使用Python 的GUI 计费系统和菜单卡
所以想象一下,我们正在开一家新餐厅或被任命为一家餐厅公司的员工,我们发现没有快速的方法来为客户开帐单,而且我们通常需要时间来计算金额客户必须支付的费用。这对我们和客户来说真的很烦人,而且很费时间。那么现在该怎么办?这是Python来救援的时候,因为我们知道它,它只需几秒钟的工作。
因此,在本文中,我们将借助 Python 的模块 Tkinter 构建一个 GUI 计费系统和一个菜单卡。
第 1 步:导入 tkinter 包
from tkinter import *第 2 步:下载所需文件
这里只有一个我们必须在这个项目中安装的文件,它将用作我们 GUI 计费系统的背景图像,或者我们可以选择任何其他图像。下载后确保我们正在创建的Python程序和这些资产在同一个文件夹中。
使用的图像:

第 3 步:制作 tkinter 窗口并设置背景
现在我们制作 tkinter 窗口并设置 GUI 的背景
Python3
# import tkinter module
from tkinter import *
# make a window
window = Tk()
# specify it's size
window.geometry("700x600")
# take a image for background
bg = PhotoImage(file='bg.png')
# label it in the background
label17 = Label(window, image=bg)
# position the image as well
label17.place(x=0, y=0)
# closing the main loop
window.mainloop()Python3
# main title
label8 = Label(window, text="Saransh Restaurant",
font="times 28 bold")
label8.place(x=350, y=20, anchor="center")
# Menu Card
label1 = Label(window, text="Menu",
font="times 28 bold")
label1.place(x=520, y=70)
label2 = Label(window, text="Aloo Paratha Rs 30",
font="times 18")
label2.place(x=450, y=120)
label3 = Label(window, text="Samosa Rs 5",
font="times 18")
label3.place(x=450, y=150)
label4 = Label(window, text="Pizza Rs 150",
font="times 18")
label4.place(x=450, y=180)
label5 = Label(window, text="Chilli Potato Rs 50",
font="times 18")
label5.place(x=450, y=210)
label6 = Label(window, text="Chowmein Rs 70",
font="times 18")
label6.place(x=450, y=240)
label7 = Label(window, text="Gulab Jamun Rs 35",
font="times 18")
label7.place(x=450, y=270)
# closing the main loop
window.mainloop()Python3
#------billing section---------
label9=Label(window,text="Select the items",
font="times 18")
label9.place(x=115,y=70)
label10=Label(window,text="Aloo Paratha",
font="times 18")
label10.place(x=20,y=120)
e1=Entry(window)
e1.place(x=20,y=150)
label11=Label(window,text="Samosa",
font="times 18")
label11.place(x=20,y=200)
e2=Entry(window)
e2.place(x=20,y=230)
label12=Label(window,text="Pizza",
font="times 18")
label12.place(x=20,y=280)
e3=Entry(window)
e3.place(x=20,y=310)
label13=Label(window,text="Chilli Potato",
font="times 18")
label13.place(x=20,y=360)
e4=Entry(window)
e4.place(x=20,y=390)
label14=Label(window,text="Chowmein",
font="times 18")
label14.place(x=250,y=120)
e5=Entry(window)
e5.place(x=250,y=150)
label15=Label(window,text="Gulab Jamun",
font="times 18")
label15.place(x=250,y=200)
e6=Entry(window)
e6.place(x=250,y=230)
# closing the main loop
window.mainloop()Python3
# function to calculate the
# price of all the orders
def calculate():
# dic for storing the food quantity and price
dic = {'aloo_partha': [e1, 30],
'samosa': [e2, 5],
'pizza': [e3, 150],
'chilli_potato': [e4, 50],
'chowmein': [e5, 70],
'gulab_jamun': [e6, 35]}
total = 0
for key, val in dic.items():
if val[0].get() != "":
total += int(val[0].get())*val[1]
label16 = Label(window,
text="Your Total Bill is - "+str(total),
font="times 18")
# position
label16.place(x=20, y=490)
# it will update the label with a new one
label16.after(1000, label16.destroy)
# refreshing the window
window.after(1000, calculate)
# execute calculate function after 1 second
window.after(1000, calculate)
window.mainloop()Python3
# import tkinter module
from tkinter import *
# make a window
window = Tk()
# specify it's size
window.geometry("700x600")
# take a image for background
bg = PhotoImage(file='bg.png')
# label it in the background
label17 = Label(window, image=bg)
# position the image as well
label17.place(x=0, y=0)
# function to calculate the
# price of all the orders
def calculate():
# dic for storing the
# food quantity and price
dic = {'aloo_partha': [e1, 30],
'samosa': [e2, 5],
'pizza': [e3, 150],
'chilli_potato': [e4, 50],
'chowmein': [e5, 70],
'gulab_jamun': [e6, 35]}
total = 0
for key, val in dic.items():
if val[0].get() != "":
total += int(val[0].get())*val[1]
label16 = Label(window,
text="Your Total Bill is - "+str(total),
font="times 18")
# position it
label16.place(x=20, y=490)
label16.after(1000, label16.destroy)
window.after(1000, calculate)
label8 = Label(window,
text="Saransh Restaurant",
font="times 28 bold")
label8.place(x=350, y=20, anchor="center")
label1 = Label(window,
text="Menu",
font="times 28 bold")
label1.place(x=520, y=70)
label2 = Label(window, text="Aloo Paratha \
Rs 30", font="times 18")
label2.place(x=450, y=120)
label3 = Label(window, text="Samosa \
Rs 5", font="times 18")
label3.place(x=450, y=150)
label4 = Label(window, text="Pizza \
Rs 150", font="times 18")
label4.place(x=450, y=180)
label5 = Label(window, text="Chilli Potato \
Rs 50", font="times 18")
label5.place(x=450, y=210)
label6 = Label(window, text="Chowmein \
Rs 70", font="times 18")
label6.place(x=450, y=240)
label7 = Label(window, text="Gulab Jamun \
Rs 35", font="times 18")
label7.place(x=450, y=270)
# billing section
label9 = Label(window, text="Select the items",
font="times 18")
label9.place(x=115, y=70)
label10 = Label(window,
text="Aloo Paratha",
font="times 18")
label10.place(x=20, y=120)
e1 = Entry(window)
e1.place(x=20, y=150)
label11 = Label(window, text="Samosa",
font="times 18")
label11.place(x=20, y=200)
e2 = Entry(window)
e2.place(x=20, y=230)
label12 = Label(window, text="Pizza",
font="times 18")
label12.place(x=20, y=280)
e3 = Entry(window)
e3.place(x=20, y=310)
label13 = Label(window,
text="Chilli Potato",
font="times 18")
label13.place(x=20, y=360)
e4 = Entry(window)
e4.place(x=20, y=390)
label14 = Label(window,
text="Chowmein",
font="times 18")
label14.place(x=250, y=120)
e5 = Entry(window)
e5.place(x=250, y=150)
label15 = Label(window,
text="Gulab Jamun",
font="times 18")
label15.place(x=250, y=200)
e6 = Entry(window)
e6.place(x=250, y=230)
# execute calculate function after 1 second
window.after(1000, calculate)
# closing the main loop
window.mainloop()输出:

第 4 步:添加标题和菜单卡
现在我们将借助“Label()”函数为 GUI 计费系统添加标题和菜单卡。 Tkinter Label 是一个小部件,用于实现我们可以放置文本或图像的显示框。开发人员可以随时更改此小部件显示的文本。它还用于执行任务,例如为文本部分下划线和跨多行跨文本。需要注意的是,一个标签一次只能使用一种字体来显示文本。要使用标签,我们只需要指定要在其中显示的内容(可以是文本、位图或图像)。
