Java中的覆盖
在任何面向对象的编程语言中,覆盖是一种功能,它允许子类或子类提供其超类或父类之一已经提供的方法的特定实现。当子类中的方法与其父类中的方法具有相同的名称、相同的参数或签名以及相同的返回类型(或子类型)时,则称子类中的方法覆盖了父类中的方法-班级。
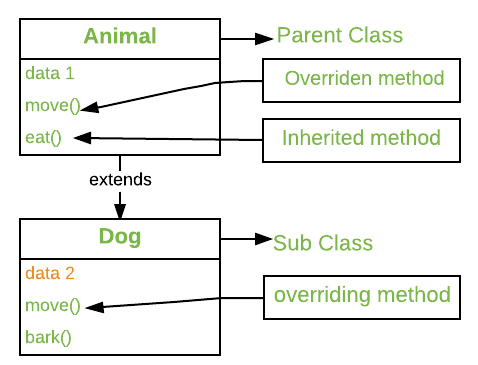
方法覆盖是Java实现运行时多态性的一种方式。执行的方法的版本将由用于调用它的对象确定。如果使用父类的对象调用方法,则执行父类中的版本,如果使用子类的对象调用方法,则执行子类中的版本。换句话说,是被引用对象的类型(而不是引用变量的类型)决定了将执行哪个版本的覆盖方法。
// A Simple Java program to demonstrate
// method overriding in java
// Base Class
class Parent {
void show()
{
System.out.println("Parent's show()");
}
}
// Inherited class
class Child extends Parent {
// This method overrides show() of Parent
@Override
void show()
{
System.out.println("Child's show()");
}
}
// Driver class
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// If a Parent type reference refers
// to a Parent object, then Parent's
// show is called
Parent obj1 = new Parent();
obj1.show();
// If a Parent type reference refers
// to a Child object Child's show()
// is called. This is called RUN TIME
// POLYMORPHISM.
Parent obj2 = new Child();
obj2.show();
}
}
Parent's show()
Child's show()
方法覆盖的规则:
- 覆盖和访问修饰符:覆盖方法的访问修饰符可以允许比被覆盖的方法更多但不能更少的访问。例如,超类中的受保护实例方法可以在子类中公开,但不能私有。这样做会产生编译时错误。
// A Simple Java program to demonstrate // Overriding and Access-Modifiers class Parent { // private methods are not overridden private void m1() { System.out.println("From parent m1()"); } protected void m2() { System.out.println("From parent m2()"); } } class Child extends Parent { // new m1() method // unique to Child class private void m1() { System.out.println("From child m1()"); } // overriding method // with more accessibility @Override public void m2() { System.out.println("From child m2()"); } } // Driver class class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent obj1 = new Parent(); obj1.m2(); Parent obj2 = new Child(); obj2.m2(); } }输出:From parent m2() From child m2() - 最终方法不能被覆盖:如果我们不希望一个方法被覆盖,我们将其声明为最终方法。请参阅将 final 与继承结合使用。
// A Java program to demonstrate that // final methods cannot be overridden class Parent { // Can't be overridden final void show() {} } class Child extends Parent { // This would produce error void show() {} }输出:
13: error: show() in Child cannot override show() in Parent void show() { } ^ overridden method is final - 静态方法不能被覆盖(Method Overriding vs Method Hiding):当你在基类中定义一个与静态方法具有相同签名的静态方法时,它被称为方法隐藏。
下表总结了当您定义与超类中的方法具有相同签名的方法时会发生什么。
Superclass Instance Method Superclass Static Method Subclass Instance Method Overrides Generates a compile-time error Subclass Static Method Generates a compile-time error Hides // Java program to show that // if the static method is redefined by // a derived class, then it is not // overriding, it is hiding class Parent { // Static method in base class // which will be hidden in subclass static void m1() { System.out.println("From parent " + "static m1()"); } // Non-static method which will // be overridden in derived class void m2() { System.out.println("From parent " + "non-static(instance) m2()"); } } class Child extends Parent { // This method hides m1() in Parent static void m1() { System.out.println("From child static m1()"); } // This method overrides m2() in Parent @Override public void m2() { System.out.println("From child " + "non-static(instance) m2()"); } } // Driver class class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent obj1 = new Child(); // As per overriding rules this // should call to class Child static // overridden method. Since static // method can not be overridden, it // calls Parent's m1() obj1.m1(); // Here overriding works // and Child's m2() is called obj1.m2(); } }输出:From parent static m1() From child non-static(instance) m2() - 私有方法不能被覆盖:私有方法不能被覆盖,因为它们在编译时是绑定的。因此,我们甚至不能覆盖子类中的私有方法。(有关详细信息,请参阅此内容)。
- 覆盖方法必须具有相同的返回类型(或子类型):从Java 5.0 开始,子类中的覆盖方法可以有不同的返回类型,但子类的返回类型应该是父类返回类型的子类型。这种现象称为协变返回类型。
- 从子类调用重写方法:我们可以使用 super 关键字在重写方法中调用父类方法。
// A Java program to demonstrate that overridden // method can be called from sub-class // Base Class class Parent { void show() { System.out.println("Parent's show()"); } } // Inherited class class Child extends Parent { // This method overrides show() of Parent @Override void show() { super.show(); System.out.println("Child's show()"); } } // Driver class class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent obj = new Child(); obj.show(); } }输出:Parent's show() Child's show() - 重写和构造函数:我们不能重写构造函数,因为父类和子类永远不能有同名的构造函数(构造函数名称必须始终与类名称相同)。
- 覆盖和异常处理:以下是在覆盖与异常处理相关的方法时要注意的两条规则。
- Rule#1:如果超类重写方法不抛出异常,子类重写方法只能抛出未检查异常,抛出已检查异常会导致编译时错误。
/* Java program to demonstrate overriding when superclass method does not declare an exception */ class Parent { void m1() { System.out.println("From parent m1()"); } void m2() { System.out.println("From parent m2()"); } } class Child extends Parent { @Override // no issue while throwing unchecked exception void m1() throws ArithmeticException { System.out.println("From child m1()"); } @Override // compile-time error // issue while throwing checked exception void m2() throws Exception { System.out.println("From child m2"); } }输出:
error: m2() in Child cannot override m2() in Parent void m2() throws Exception{ System.out.println("From child m2");} ^ overridden method does not throw Exception - Rule#2:如果超类重写方法确实抛出异常,子类重写方法只能抛出相同的子类异常。在异常层次结构中抛出父异常将导致编译时错误。如果子类覆盖的方法没有抛出任何异常,也没有问题。
// Java program to demonstrate overriding when // superclass method does declare an exception class Parent { void m1() throws RuntimeException { System.out.println("From parent m1()"); } } class Child1 extends Parent { @Override // no issue while throwing same exception void m1() throws RuntimeException { System.out.println("From child1 m1()"); } } class Child2 extends Parent { @Override // no issue while throwing subclass exception void m1() throws ArithmeticException { System.out.println("From child2 m1()"); } } class Child3 extends Parent { @Override // no issue while not throwing any exception void m1() { System.out.println("From child3 m1()"); } } class Child4 extends Parent { @Override // compile-time error // issue while throwing parent exception void m1() throws Exception { System.out.println("From child4 m1()"); } }输出:
error: m1() in Child4 cannot override m1() in Parent void m1() throws Exception ^ overridden method does not throw Exception
- Rule#1:如果超类重写方法不抛出异常,子类重写方法只能抛出未检查异常,抛出已检查异常会导致编译时错误。
- 覆盖和抽象方法:接口或抽象类中的抽象方法意味着在派生的具体类中被覆盖,否则将引发编译时错误。
- 覆盖和 synchronized/strictfp 方法: synchronized/strictfp 修饰符与方法的存在对覆盖规则没有影响,即同步/strictfp 方法有可能覆盖非同步/strictfp 方法,反之亦然。
笔记 :
- 在 C++ 中,我们需要 virtual 关键字来实现覆盖或运行时多态。在Java中,方法默认是虚拟的。
- 我们可以有多级方法覆盖。
// A Java program to demonstrate // multi-level overriding // Base Class class Parent { void show() { System.out.println("Parent's show()"); } } // Inherited class class Child extends Parent { // This method overrides show() of Parent void show() { System.out.println("Child's show()"); } } // Inherited class class GrandChild extends Child { // This method overrides show() of Parent void show() { System.out.println("GrandChild's show()"); } } // Driver class class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent obj1 = new GrandChild(); obj1.show(); } }输出:GrandChild's show() - 覆盖与重载:
- 重载是关于相同的方法有不同的签名。覆盖是关于相同的方法,相同的签名但通过继承连接的不同类。
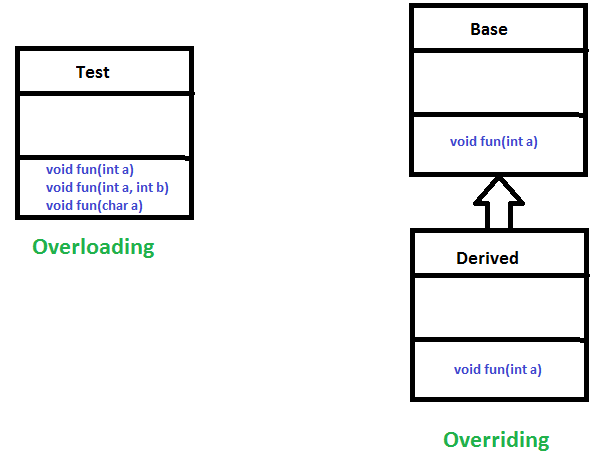
- 重载是编译器时多态性的一个例子,而覆盖是运行时多态性的一个例子。
- 重载是关于相同的方法有不同的签名。覆盖是关于相同的方法,相同的签名但通过继承连接的不同类。
为什么方法覆盖?
如前所述,重写方法允许Java支持运行时多态性。多态性对于面向对象编程至关重要,原因之一是:它允许通用类指定对其所有派生类都通用的方法,同时允许子类定义部分或所有这些方法的特定实现。重写方法是Java实现多态的“一个接口,多个方法”方面的另一种方式。
动态方法分派是面向对象设计对代码重用和健壮性带来的最强大的机制之一。现有代码库无需重新编译即可调用新类实例上的方法,同时保持干净的抽象接口的能力是一个非常强大的工具。
重写方法允许我们调用任何派生类的方法,甚至不知道派生类对象的类型。
何时应用方法覆盖?(示例)
覆盖和继承:成功应用多态性的部分关键是理解超类和子类形成一个层次结构,从较小的专业化到较大的专业化。正确使用,超类提供了子类可以直接使用的所有元素。它还定义了派生类必须自己实现的那些方法。这允许子类灵活地定义其方法,但仍然强制执行一致的接口。因此,通过将继承与重写方法相结合,超类可以定义将由其所有子类使用的方法的一般形式。
让我们看一个使用方法覆盖的更实际的例子。考虑一个组织的员工管理软件,让代码有一个简单的基类 Employee,该类有 raiseSalary()、transfer()、promote() 等方法。不同类型的员工,如 Manager、Engineer 等。 .etc 可能具有基类 Employee 中存在的方法的实现。在我们完整的软件中,我们只需要到处传递员工列表并调用适当的方法,甚至不知道员工的类型。例如,我们可以通过遍历员工列表轻松提高所有员工的工资。每种类型的员工都可能在其类中具有其逻辑,我们不必担心,因为如果针对特定员工类型存在 raiseSalary(),则只会调用该方法。
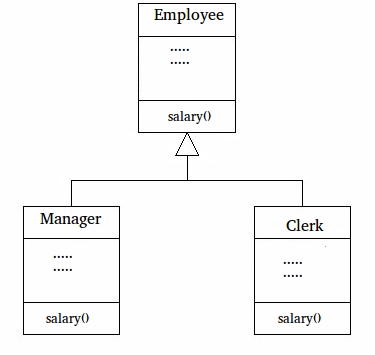
// A Simple Java program to demonstrate application
// of overriding in Java
// Base Class
class Employee {
public static int base = 10000;
int salary()
{
return base;
}
}
// Inherited class
class Manager extends Employee {
// This method overrides salary() of Parent
int salary()
{
return base + 20000;
}
}
// Inherited class
class Clerk extends Employee {
// This method overrides salary() of Parent
int salary()
{
return base + 10000;
}
}
// Driver class
class Main {
// This method can be used to print the salary of
// any type of employee using base class reference
static void printSalary(Employee e)
{
System.out.println(e.salary());
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Employee obj1 = new Manager();
// We could also get type of employee using
// one more overridden method.loke getType()
System.out.print("Manager's salary : ");
printSalary(obj1);
Employee obj2 = new Clerk();
System.out.print("Clerk's salary : ");
printSalary(obj2);
}
}
Manager's salary : 30000
Clerk's salary : 20000
相关文章:
- Java中的动态方法分派或运行时多态性
- 覆盖 Object 类的 equals() 方法
- 覆盖 Object 类的 toString() 方法
- Java中的重载
- Java程序的输出|第 18 组(覆盖)