编写程序删除一棵树
要删除一棵树,我们必须遍历这棵树的所有节点,并一一删除。那么,我们应该使用哪种遍历——中序横断、前序横断或后序横断?答案很简单。我们应该使用后序横向,因为在删除父节点之前,我们应该先删除它的子节点。
我们可以删除具有额外空间复杂度的其他遍历的树,但是如果我们有可用的后序遍历,那么我们为什么要进行其他遍历,它可以在不以相同时间复杂度存储任何内容的情况下完成工作。
对于下面的树,节点按 4、5、2、3、1 的顺序删除。
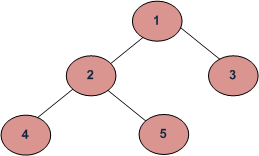
注意:在Java中会发生自动垃圾收集,所以我们可以简单地将root设为null来删除树“root = null”;
C++
// C++ program to Delete a Tree
#include
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data,
pointer to left child and
a pointer to right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
/* Constructor that allocates
a new node with the given data
and NULL left and right pointers. */
node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
this->left = NULL;
this->right = NULL;
}
};
/* This function traverses tree
in post order to delete each
and every node of the tree */
void deleteTree(node* node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
/* first delete both subtrees */
deleteTree(node->left);
deleteTree(node->right);
/* then delete the node */
cout << "\n Deleting node: " << node->data;
delete node;
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
node *root = new node(1);
root->left = new node(2);
root->right = new node(3);
root->left->left = new node(4);
root->left->right = new node(5);
deleteTree(root);
root = NULL;
cout << "\n Tree deleted ";
return 0;
}
//This code is contributed by rathbhupendra C
// C program to Delete a Tree
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
/* This function traverses tree in post order to
to delete each and every node of the tree */
void deleteTree(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
/* first delete both subtrees */
deleteTree(node->left);
deleteTree(node->right);
/* then delete the node */
printf("\n Deleting node: %d", node->data);
free(node);
}
/* Driver program to test deleteTree function*/
int main()
{
struct node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
deleteTree(root);
root = NULL;
printf("\n Tree deleted ");
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to delete a tree
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/* This function traverses tree in post order to
to delete each and every node of the tree */
void deleteTree(Node node)
{
// In Java automatic garbage collection
// happens, so we can simply make root
// null to delete the tree
root = null;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Print all root-to-leaf paths of the input tree */
tree.deleteTree(tree.root);
tree.root = null;
System.out.println("Tree deleted");
}
}Python3
""" program to Delete a Tree """
# Helper function that allocates a new
# node with the given data and None
# left and right pointers.
class newNode:
# Construct to create a new node
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
""" This function traverses tree in post order to
to delete each and every node of the tree """
def deleteTree( node) :
if node != None:
deleteTree(node.left)
deleteTree(node.right)
del node
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right = newNode(5)
deleteTree(root)
root = None
print("Tree deleted ")
# This code is contributed by
# Shubham Prashar(shubhamprashar)C#
using System;
// C# program to delete a tree
// A binary tree node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
public Node root;
/* This function traverses tree in post order to
to delete each and every node of the tree */
public virtual void deleteTree(Node node)
{
// In Java automatic garbage collection
// happens, so we can simply make root
// null to delete the tree
root = null;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Print all root-to-leaf paths of the input tree */
tree.deleteTree(tree.root);
tree.root = null;
Console.WriteLine("Tree deleted");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13Javascript
C++
// CPP program to Delete a Tree
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return(Node);
}
/* This function is same as deleteTree()
in the previous program */
void _deleteTree(node* node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
/* first delete both subtrees */
_deleteTree(node->left);
_deleteTree(node->right);
/* then delete the node */
cout << "Deleting node: " << node->data << endl;
delete node;
}
/* Deletes a tree and sets the root as NULL */
void deleteTree(node** node_ref)
{
_deleteTree(*node_ref);
*node_ref = NULL;
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
// Note that we pass the address of root here
deleteTree(&root);
cout << "Tree deleted ";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra C
// C program to Delete a Tree
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
/* This function is same as deleteTree() in the previous program */
void _deleteTree(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
/* first delete both subtrees */
_deleteTree(node->left);
_deleteTree(node->right);
/* then delete the node */
printf("\n Deleting node: %d", node->data);
free(node);
}
/* Deletes a tree and sets the root as NULL */
void deleteTree(struct node** node_ref)
{
_deleteTree(*node_ref);
*node_ref = NULL;
}
/* Driver program to test deleteTree function*/
int main()
{
struct node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
// Note that we pass the address of root here
deleteTree(&root);
printf("\n Tree deleted ");
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to delete a tree
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and pointer to right child */
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
static Node root;
/* This function is same as deleteTree() in the previous program */
void deleteTree(Node node)
{
// In Java automatic garbage collection
// happens, so we can simply make root
// null to delete the tree
root = null;
}
/* Wrapper function that deletes the tree and
sets root node as null */
void deleteTreeRef(Node nodeRef)
{
deleteTree(nodeRef);
nodeRef=null;
}
/* Driver program to test deleteTree function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Note that we pass root node here */
tree.deleteTreeRef(root);
System.out.println("Tree deleted");
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal(mayank_24)Python3
# Python3 program to count all nodes
# having k leaves in subtree rooted with them
# A binary tree node has data, pointer to
# left child and a pointer to right child
# Helper function that allocates a new node
# with the given data and None left and
# right pointers
class newNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
''' This function is same as deleteTree()