Syntax: w = Label ( master, option, … )
Parameters:
- master: This represents the parent window
- options: These options can be used as key-value pairs separated by commas
蟒蛇3
# main title
label8 = Label(window, text="Saransh Restaurant",
font="times 28 bold")
label8.place(x=350, y=20, anchor="center")
# Menu Card
label1 = Label(window, text="Menu",
font="times 28 bold")
label1.place(x=520, y=70)
label2 = Label(window, text="Aloo Paratha Rs 30",
font="times 18")
label2.place(x=450, y=120)
label3 = Label(window, text="Samosa Rs 5",
font="times 18")
label3.place(x=450, y=150)
label4 = Label(window, text="Pizza Rs 150",
font="times 18")
label4.place(x=450, y=180)
label5 = Label(window, text="Chilli Potato Rs 50",
font="times 18")
label5.place(x=450, y=210)
label6 = Label(window, text="Chowmein Rs 70",
font="times 18")
label6.place(x=450, y=240)
label7 = Label(window, text="Gulab Jamun Rs 35",
font="times 18")
label7.place(x=450, y=270)
# closing the main loop
window.mainloop()
输出:
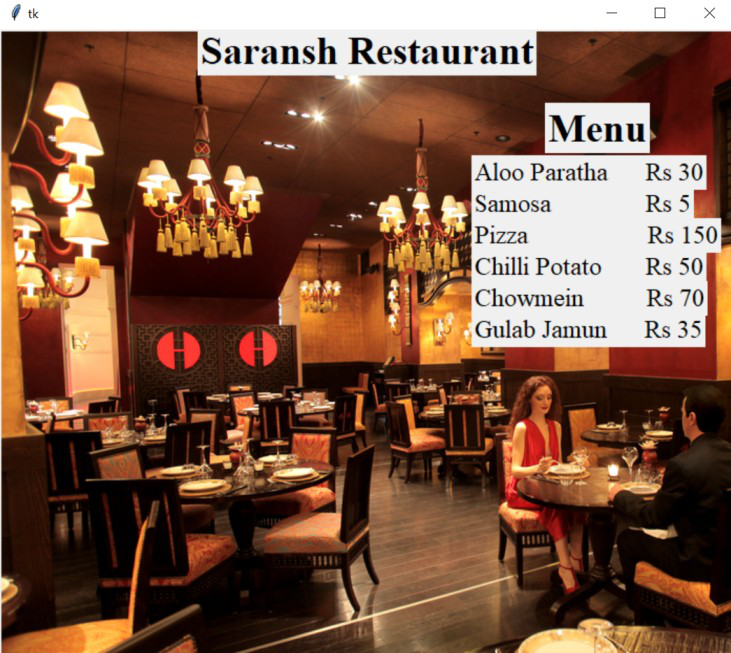
第 5 步:添加计费部分
现在我们将使用相同的标签小部件和条目小部件来添加计费部分。 Entry Widget 是一个 Tkinter Widget,用于输入或显示单行文本。此外, Label.place(x,y) 表示标签在 tkinter 窗口中的位置。
Syntax: entry = tk.Entry(parent, options)
Parameters:
- parent: This represents the parent window
- options: These options can be used as key-value pairs separated by commas
蟒蛇3
#------billing section---------
label9=Label(window,text="Select the items",
font="times 18")
label9.place(x=115,y=70)
label10=Label(window,text="Aloo Paratha",
font="times 18")
label10.place(x=20,y=120)
e1=Entry(window)
e1.place(x=20,y=150)
label11=Label(window,text="Samosa",
font="times 18")
label11.place(x=20,y=200)
e2=Entry(window)
e2.place(x=20,y=230)
label12=Label(window,text="Pizza",
font="times 18")
label12.place(x=20,y=280)
e3=Entry(window)
e3.place(x=20,y=310)
label13=Label(window,text="Chilli Potato",
font="times 18")
label13.place(x=20,y=360)
e4=Entry(window)
e4.place(x=20,y=390)
label14=Label(window,text="Chowmein",
font="times 18")
label14.place(x=250,y=120)
e5=Entry(window)
e5.place(x=250,y=150)
label15=Label(window,text="Gulab Jamun",
font="times 18")
label15.place(x=250,y=200)
e6=Entry(window)
e6.place(x=250,y=230)
# closing the main loop
window.mainloop()
输出:

第六步:计算账单并刷新窗口
之后,我们必须添加计算函数,该函数将每秒执行一次。在计算函数,我们必须做简单的数学运算,如果 e.get() 返回一个空字符串,则表示没有为该特定食物选择数量,否则如果 e.get() 中存在任何值,则因为它是字符串类型,我们将其转换为 int 类型并将此食物数量乘以该食物的价格。食物变量及其数量和价格保存在字典中。我们在字典中查找每个键,并相应地增加我们的 'total' 变量。之后,我们制作另一个标签,我们使用 total 变量的值来显示订购的食物总量。然后我们发出一个命令,每 1000 毫秒后我们刷新窗口以再次计算订购的食物总量,这将更新我们的 GUI。此外,通过销毁前一个标签并每秒更新一个新标签来更新总金额标签。
蟒蛇3
# function to calculate the
# price of all the orders
def calculate():
# dic for storing the food quantity and price
dic = {'aloo_partha': [e1, 30],
'samosa': [e2, 5],
'pizza': [e3, 150],
'chilli_potato': [e4, 50],
'chowmein': [e5, 70],
'gulab_jamun': [e6, 35]}
total = 0
for key, val in dic.items():
if val[0].get() != "":
total += int(val[0].get())*val[1]
