match n
{
Some(n)=>println!("Element of vector {}",n),
None=>println!("None"),
}
}
fn main() {
let v = vec!['G','E','E','K','S'];
// here index is the non negative value which is
// smaller than the size of the vector
let index: usize = 3;
// getting value at given index value
let ch: Option<&char> = v.get(index);
value(ch);
}Rust
fn main() {
let v = vec!['G','E','E','K','S'];
print!("Vector elements : ");
//loop to interate elements in vector
for i in v
{
// iterating through i on the the vector
print!("{} ",i);
}
print!("\n",);
}Rust
fn main() {
let mut v : Vec = Vec::new();
v.push('A');
v.push('B');
v.push('C');
// now vector elements will be
// loop to interate elements in vector
for i in v
{
// iterating through i on the the vector
print!("{} ",i);
}
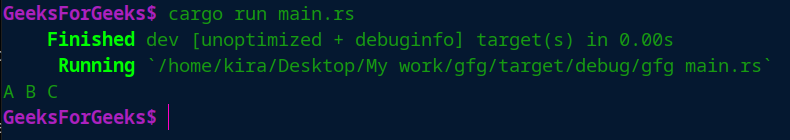
print!("\n");
} 输出:

2. 在 Rust 中使用宏:
let v = vec!['G','E','E','K','S']; 这里这个向量是使用宏vec!创建的。它存储了我们在这里提供的 char 类型的值。
锈
fn main() {
let v = vec!['G','E','E','K','S'];
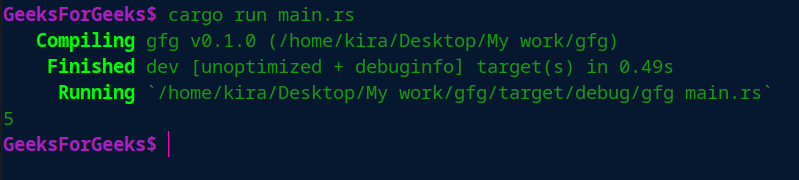
// printing the size of vector
println!("{ }",v.len());
}
输出:
访问向量:
下面列出的方法可用于在 Rust 编程中访问向量。
1. 使用下标运算符:
与其他语言中的索引概念类似,下标运算符可用于通过其索引直接访问向量中的值。重要的是要注意索引从 0 开始。
let v = vec!['G','E','E','K;','S'];
//here index is the integer non negative value which is smaller than the size of the vector.
char ch = v [ index ];例子:
锈
fn main() {
let v = vec!['G','E','E','K','S'];
// here index is the non negative value which is smaller than the size of the vector
let index: usize = 3;
//getting value at given index value
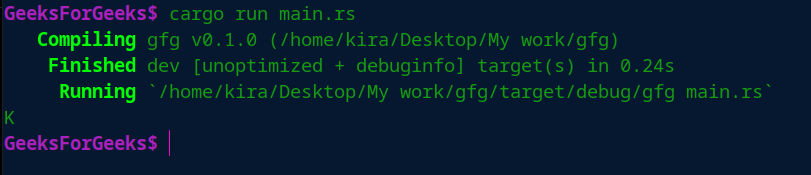
let ch: char = v[index];
print!("{ }\n",ch);
}
输出:
2.使用get()方法
访问向量元素的第二种方法是使用 get(index) 方法,将向量的索引作为参数传递。它返回类型为 Option<&t> 的值。
let v = vec!['G','E','E','K;','S'];
//here index is the integer non negative value which is smaller than the size of the vector.
let value: Option<&char> = v.get(index); 例子:
锈
// Method to print the get value
fn value(n:Option<&char>)
{
match n
{
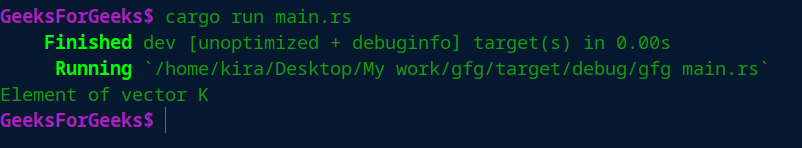
Some(n)=>println!("Element of vector {}",n),
None=>println!("None"),
}
}
fn main() {
let v = vec!['G','E','E','K','S'];
// here index is the non negative value which is
// smaller than the size of the vector
let index: usize = 3;
// getting value at given index value
let ch: Option<&char> = v.get(index);
value(ch);
}
输出:
3. 对向量进行迭代:
为了访问向量,我们也可以像在其他编程语言中所做的那样遍历向量。我们可以使用for 循环来遍历一个向量。
let v = vec!['G','E','E','K;','S'];
print!("Vector elements :");
for i in v
{
// iterating through i on the the vector
print!("{} ",i);
} 例子:
锈
fn main() {
let v = vec!['G','E','E','K','S'];
print!("Vector elements : ");
//loop to interate elements in vector
for i in v
{
// iterating through i on the the vector
print!("{} ",i);
}
print!("\n",);
}
输出:
更新向量:
创建向量后,我们可以使用 push() 方法更新向量。如果向量大小小于向量容量,或者如果向量大小大于向量容量,则推送新元素,然后分配向量大小的两倍空间,然后复制新分配的向量中的所有元素并释放内存前一个向量。
它推动向量末尾的元素。
let mut v : Vec = Vec::new();
vec.push('A');
vec.push('B');
vec.push('C');
// now vector size will be 3 例子:
锈
fn main() {
let mut v : Vec = Vec::new();
v.push('A');
v.push('B');
v.push('C');
// now vector elements will be
// loop to interate elements in vector
for i in v
{
// iterating through i on the the vector
print!("{} ",i);
}
print!("\n");
}
输出: