查找字符串数组是否可以链接形成一个圆圈 |设置 1
给定一个字符串数组,找出给定的字符串是否可以链接成一个圆圈。如果 X 的最后一个字符与 Y 的第一个字符相同,则可以将一个字符串X 放在另一个字符串Y 之前。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {"geek", "king"}
Output: Yes, the given strings can be chained.
Note that the last character of first string is same
as first character of second string and vice versa is
also true.
Input: arr[] = {"for", "geek", "rig", "kaf"}
Output: Yes, the given strings can be chained.
The strings can be chained as "for", "rig", "geek"
and "kaf"
Input: arr[] = {"aab", "bac", "aaa", "cda"}
Output: Yes, the given strings can be chained.
The strings can be chained as "aaa", "aab", "bac"
and "cda"
Input: arr[] = {"aaa", "bbb", "baa", "aab"};
Output: Yes, the given strings can be chained.
The strings can be chained as "aaa", "aab", "bbb"
and "baa"
Input: arr[] = {"aaa"};
Output: Yes
Input: arr[] = {"aaa", "bbb"};
Output: No
Input : arr[] = ["abc", "efg", "cde", "ghi", "ija"]
Output : Yes
These strings can be reordered as, “abc”, “cde”, “efg”,
“ghi”, “ija”
Input : arr[] = [“ijk”, “kji”, “abc”, “cba”]
Output : No这个想法是创建一个所有字符的有向图,然后找出它们是否是图中的欧拉回路。
下图给出了一些字符串数组的图形表示,
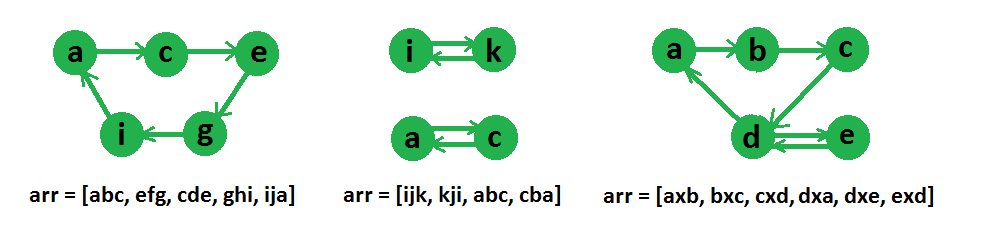
如果存在欧拉回路,则可以形成链,否则不会。
请注意,只有当每个顶点的入度和出度相同并且所有非零度顶点形成单个强连通分量时,有向图才具有欧拉回路。
以下是算法的详细步骤。
1)创建一个顶点数等于字母大小的有向图g。我们在下面的程序中创建了一个有 26 个顶点的图。
2) 对给定的字符串数组中的每个字符串执行以下操作。
.....a)从给定图形的第一个字符到最后一个字符添加一条边。
3)如果创建的图有欧拉回路,则返回true,否则返回false。
以下是上述算法的 C++ 和Python实现。
C++
// A C++ program to check if a given directed graph is Eulerian or not
#include
#include
#define CHARS 26
using namespace std;
// A class that represents an undirected graph
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list *adj; // A dynamic array of adjacency lists
int *in;
public:
// Constructor and destructor
Graph(int V);
~Graph() { delete [] adj; delete [] in; }
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w) { adj[v].push_back(w); (in[w])++; }
// Method to check if this graph is Eulerian or not
bool isEulerianCycle();
// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
bool isSC();
// Function to do DFS starting from v. Used in isConnected();
void DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[]);
Graph getTranspose();
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
in = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
in[i] = 0;
}
/* This function returns true if the directed graph has an eulerian
cycle, otherwise returns false */
bool Graph::isEulerianCycle()
{
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if (isSC() == false)
return false;
// Check if in degree and out degree of every vertex is same
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() != in[i])
return false;
return true;
}
// A recursive function to do DFS starting from v
void Graph::DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFSUtil(*i, visited);
}
// Function that returns reverse (or transpose) of this graph
// This function is needed in isSC()
Graph Graph::getTranspose()
{
Graph g(V);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for(i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
{
g.adj[*i].push_back(v);
(g.in[v])++;
}
}
return g;
}
// This function returns true if all non-zero degree vertices of
// graph are strongly connected. Please refer
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/connectivity-in-a-directed-graph/
bool Graph::isSC()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited (For first DFS)
bool visited[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Find the first vertex with non-zero degree
int n;
for (n = 0; n < V; n++)
if (adj[n].size() > 0)
break;
// Do DFS traversal starting from first non zero degree vertex.
