Linux 中的 Incron 命令与示例
Incron 是一个“inotify cron”系统。它的工作方式与常规 cron 非常相似,但是,cron 作业是由某个时刻触发的(每周日,每天上午 12 点等),而 incron 作业由文件系统事件(例如创建、删除或修改文件或目录)。以下是一些可以使用incron 的示例:
- 监控文件使用和统计
- 如果在配置文件中进行了更改,则通知程序(例如服务器守护程序)。
- 防止关键文件的更改。
- 自动更改备份或版本控制。
- 处理上传的文件。
注意:由于 incron 不是递归的,因此您还必须添加您希望它查看的所有子目录。不要在您监视的目录中的 incron 作业中执行任何操作以避免循环。
安装和配置 Incron:
使用以下命令安装 incron。
$sudo apt-get install incron配置:要配置 incron 访问,我们必须配置/etc/incron.allow和/etc/incron.deny文件。
- /etc/incron.allow :如果此文件存在,则只有此处列出的用户可以使用 incron。
- /etc/incron.deny :如果此文件存在,则只有此处未列出的用户可以使用 incron。
如果这些文件都不存在,系统上的每个用户都可以使用 incron。
句法:
在这里:
-
是要观看的目录的绝对路径。 -
是事件掩码(符号或数字形式)。 Event Symbols (Masks):
IN_ACCESS File was accessed (read).
IN_ATTRIB Metadata changed (permissions, timestamps, extended attributes, etc.).
IN_CLOSE_WRITE File opened for writing was closed.
IN_CLOSE_NOWRITE File not opened for writing was closed.
IN_CREATE File/directory created in watched directory.
IN_DELETE File/directory deleted from watched directory.
IN_DELETE_SELF Watched file/directory was itself deleted.
IN_MODIFY File was modified.
IN_MOVE_SELF Watched file/directory was itself moved.
IN_MOVED_FROM File moved out of watched directory.
IN_MOVED_TO File moved into watched directory.
IN_OPEN File was opened. 是带有参数的可执行文件(或脚本)。 The following wildcards may be used inside the command specification.
$$ Prints a dollar sign
$@ Add the watched filesystem path
$# Add the event-related file name
$% Add the event flags (textually)
$& Add the event flags (numerically)
设置 Incron
安装和配置完成后,您需要使用以下命令启动 incron 守护进程:
$ /etc/init.d/incrond start
OR
$ systemctl start incron.service您可以使用以下方法检查 incron 状态:
$ systemctl status incron.service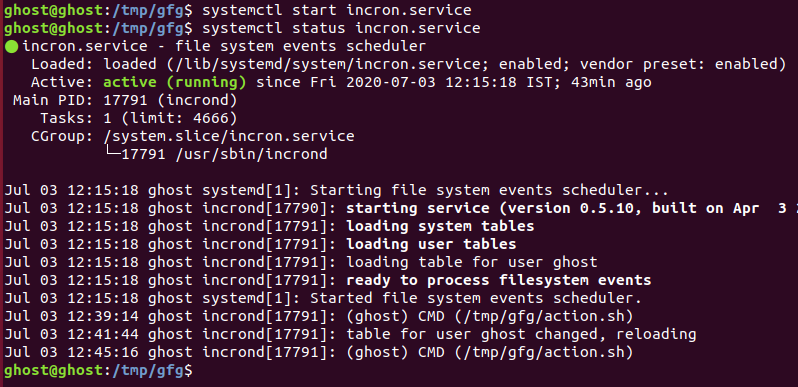
现在您必须将您的用户或 root 添加到/etc/incron.allow配置中。文件,以便该用户可以访问corntab。
$ sudo nano /etc/incron.allow使用 incrontab 命令,您可以列出 (-l)、编辑 (-e) 和删除 (-r) incrontab 条目。
$ incrontab -l
$ incrontab -e
$ incrontab -r
监控文件
假设,我们想要监视一个文件( /tmp/gfg/myfile.txt ),并且对于每次更改,我们想要将修改的日期和时间记录到日志文件( /tmp/logs/mylogs.txt )中。
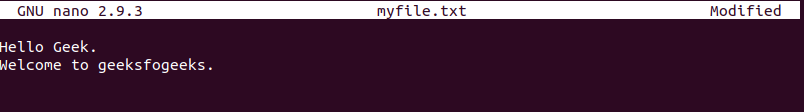
1. “myfile.txt”的内容如下所示。 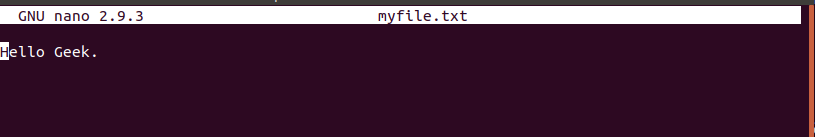
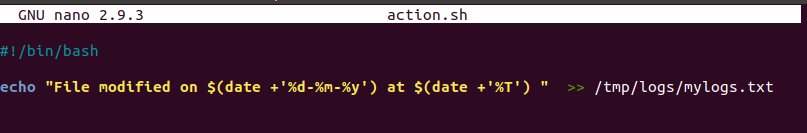
2.创建一个名为“ action.sh ”的脚本,将日期和时间记录到日志文件中,我们将在每次更改 myfile.txt 时运行此脚本。
3.现在您可以使用命令编辑 crontab。
$ crontab -e: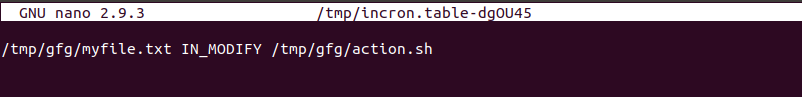
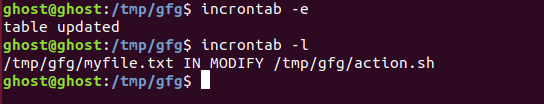
4.现在让我们对 myfile.txt 进行更改。
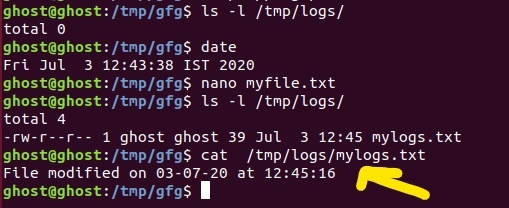
5.如果我们看到日志,我们可以看到更改的日期和时间。
监控目录
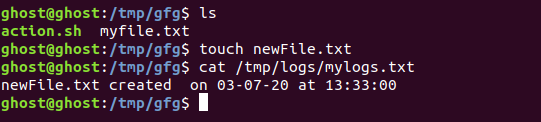
现在让我们监视目录( /tmp/gfg/ ),对于每个新文件/目录,我们将创建的日期和时间记录到日志文件( /tmp/logs/mylogs.txt )中。
1.打开 incrontab 文件。这里我们在命令中传递“ $# ”通配符,它将事件相关的文件名传递给命令。

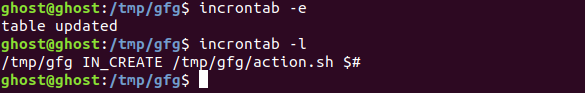
2.我们将更新action.sh。这里我们使用作为参数传递的“$#”通配符。
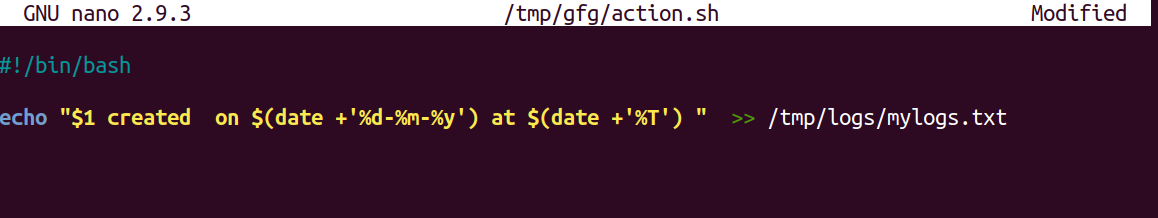
3.现在让我们通过在 gfg 目录中创建一个新文件来尝试一下,并在日志文件中查看结果: