带有示例的Java For 循环
当我们需要重复执行一个语句块时, Java中的循环就派上用场了。
Java for 循环提供了一种编写循环结构的简洁方式。 for 语句在一行中使用初始化、条件和递增/递减,从而提供更短、易于调试的循环结构。
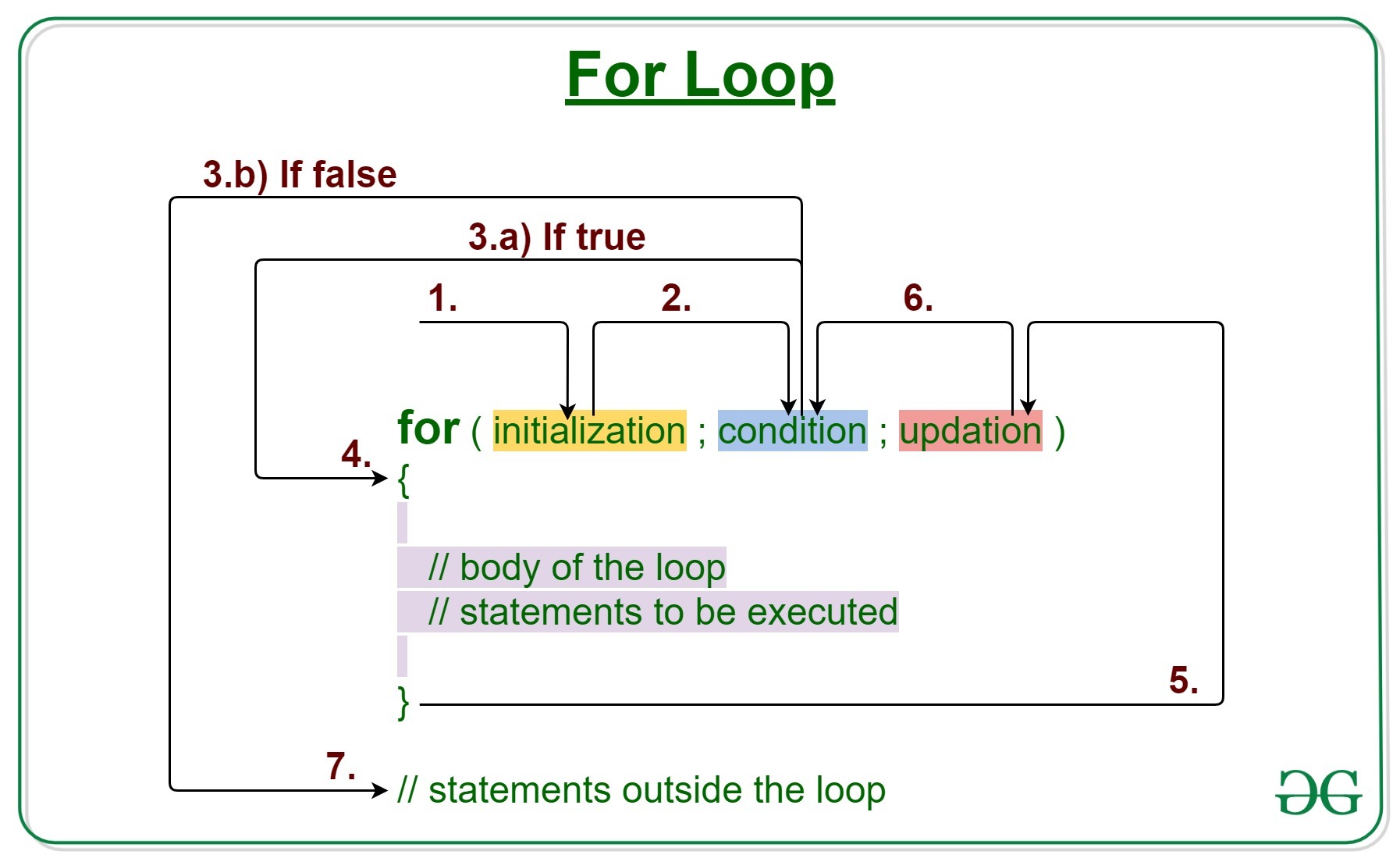
句法:
for (initialization expr; test expr; update exp)
{
// body of the loop
// statements we want to execute
} For 循环的各个部分是:
1.初始化表达式:在这个表达式中,我们必须将循环计数器初始化为某个值。
例子:
int i=1; 2.测试表达式:在这个表达式中,我们要测试条件。如果条件评估为真,我们将执行循环体并转到更新表达式。否则,我们将退出 for 循环。
例子:
i <= 10 3.更新表达式:执行循环体后,此表达式将循环变量增加/减少某个值。
例子:
i++; For 循环如何执行?
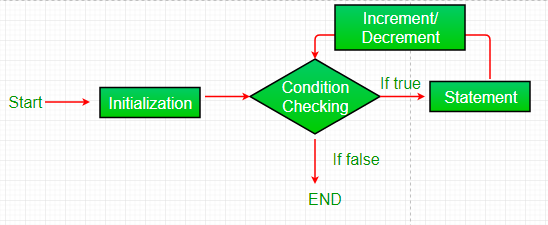
- 控制落入 for 循环。初始化完成
- 流程跳转到 Condition
- 条件经过测试。
- 如果 Condition 为真,则流量进入 Body
- 如果 Condition 产生 false,则流程将超出循环
- 循环体内的语句被执行。
- 流程进入更新
- 发生更新,流程再次进入第 3 步
- for 循环已结束,流程已流出。
循环流程图(For Control Flow):
示例 1:该程序将尝试打印 5 次“Hello World”。
Java
// Java program to illustrate for loop
class forLoopDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Writing a for loop
// to print Hello World 5 times
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}Java
// Java program to illustrate for loop.
class forLoopDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int sum = 0;
// for loop begins
// and runs till x <= 20
for (int x = 1; x <= 20; x++) {
sum = sum + x;
}
System.out.println("Sum: " + sum);
}
}Java
// Java program to illustrate enhanced for loop
public class enhancedforloop {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String array[] = { "Ron", "Harry", "Hermoine" };
// enhanced for loop
for (String x : array) {
System.out.println(x);
}
/* for loop for same function
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
{
System.out.println(array[i]);
}
*/
}
}Output:
Hello World
Hello World
Hello World
Hello World
Hello World时间复杂度: O(1)
辅助空间: O(1)
空运行示例 1:程序将以下列方式执行。
1. Program starts.
2. i is initialized with value 1.
3. Condition is checked. 1 <= 5 yields true.
3.a) "Hello World" gets printed 1st time.
3.b) Updation is done. Now i = 2.
4. Condition is checked. 2 <= 5 yields true.
4.a) "Hello World" gets printed 2nd time.
4.b) Updation is done. Now i = 3.
5. Condition is checked. 3 <= 5 yields true.
5.a) "Hello World" gets printed 3rd time
5.b) Updation is done. Now i = 4.
6. Condition is checked. 4 <= 5 yields true.
6.a) "Hello World" gets printed 4th time
6.b) Updation is done. Now i = 5.
7. Condition is checked. 5 <= 5 yields true.
7.a) "Hello World" gets printed 5th time
7.b) Updation is done. Now i = 6.
8. Condition is checked. 6 <= 5 yields false.
9. Flow goes outside the loop. Program terminates.示例 2:以下程序打印从 1 到 20 的 x 的总和。
Java
// Java program to illustrate for loop.
class forLoopDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int sum = 0;
// for loop begins
// and runs till x <= 20
for (int x = 1; x <= 20; x++) {
sum = sum + x;
}
System.out.println("Sum: " + sum);
}
}
Sum: 210增强的 For 循环或Java For-Each 循环
Java还包括在Java 5 中引入的另一个版本的 for 循环。增强的 for 循环提供了一种更简单的方法来遍历集合或数组的元素。它不灵活,只有在需要以顺序方式遍历元素而不知道当前处理的元素的索引时才应该使用它。
注意:当使用增强的for循环时,对象/变量是不可变的,即它确保数组中的值不能被修改,因此可以说是一个只读循环,你不能更新值,而不是可以修改值的其他循环。
句法:
for (T element:Collection obj/array)
{
// loop body
// statement(s)
}让我们举一个例子来演示如何使用增强的 for 循环来简化工作。假设有一个名称数组,我们想要打印该数组中的所有名称。让我们通过这个简单的实现来看看这两个示例之间的区别:
Java
// Java program to illustrate enhanced for loop
public class enhancedforloop {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String array[] = { "Ron", "Harry", "Hermoine" };
// enhanced for loop
for (String x : array) {
System.out.println(x);
}
/* for loop for same function
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
{
System.out.println(array[i]);
}
*/
}
}
Ron
Harry
Hermoine时间复杂度: O(1)
辅助空间: O(1)
建议:尽可能使用这种形式的陈述而不是一般形式。 (根据Java文档。)
https://youtu.be/JkSQ8KtOA14
- Java中的循环
- Java中的 For 循环 |要点
- 理解Java中的 for 循环
- Java while 循环与示例
- Java do-while 循环与示例
- Java中的for-each循环
- C、C++、 Java中for和while循环的区别
- C、C++、 Java中for和do-while循环的区别