label16 = Label(window,
text="Your Total Bill is - "+str(total),
font="times 18")
# position
label16.place(x=20, y=490)
# it will update the label with a new one
label16.after(1000, label16.destroy)
# refreshing the window
window.after(1000, calculate)
# execute calculate function after 1 second
window.after(1000, calculate)
window.mainloop()
输出:

下面是完整的实现:
蟒蛇3
# import tkinter module
from tkinter import *
# make a window
window = Tk()
# specify it's size
window.geometry("700x600")
# take a image for background
bg = PhotoImage(file='bg.png')
# label it in the background
label17 = Label(window, image=bg)
# position the image as well
label17.place(x=0, y=0)
# function to calculate the
# price of all the orders
def calculate():
# dic for storing the
# food quantity and price
dic = {'aloo_partha': [e1, 30],
'samosa': [e2, 5],
'pizza': [e3, 150],
'chilli_potato': [e4, 50],
'chowmein': [e5, 70],
'gulab_jamun': [e6, 35]}
total = 0
for key, val in dic.items():
if val[0].get() != "":
total += int(val[0].get())*val[1]
label16 = Label(window,
text="Your Total Bill is - "+str(total),
font="times 18")
# position it
label16.place(x=20, y=490)
label16.after(1000, label16.destroy)
window.after(1000, calculate)
label8 = Label(window,
text="Saransh Restaurant",
font="times 28 bold")
label8.place(x=350, y=20, anchor="center")
label1 = Label(window,
text="Menu",
font="times 28 bold")
label1.place(x=520, y=70)
label2 = Label(window, text="Aloo Paratha \
Rs 30", font="times 18")
label2.place(x=450, y=120)
label3 = Label(window, text="Samosa \
Rs 5", font="times 18")
label3.place(x=450, y=150)
label4 = Label(window, text="Pizza \
Rs 150", font="times 18")
label4.place(x=450, y=180)
label5 = Label(window, text="Chilli Potato \
Rs 50", font="times 18")
label5.place(x=450, y=210)
label6 = Label(window, text="Chowmein \
Rs 70", font="times 18")
label6.place(x=450, y=240)
label7 = Label(window, text="Gulab Jamun \
Rs 35", font="times 18")
label7.place(x=450, y=270)
# billing section
label9 = Label(window, text="Select the items",
font="times 18")
label9.place(x=115, y=70)
label10 = Label(window,
text="Aloo Paratha",
font="times 18")
label10.place(x=20, y=120)
e1 = Entry(window)
e1.place(x=20, y=150)
label11 = Label(window, text="Samosa",
font="times 18")
label11.place(x=20, y=200)
e2 = Entry(window)
e2.place(x=20, y=230)
label12 = Label(window, text="Pizza",
font="times 18")
label12.place(x=20, y=280)
e3 = Entry(window)
e3.place(x=20, y=310)
label13 = Label(window,
text="Chilli Potato",
font="times 18")
label13.place(x=20, y=360)
e4 = Entry(window)
e4.place(x=20, y=390)
label14 = Label(window,
text="Chowmein",
font="times 18")
label14.place(x=250, y=120)
e5 = Entry(window)
e5.place(x=250, y=150)
label15 = Label(window,
text="Gulab Jamun",
font="times 18")
label15.place(x=250, y=200)
e6 = Entry(window)
e6.place(x=250, y=230)
# execute calculate function after 1 second
window.after(1000, calculate)
# closing the main loop
window.mainloop()
输出: