Python MySQL – Where 子句
MySQL数据库中使用where子句根据需要的条件过滤数据。您可以使用 where 子句获取、删除或更新 MySQL 数据库中的特定数据集。
句法
SELECT column1, column2, …. columnN FROM [TABLE NAME] WHERE [CONDITION];
上述语法用于显示符合条件的一组数据。
示例:考虑以下名为 College 的数据库,并有一个表名作为学生。
数据库架构:
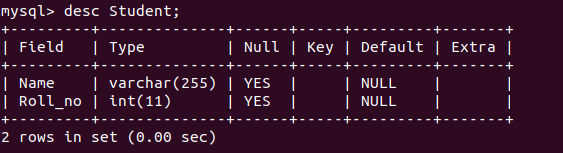
数据库:
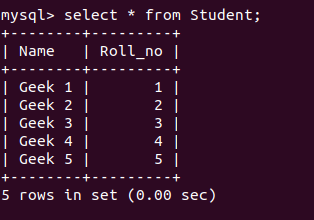
Python中的 Where 子句
在Python中使用 where 子句的步骤是:
- 首先在 MySQL 和Python程序之间建立一个连接。它是通过导入 mysql.connector 包并使用 mysql.connector.connect() 方法来完成的,用于将用户名、密码、主机(可选默认值:localhost)和数据库(可选)作为参数传递给它。
- 现在,使用 cursor() 方法在上面创建的连接对象上创建一个游标对象。数据库游标是一种控制结构,可以遍历数据库中的记录。
- 然后,通过 execute() 方法执行 where 子句语句。
Python3
import mysql.connector
#Establishing connection
conn = mysql.connector.connect(user='your_username',
host='localhost',
password ='your_password',
database='College')
# Creating a cursor object using
# the cursor() method
mycursor = conn.cursor();
# SQL Query
sql = "select * from Student where Roll_no >= 3;"
# Executing query
mycursor.execute(sql)
myresult = mycursor.fetchall()
for x in myresult:
print(x)
# Closing the connection
conn.close()输出:
