JavaScript 中 stopPropagation 与 stopImmediatePropagation 的区别
每次调用注册的事件时,事件都会传播或冒泡直到窗口对象级别。例如,让我们考虑一个包含另一个子 div 元素(“Div child”)的父 div 元素(“Div Parent”),并且对于两者,都注册了一个点击事件。如果单击子 div,则该事件将在所有位置(即父对象和子对象)触发。
StopPropagation() 事件方法:防止在顶级 DOM 层次结构中传播任何处理程序以执行。它阻止点击事件冒泡到父元素。
示例:在此方法中,单击
元素,则会发生第二个和第一个事件处理程序,因为
元素在
HTML
GeeskforGeeks
Acomputer Science Portal for Geeks
Click on this span element.
event.stopPropagation() stops the click event
from bubbling to the parent elements.
HTML
GeeskforGeeks
Click on this div element.
event.stopImmediatePropagation() stop
the second and third event.
输出:
- 单击元素之前:

- 单击 元素后:
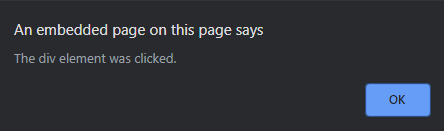
- 单击
元素后:
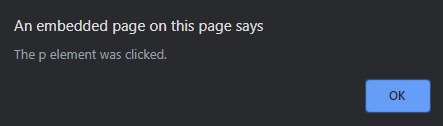
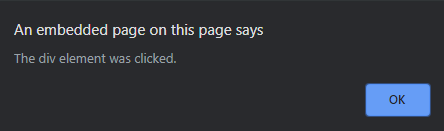
- 单击 元素后:
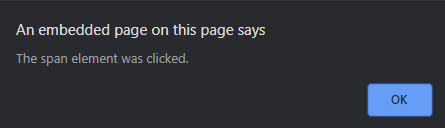
StopImmediatePropagation() 事件方法:防止任何其他处理程序和顶级 DOM 层次结构的传播。它停止在此事件之后分配的其他事件。
示例: StopImmediatePropagation() 事件停止下一个事件。HTML
GeeskforGeeks
Click on this div element.event.stopImmediatePropagation() stop the second and third event.
输出:
- 在单击 div 元素之前:
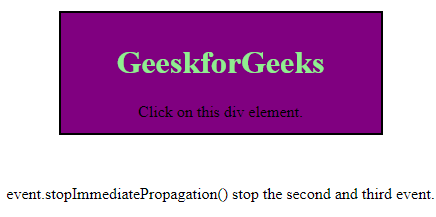
- 单击 div 元素后:
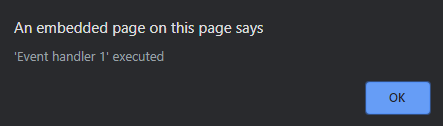
stopPropagation 与 stopImmediatePropagation
stopPropagation stopImmediatePropagation It will allow other handlers on the same element to be executed, prevent handlers on parent elements from running. It will prevents every event from running. It will allow more than one handler to be executed one by one. It will depend on you where you used this, that handler will be the last one to be executed. If you create a table containing ,
and . If you set three event handler for then other two event handler will also run with this one. But in this case if you do the same things the other two event handlers won’t run.
- 单击