编写一个程序来找到一棵树的最大深度或高度
给定一棵二叉树,求它的高度。空树的高度为-1,有一个节点的树的高度为0,下面的树的高度为2。
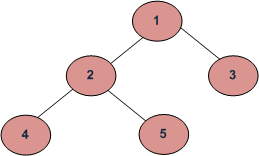
递归计算节点的左右子树的高度,并将高度分配给节点,作为两个孩子的高度的最大值加1。有关详细信息,请参见下面的伪代码和程序。
算法:
maxDepth()
1. If tree is empty then return -1
2. Else
(a) Get the max depth of left subtree recursively i.e.,
call maxDepth( tree->left-subtree)
(a) Get the max depth of right subtree recursively i.e.,
call maxDepth( tree->right-subtree)
(c) Get the max of max depths of left and right
subtrees and add 1 to it for the current node.
max_depth = max(max dept of left subtree,
max depth of right subtree)
+ 1
(d) Return max_depth有关上述示例树的递归函数maxDepth() 的执行,请参见下图。
maxDepth('1') = max(maxDepth('2'), maxDepth('3')) + 1
= 1 + 1
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
maxDepth('2') = 1 maxDepth('3') = 0
= max(maxDepth('4'), maxDepth('5')) + 1
= 1 + 0 = 1
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
maxDepth('4') = 0 maxDepth('5') = 0执行:
C++
// C++ program to find height of tree
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
/* Compute the "maxDepth" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int maxDepth(node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return -1;
else
{
/* compute the depth of each subtree */
int lDepth = maxDepth(node->left);
int rDepth = maxDepth(node->right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lDepth > rDepth)
return(lDepth + 1);
else return(rDepth + 1);
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return(Node);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
cout << "Height of tree is " << maxDepth(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Srivastav C
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Compute the "maxDepth" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int maxDepth(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return -1;
else {
/* compute the depth of each subtree */
int lDepth = maxDepth(node->left);
int rDepth = maxDepth(node->right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lDepth > rDepth)
return (lDepth + 1);
else
return (rDepth + 1);
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("Height of tree is %d", maxDepth(root));
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find height of tree
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* Compute the "maxDepth" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int maxDepth(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return -1;
else
{
/* compute the depth of each subtree */
int lDepth = maxDepth(node.left);
int rDepth = maxDepth(node.right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lDepth > rDepth)
return (lDepth + 1);
else
return (rDepth + 1);
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Height of tree is : " +
tree.maxDepth(tree.root));
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Amit SrivastavPython3
# Python3 program to find the maximum depth of tree
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Compute the "maxDepth" of a tree -- the number of nodes
# along the longest path from the root node down to the
# farthest leaf node
def maxDepth(node):
if node is None:
return -1 ;
else :
# Compute the depth of each subtree
lDepth = maxDepth(node.left)
rDepth = maxDepth(node.right)
# Use the larger one
if (lDepth > rDepth):
return lDepth+1
else:
return rDepth+1
# Driver program to test above function
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print ("Height of tree is %d" %(maxDepth(root)))
# This code is contributed by Amit SrivastavC#
// C# program to find height of tree
using System;
// A binary tree node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* Compute the "maxDepth" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int maxDepth(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return -1;
else
{
/* compute the depth of each subtree */
int lDepth = maxDepth(node.left);
int rDepth = maxDepth(node.right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lDepth > rDepth)
return (lDepth + 1);
else
return (rDepth + 1);
}
}
/* Driver code */
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Height of tree is : " +
tree.maxDepth(tree.root));
}
}
// This code has been contributed by
// Correction done by Amit SrivastavJavascript
C++
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// A Tree node
struct Node
{
int key;
struct Node* left, *right;
};
// Utility function to create a new node
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);
}
/*Function to find the height(depth) of the tree*/
int height(struct Node* root){
//Initialising a variable to count the
//height of tree
int depth = 0;
queueq;
//Pushing first level element along with NULL
q.push(root);
q.push(NULL);
while(!q.empty()){
Node* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
//When NULL encountered, increment the value
if(temp == NULL){
depth++;
}
//If NULL not encountered, keep moving
if(temp != NULL){
if(temp->left){
q.push(temp->left);
}
if(temp->right){
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
//If queue still have elements left,
//push NULL again to the queue.
else if(!q.empty()){
q.push(NULL);
}
}
return depth;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
// Let us create Binary Tree shown in above example
Node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(12);
root->right = newNode(13);
root->right->left = newNode(14);
root->right->right = newNode(15);
root->right->left->left = newNode(21);
root->right->left->right = newNode(22);
root->right->right->left = newNode(23);
root->right->right->right = newNode(24);
cout<<"Height(Depth) of tree is: "< 输出
Height of tree is 2时间复杂度: O(n)(请参阅我们的帖子树遍历了解详细信息)
方法2:解决这个问题的另一种方法是做Level Order Traversal。在进行级别顺序遍历时,在将每个级别的节点添加到队列中时,我们必须添加NULL 节点,以便每当遇到它时,我们可以增加变量的值并计算该级别。
执行:
C++
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// A Tree node
struct Node
{
int key;
struct Node* left, *right;
};
// Utility function to create a new node
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);
}
/*Function to find the height(depth) of the tree*/
int height(struct Node* root){
//Initialising a variable to count the
//height of tree
int depth = 0;
queueq;
//Pushing first level element along with NULL
q.push(root);
q.push(NULL);
while(!q.empty()){
Node* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
//When NULL encountered, increment the value
if(temp == NULL){
depth++;
}
//If NULL not encountered, keep moving
if(temp != NULL){
if(temp->left){
q.push(temp->left);
}
if(temp->right){
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
//If queue still have elements left,
//push NULL again to the queue.
else if(!q.empty()){
q.push(NULL);
}
}
return depth;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
// Let us create Binary Tree shown in above example
Node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(12);
root->right = newNode(13);
root->right->left = newNode(14);
root->right->right = newNode(15);
root->right->left->left = newNode(21);
root->right->left->right = newNode(22);
root->right->right->left = newNode(23);
root->right->right->right = newNode(24);
cout<<"Height(Depth) of tree is: "< 时间复杂度: O(n)
空间复杂度: O(n)
参考:
http://cslibrary.stanford.edu/110/BinaryTrees.html