in the previous program '''
def _deleteTree(node):
if (node == None):
return
# first delete both subtrees
_deleteTree(node.left)
_deleteTree(node.right)
# then delete the node
print("Deleting node: ",
node.data)
node = None
# Deletes a tree and sets the root as NULL
def deleteTree(node_ref):
_deleteTree(node_ref[0])
node_ref[0] = None
# Driver code
root = [0]
root[0] = newNode(1)
root[0].left = newNode(2)
root[0].right = newNode(3)
root[0].left.left = newNode(4)
root[0].left.right = newNode(5)
# Note that we pass the address
# of root here
deleteTree(root)
print("Tree deleted ")
# This code is contributed by SHUBHAMSINGH10C#
using System;
// C# program to delete a tree
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and pointer to right child */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
public static Node root;
/* This function is same as deleteTree() in the previous program */
public virtual void deleteTree(Node node)
{
// In Java automatic garbage collection
// happens, so we can simply make root
// null to delete the tree
root = null;
}
/* Wrapper function that deletes the tree and
sets root node as null */
public virtual void deleteTreeRef(Node nodeRef)
{
deleteTree(nodeRef);
nodeRef = null;
}
/* Driver program to test deleteTree function */
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
BinaryTree.root = new Node(1);
BinaryTree.root.left = new Node(2);
BinaryTree.root.right = new Node(3);
BinaryTree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
BinaryTree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Note that we pass root node here */
tree.deleteTreeRef(root);
Console.WriteLine("Tree deleted");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13Javascript
上面的 deleteTree()函数会删除树,但不会将根更改为 NULL,如果 deleteTree() 的用户没有将根更改为 NULL 并尝试使用根指针访问值,这可能会导致问题。我们可以修改 deleteTree()函数以引用根节点,这样就不会出现这个问题。请参阅以下代码。
C++
// CPP program to Delete a Tree
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return(Node);
}
/* This function is same as deleteTree()
in the previous program */
void _deleteTree(node* node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
/* first delete both subtrees */
_deleteTree(node->left);
_deleteTree(node->right);
/* then delete the node */
cout << "Deleting node: " << node->data << endl;
delete node;
}
/* Deletes a tree and sets the root as NULL */
void deleteTree(node** node_ref)
{
_deleteTree(*node_ref);
*node_ref = NULL;
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
// Note that we pass the address of root here
deleteTree(&root);
cout << "Tree deleted ";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
// C program to Delete a Tree
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
/* This function is same as deleteTree() in the previous program */
void _deleteTree(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL) return;
/* first delete both subtrees */
_deleteTree(node->left);
_deleteTree(node->right);
/* then delete the node */
printf("\n Deleting node: %d", node->data);
free(node);
}
/* Deletes a tree and sets the root as NULL */
void deleteTree(struct node** node_ref)
{
_deleteTree(*node_ref);
*node_ref = NULL;
}
/* Driver program to test deleteTree function*/
int main()
{
struct node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
// Note that we pass the address of root here
deleteTree(&root);
printf("\n Tree deleted ");
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to delete a tree
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and pointer to right child */
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
static Node root;
/* This function is same as deleteTree() in the previous program */
void deleteTree(Node node)
{
// In Java automatic garbage collection
// happens, so we can simply make root
// null to delete the tree
root = null;
}
/* Wrapper function that deletes the tree and
sets root node as null */
void deleteTreeRef(Node nodeRef)
{
deleteTree(nodeRef);
nodeRef=null;
}
/* Driver program to test deleteTree function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Note that we pass root node here */
tree.deleteTreeRef(root);
System.out.println("Tree deleted");
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal(mayank_24)
Python3
# Python3 program to count all nodes
# having k leaves in subtree rooted with them
# A binary tree node has data, pointer to
# left child and a pointer to right child
# Helper function that allocates a new node
# with the given data and None left and
# right pointers
class newNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
''' This function is same as deleteTree()
in the previous program '''
def _deleteTree(node):
if (node == None):
return
# first delete both subtrees
_deleteTree(node.left)
_deleteTree(node.right)
# then delete the node
print("Deleting node: ",
node.data)
node = None
# Deletes a tree and sets the root as NULL
def deleteTree(node_ref):
_deleteTree(node_ref[0])
node_ref[0] = None
# Driver code
root = [0]
root[0] = newNode(1)
root[0].left = newNode(2)
root[0].right = newNode(3)
root[0].left.left = newNode(4)
root[0].left.right = newNode(5)
# Note that we pass the address
# of root here
deleteTree(root)
print("Tree deleted ")
# This code is contributed by SHUBHAMSINGH10
C#
using System;
// C# program to delete a tree
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and pointer to right child */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
public static Node root;
/* This function is same as deleteTree() in the previous program */
public virtual void deleteTree(Node node)
{
// In Java automatic garbage collection
// happens, so we can simply make root
// null to delete the tree
root = null;
}
/* Wrapper function that deletes the tree and
sets root node as null */
public virtual void deleteTreeRef(Node nodeRef)
{
deleteTree(nodeRef);
nodeRef = null;
}
/* Driver program to test deleteTree function */
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
BinaryTree.root = new Node(1);
BinaryTree.root.left = new Node(2);
BinaryTree.root.right = new Node(3);
BinaryTree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
BinaryTree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
/* Note that we pass root node here */
tree.deleteTreeRef(root);
Console.WriteLine("Tree deleted");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13
Javascript
输出:
Deleting node: 4
Deleting node: 5
Deleting node: 2
Deleting node: 3
Deleting node: 1
Tree deleted 时间复杂度: O(n)
空间复杂度:如果我们不考虑函数调用的堆栈大小,那么 O(1) 否则 O(n)