DFSUtil(n, visited);
// If DFS traversal doesn’t visit all vertices, then return false.
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() > 0 && visited[i] == false)
return false;
// Create a reversed graph
Graph gr = getTranspose();
// Mark all the vertices as not visited (For second DFS)
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Do DFS for reversed graph starting from first vertex.
// Starting Vertex must be same starting point of first DFS
gr.DFSUtil(n, visited);
// If all vertices are not visited in second DFS, then
// return false
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() > 0 && visited[i] == false)
return false;
return true;
}
// This function takes an of strings and returns true
// if the given array of strings can be chained to
// form cycle
bool canBeChained(string arr[], int n)
{
// Create a graph with 'alpha' edges
Graph g(CHARS);
// Create an edge from first character to last character
// of every string
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
string s = arr[i];
g.addEdge(s[0]-'a', s[s.length()-1]-'a');
}
// The given array of strings can be chained if there
// is an eulerian cycle in the created graph
return g.isEulerianCycle();
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
string arr1[] = {"for", "geek", "rig", "kaf"};
int n1 = sizeof(arr1)/sizeof(arr1[0]);
canBeChained(arr1, n1)? cout << "Can be chained \n" :
cout << "Can't be chained \n";
string arr2[] = {"aab", "abb"};
int n2 = sizeof(arr2)/sizeof(arr2[0]);
canBeChained(arr2, n2)? cout << "Can be chained \n" :
cout << "Can't be chained \n";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to check if a given
// directed graph is Eulerian or not
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
// A class that represents an
// undirected graph
class GFG{
static final int CHARS = 26;
// No. of vertices
int V;
// A dynamic array of adjacency lists
List> adj;
int[] in;
// Constructor
GFG(int V)
{
this.V = V;
in = new int[V];
adj = new ArrayList<>(CHARS);
for(int i = 0; i < CHARS; i++)
{
adj.add(i, new ArrayList<>());
}
}
// Function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj.get(v).add(w);
in[w]++;
}
// Method to check if this graph
// is Eulerian or not
boolean isEulerianCycle()
{
// Check if all non-zero degree
// vertices are connected
if (!isSC())
return false;
// Check if in degree and out
// degree of every vertex is same
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj.get(i).size() != in[i])
return false;
return true;
}
// This function returns true if all
// non-zero degree vertices of graph
// are strongly connected. Please refer
boolean isSC()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not
// visited (For first DFS)
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Find the first vertex with
// non-zero degree
int n;
for(n = 0; n < V; n++)
if (adj.get(n).size() > 0)
break;
// Do DFS traversal starting from
// first non zero degree vertex.
DFSUtil(n, visited);
// If DFS traversal doesn't visit all
// vertices, then return false.
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj.get(i).size() > 0 && !visited[i])
return false;
// Create a reversed graph
GFG gr = getTranspose();
// Mark all the vertices as not
// visited (For second DFS)
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Do DFS for reversed graph starting
// from first vertex. Starting Vertex
// must be same starting point of first DFS
gr.DFSUtil(n, visited);
// If all vertices are not visited in
// second DFS, then return false
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj.get(i).size() > 0 && !visited[i])
return false;
return true;
}
// Function to do DFS starting from v.
// Used in isConnected();
// A recursive function to do DFS
// starting from v
void DFSUtil(int v, boolean[] visited)
{
// Mark the current node as
// visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
for(Integer i : adj.get(v))
if (!visited[i])
{
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
}
// Function that returns reverse
// (or transpose) of this graph
// This function is needed in isSC()
GFG getTranspose()
{
GFG g = new GFG(V);
for(int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
for(Integer i : adj.get(v))
{
g.adj.get(i).add(v);
g.in[v]++;
}
}
return g;
}
// This function takes an of strings
// and returns true if the given array
// of strings can be chained to form cycle
static boolean canBeChained(String[] arr, int n)
{
// Create a graph with 'alpha' edges
GFG g = new GFG(CHARS);
// Create an edge from first character
// to last character of every string
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
String s = arr[i];
g.addEdge(s.charAt(0) - 'a',
s.charAt(s.length() - 1) - 'a');
}
// The given array of strings can be
// chained if there is an eulerian
// cycle in the created graph
return g.isEulerianCycle();
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
String[] arr1 = { "for", "geek",
"rig", "kaf" };
int n1 = arr1.length;
System.out.println((canBeChained(arr1, n1) ?
"Can be chained " :
"Can't be chained "));
String[] arr2 = { "aab", "abb" };
int n2 = arr2.length;
System.out.println((canBeChained(arr2, n2) ?
"Can be chained " :
"Can't be chained "));
}
}
// This code is contributed by abhay379201 Python3
# Python program to check if a given directed graph is Eulerian or not
CHARS = 26
# A class that represents an undirected graph
class Graph(object):
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V # No. of vertices
self.adj = [[] for x in range(V)] # a dynamic array
self.inp = [0] * V
# function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self, v, w):
self.adj[v].append(w)
self.inp[w]+=1
# Method to check if this graph is Eulerian or not
def isSC(self):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited (For first DFS)
visited = [False] * self.V
# Find the first vertex with non-zero degree
n = 0
for n in range(self.V):
if len(self.adj[n]) > 0:
break
# Do DFS traversal starting from first non zero degree vertex.
self.DFSUtil(n, visited)
# If DFS traversal doesn't visit all vertices, then return false.
for i in range(self.V):
if len(self.adj[i]) > 0 and visited[i] == False:
return False
# Create a reversed graph
gr = self.getTranspose()
# Mark all the vertices as not visited (For second DFS)
for i in range(self.V):
visited[i] = False
# Do DFS for reversed graph starting from first vertex.
# Starting Vertex must be same starting point of first DFS
gr.DFSUtil(n, visited)
# If all vertices are not visited in second DFS, then
# return false
for i in range(self.V):
if len(self.adj[i]) > 0 and visited[i] == False:
return False
return True
# This function returns true if the directed graph has an eulerian
# cycle, otherwise returns false
def isEulerianCycle(self):
# Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if self.isSC() == False:
return False
# Check if in degree and out degree of every vertex is same
for i in range(self.V):
if len(self.adj[i]) != self.inp[i]:
return False
return True
# A recursive function to do DFS starting from v
def DFSUtil(self, v, visited):
# Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = True
# Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
for i in range(len(self.adj[v])):
if not visited[self.adj[v][i]]:
self.DFSUtil(self.adj[v][i], visited)
# Function that returns reverse (or transpose) of this graph
# This function is needed in isSC()
def getTranspose(self):
g = Graph(self.V)
for v in range(self.V):
# Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
for i in range(len(self.adj[v])):
g.adj[self.adj[v][i]].append(v)
g.inp[v]+=1
return g
# This function takes an of strings and returns true
# if the given array of strings can be chained to
# form cycle
def canBeChained(arr, n):
# Create a graph with 'alpha' edges
g = Graph(CHARS)
# Create an edge from first character to last character
# of every string
for i in range(n):
s = arr[i]
g.addEdge(ord(s[0])-ord('a'), ord(s[len(s)-1])-ord('a'))
# The given array of strings can be chained if there
# is an eulerian cycle in the created graph
return g.isEulerianCycle()
# Driver program
arr1 = ["for", "geek", "rig", "kaf"]
n1 = len(arr1)
if canBeChained(arr1, n1):
print ("Can be chained")
else:
print ("Cant be chained")
arr2 = ["aab", "abb"]
n2 = len(arr2)
if canBeChained(arr2, n2):
print ("Can be chained")
else:
print ("Can't be chained")
# This code is contributed by BHAVYA JAIN输出:
Can be chained
Can't be chained