📌 相关文章
- 函数覆盖(1)
- 函数覆盖
- 函数覆盖 (1)
- 如何覆盖 JavaScript函数?
- 如何覆盖 JavaScript函数?(1)
- 函数覆盖 - 任何代码示例
- Java-覆盖
- Java-覆盖(1)
- Java中的覆盖
- Java-覆盖
- Java-覆盖(1)
- C#方法覆盖
- F#方法覆盖
- C#方法覆盖(1)
- C++ 中的函数重载与函数覆盖(1)
- C++ 中的函数重载与函数覆盖
- 覆盖包css(1)
- Python中的方法覆盖(1)
- Python中的方法覆盖
- jquery 用户函数覆盖 - Javascript (1)
- 覆盖包css代码示例
- 红宝石 |范围覆盖?()函数
- 红宝石 |范围覆盖?()函数(1)
- PHP的函数重载和覆盖(1)
- PHP的函数重载和覆盖
- 检查二叉树的覆盖和未覆盖节点的总和
- 检查二叉树的覆盖和未覆盖节点的总和(1)
- jquery 用户函数覆盖 - Javascript 代码示例
- 如何覆盖自举程序的SASS函数?
📜 C++函数覆盖
📅 最后修改于: 2020-09-25 04:54:30 🧑 作者: Mango
在本教程中,我们将借助示例来学习C++中的函数重写。
众所周知,继承是OOP的一项功能,它使我们能够从基类创建派生类。派生类继承基类的功能。
假设在派生类和基类中都定义了相同的函数 。现在,如果我们使用派生类的对象调用此函数 ,则将执行派生类的函数 。
这在C++中称为函数重写 。在派生类的函数覆盖在基类的函数 。
示例1:C++函数重写
// C++ program to demonstrate function overriding
#include
using namespace std;
class Base {
public:
void print() {
cout << "Base Function" << endl;
}
};
class Derived : public Base {
public:
void print() {
cout << "Derived Function" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Derived derived1;
derived1.print();
return 0;
} 输出
Derived Function在这里,在Base类和Derived类中都定义了相同的函数 print() 。
因此,当我们从Derived对象derived1调用print() ,通过覆盖Base的函数来执行Derived的print() 。

C++中的访问覆盖函数
要访问基类的重写函数 ,我们使用范围解析运算符 :: 。
我们还可以通过使用基类的指针指向派生类的对象,然后从该指针调用该函数来访问重写的函数 。
示例2:对基类的C++访问重写函数
// C++ program to access overridden function
// in main() using the scope resolution operator ::
#include
using namespace std;
class Base {
public:
void print() {
cout << "Base Function" << endl;
}
};
class Derived : public Base {
public:
void print() {
cout << "Derived Function" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Derived derived1, derived2;
derived1.print();
// access print() function of the Base class
derived2.Base::print();
return 0;
} 输出
Derived Function
Base Function在这里,这句话
derived2.Base::print();访问基类的print() 函数 。
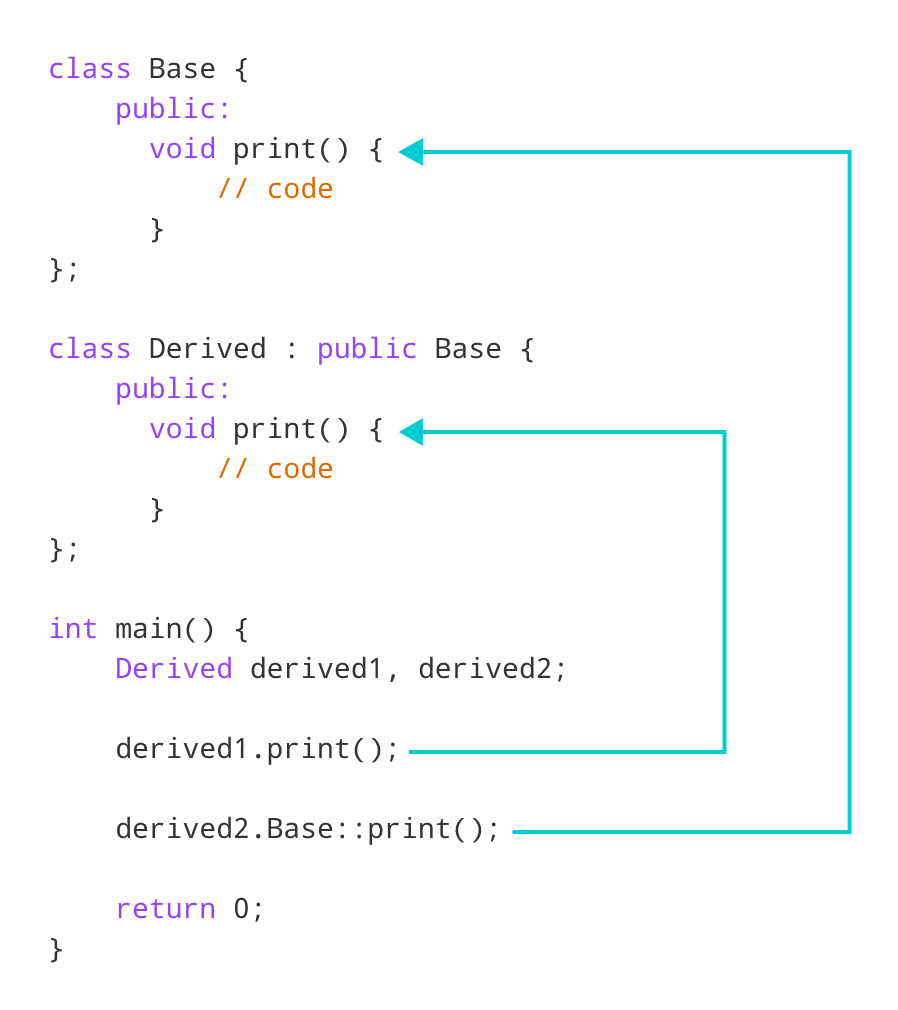
示例3:派生类的C++调用重写函数
// C++ program to call the overridden function
// from a member function of the derived class
#include
using namespace std;
class Base {
public:
void print() {
cout << "Base Function" << endl;
}
};
class Derived : public Base {
public:
void print() {
cout << "Derived Function" << endl;
// call overridden function
Base::print();
}
};
int main() {
Derived derived1;
derived1.print();
return 0;
} 输出
Derived Function
Base Function在此程序中,我们在Derived类本身内部调用了重写函数 。
class Derived : public Base {
public:
void print() {
cout << "Derived Function" << endl;
Base::print();
}
};注意代码Base::print(); ,它在Derived类中调用重写的函数 。
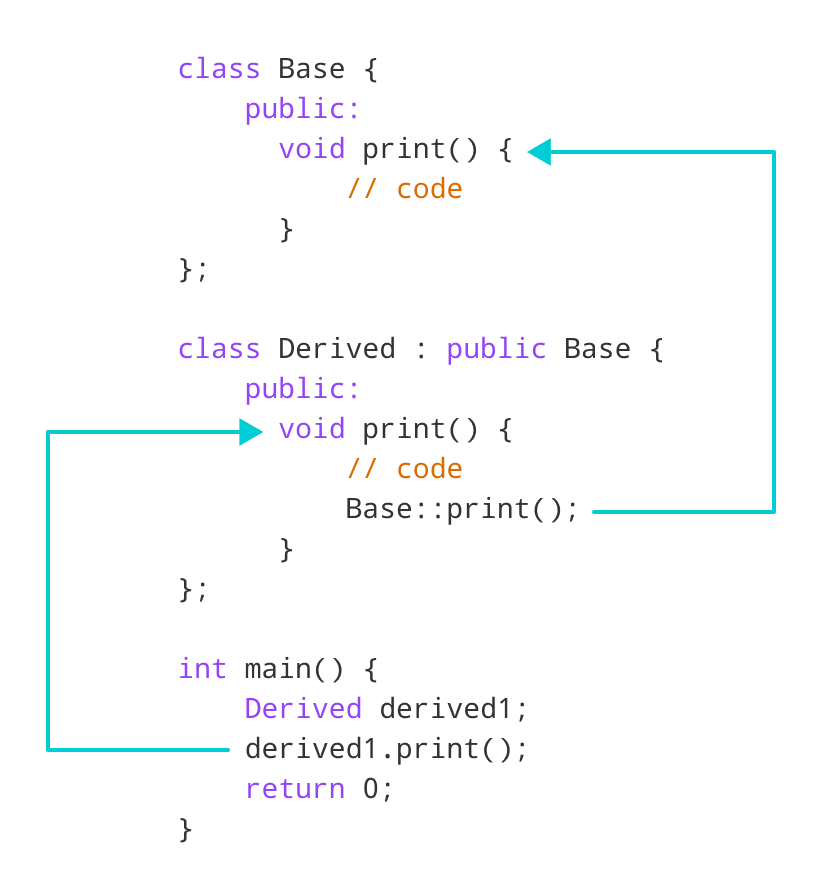
示例4:使用指针的C++调用重写函数
// C++ program to access overridden function using pointer
// of Base type that points to an object of Derived class
#include
using namespace std;
class Base {
public:
void print() {
cout << "Base Function" << endl;
}
};
class Derived : public Base {
public:
void print() {
cout << "Derived Function" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Derived derived1;
// pointer of Base type that points to derived1
Base* ptr = &derived1
// call function of Base class using ptr
ptr->print();
return 0;
} 输出
Base Function在此程序中,我们创建了一个名为ptr的Base类型的指针。该指针指向Derived对象Derived对象derived1 。
// pointer of Base type that points to derived1
Base* ptr = &derived1当我们使用ptr调用print() 函数 ,它将从Base调用重写的函数 。
// call function of Base class using ptr
ptr->print();这是因为即使ptr指向Derived对象,它实际上也是Base类型。因此,它调用Base的成员 函数 。
为了覆盖Base 函数而不是访问它,我们需要在Base类中使用虚函数。