Java中的 IdentityHashMap 类
IdentityHashMap使用 Hashtable 实现 Map 接口,在比较键(和值)时使用引用相等代替对象相等。此类不是通用 Map 实现。虽然这个类实现了 Map 接口,但它故意违反了 Map 的一般合同,该合同要求在比较对象时使用 equals() 方法。当用户需要通过引用比较对象时使用此类。它属于Java.util包。
IdentityHashMap 的特点
- 它遵循引用相等,而不是使用 equals() 方法,而是使用 ==运算符。
- 它不同步,必须在外部同步。
- 迭代器是快速失败的,抛出ConcurrentModificationException以尝试在迭代时进行修改。
- 此类为基本操作(get 和 put)提供恒定时间性能,假设系统身份哈希函数(System.identityHashCode(Object)) 将元素正确地分散在桶中。 IdentityHashMap 不使用 hashCode() 方法,而是使用 System.identityHashCode() 方法。这是一个显着的区别,因为现在您可以使用可变对象作为 Map 中的键,当映射存储在 IdentityHashMap 中时,其哈希码可能会发生变化。
宣言:
public class IdentityHashMap
这里, K是键对象类型, V是值对象类型。
IdentityHashMap 的层次结构
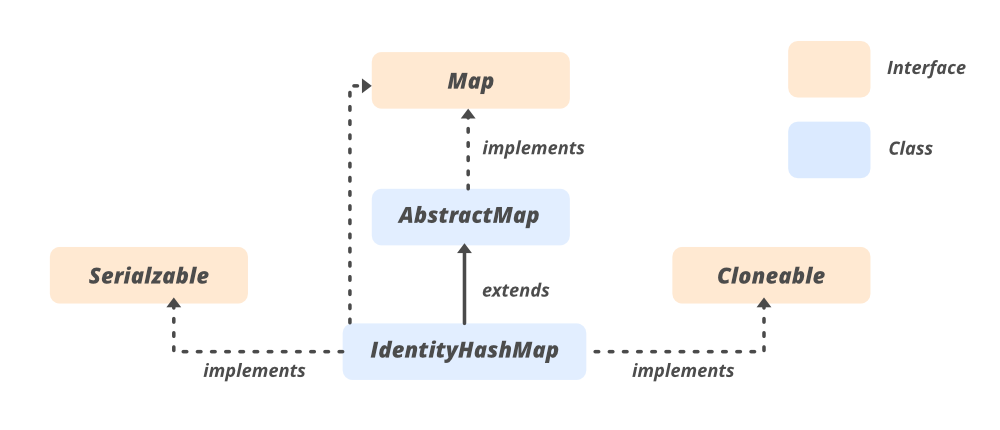
它实现了 Serializable 、 Cloneable 、 Map
例子:
Java
// Java code to demonstrate IdentityHashMap
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// creating an instance of IdentityHashMap
Map ihm = new IdentityHashMap<>();
// Putting key and value pair
// in a IdentityHashMap Object
ihm.put("ihmkey","ihmvalue");
ihm.put(new String("ihmkey"),"ihmvalue1");
// ihm.size() will print 2 since it
// compares the objects by reference
System.out.println("Size of IdentityHashMap--"+ihm.size());
}
} Java
// Java code to illustrate
// adding elements to IdentityHashMap
import java.util.*;
public class AddingElementsToIdentityHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty IdentityHashMap
Map identity_hash
= new IdentityHashMap();
// Mapping string values to int keys
// using put() method
identity_hash.put(10, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(15, "4");
identity_hash.put(20, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(25, "Welcomes");
identity_hash.put(30, "You");
// Displaying the IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("Initial Mappings are: "
+ identity_hash);
// Inserting existing key along with new value
// previous value gets returned and stored in
// returned_value
String returned_value
= (String)identity_hash.put(20, "All");
// Verifying the returned value
System.out.println("Returned value is: "
+ returned_value);
// Displaying the new map
System.out.println("New map is: " + identity_hash);
// Creating a new Identityhash map and copying
Map new_Identityhash_map
= new IdentityHashMap();
new_Identityhash_map.putAll(identity_hash);
// Displaying the final IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("The new map: "
+ new_Identityhash_map);
}
} Java
// Java code to illustrate removing
// elements from IdentityHashMap
import java.util.*;
public class RemovingMappingsFromIdentityHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty IdentityHashMap
Map Identity_hash = new
IdentityHashMap();
// Mapping string values to int keys
Identity_hash.put(10, "Geeks");
Identity_hash.put(15, "4");
Identity_hash.put(20, "Geeks");
Identity_hash.put(25, "Welcomes");
Identity_hash.put(30, "You");
// Displaying the IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("Initial Mappings are: " +
Identity_hash);
// Removing the existing key mapping
String returned_value =
(String)Identity_hash.remove(20);
// Verifying the returned value
System.out.println("Returned value is: " +
returned_value);
// Displaying the new map
System.out.println("New map is: " + Identity_hash);
}
} Java
// Java code to illustrate the accessing
// elements from IdentityHashMap
import java.util.*;
public class AccessingElementsFromIdentityHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty IdentityHashMap
Map identity_hash
= new IdentityHashMap();
// Mapping string values to int keys
identity_hash.put(10, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(15, "4");
identity_hash.put(20, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(25, "Welcomes");
identity_hash.put(30, "You");
// Displaying the IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("Initial Mappings are: "
+ identity_hash);
// Getting the value of 25
System.out.println("The Value is: "
+ identity_hash.get(25));
// Getting the value of 10
System.out.println("The Value is: "
+ identity_hash.get(10));
// Using keySet() to get the set view of keys
System.out.println("The set is: " + identity_hash.keySet());
// Using entrySet() to get the set view
System.out.println("The set is: " +
identity_hash.entrySet());
}
} Java
// Java code to illustrate the
// iterating over IdentityHashmap
import java.util.*;
public class IteratingIdentityHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty IdentityHashMap
IdentityHashMap identity_hash
= new IdentityHashMap();
// Mapping string values to int keys
identity_hash.put(10, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(15, "4");
identity_hash.put(20, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(25, "Welcomes");
identity_hash.put(30, "You");
// Displaying the IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("Initial Mappings are: "
+ identity_hash);
// Create an Iterator over the
// IdentityHashMap
Iterator >
itr = identity_hash.entrySet().iterator();
// The hasNext() method is used to check if there is
// a next element The next() method is used to
// retrieve the next element
while (itr.hasNext()) {
IdentityHashMap.Entry entry
= itr.next();
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey()
+ ", Value = "
+ entry.getValue());
}
}
} Java
// Java code to demonstrate IdentityHashMap and
// illustration of how it is different from HashMap
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating HashMap and IdentityHashMap objects
Map hm = new HashMap<>();
Map ihm = new IdentityHashMap<>();
// Putting key and value in HashMap and IdentityHashMap Object
hm.put("hmkey","hmvalue");
hm.put(new String("hmkey"),"hmvalue1");
ihm.put("ihmkey","ihmvalue");
ihm.put(new String("ihmkey"),"ihmvalue1");
// Print Size of HashMap and WeakHashMap Object
// hm.size() will print 1 since it compares the objects logically
// and both the keys are same
System.out.println("Size of HashMap is : "+hm.size());
// ihm.size() will print 2 since it compares the objects by reference
System.out.println("Size of IdentityHashMap is : "+ihm.size());
}
} Size of IdentityHashMap--2IdentityHashMap 的构造函数
我们可以通过两种方式创建IdentityHashMap的实例:
IdentityHashMap ihm = new IdentityHashMap();
(or)
Map hm = new IdentityHashMap(); 1. IdentityHashMap():构造一个新的空身份哈希映射,具有默认的预期最大大小。
IdentityHashMap
2. IdentityHashMap(int expectedMaxSize):构造一个具有指定预期最大大小的新的空映射。
IdentityHashMap
3. IdentityHashMap(Map m):构造一个新的身份哈希映射,包含指定映射中的键值映射。
IdentityHashMap
IdentityHashMap 的基本操作
1.添加元素
要将映射插入或添加到 IdentityHashMap,我们有 put() 和 putAll() 方法。 put() 可以将特定的键和它映射的值插入到特定的映射中。如果传递了现有键,则先前的值将被新值替换。 putAll() 将所有元素(即映射)从一个映射复制到另一个映射。
Java
// Java code to illustrate
// adding elements to IdentityHashMap
import java.util.*;
public class AddingElementsToIdentityHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty IdentityHashMap
Map identity_hash
= new IdentityHashMap();
// Mapping string values to int keys
// using put() method
identity_hash.put(10, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(15, "4");
identity_hash.put(20, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(25, "Welcomes");
identity_hash.put(30, "You");
// Displaying the IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("Initial Mappings are: "
+ identity_hash);
// Inserting existing key along with new value
// previous value gets returned and stored in
// returned_value
String returned_value
= (String)identity_hash.put(20, "All");
// Verifying the returned value
System.out.println("Returned value is: "
+ returned_value);
// Displaying the new map
System.out.println("New map is: " + identity_hash);
// Creating a new Identityhash map and copying
Map new_Identityhash_map
= new IdentityHashMap();
new_Identityhash_map.putAll(identity_hash);
// Displaying the final IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("The new map: "
+ new_Identityhash_map);
}
}
Initial Mappings are: {10=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You, 20=Geeks, 15=4}
Returned value is: Geeks
New map is: {10=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You, 20=All, 15=4}
The new map: {10=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You, 20=All, 15=4} 2. 移除元素
为了删除映射,我们使用了一个 IdentityHashMap 类的内置方法 remove(),用于从映射中删除任何特定键的映射。
Java
// Java code to illustrate removing
// elements from IdentityHashMap
import java.util.*;
public class RemovingMappingsFromIdentityHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty IdentityHashMap
Map Identity_hash = new
IdentityHashMap();
// Mapping string values to int keys
Identity_hash.put(10, "Geeks");
Identity_hash.put(15, "4");
Identity_hash.put(20, "Geeks");
Identity_hash.put(25, "Welcomes");
Identity_hash.put(30, "You");
// Displaying the IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("Initial Mappings are: " +
Identity_hash);
// Removing the existing key mapping
String returned_value =
(String)Identity_hash.remove(20);
// Verifying the returned value
System.out.println("Returned value is: " +
returned_value);
// Displaying the new map
System.out.println("New map is: " + Identity_hash);
}
}
Initial Mappings are: {10=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You, 20=Geeks, 15=4}
Returned value is: Geeks
New map is: {10=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You, 15=4}3. 访问元素
我们可以使用 get() 方法访问 IdentityHashMap 的元素,下面给出了这个例子。
Java
// Java code to illustrate the accessing
// elements from IdentityHashMap
import java.util.*;
public class AccessingElementsFromIdentityHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty IdentityHashMap
Map identity_hash
= new IdentityHashMap();
// Mapping string values to int keys
identity_hash.put(10, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(15, "4");
identity_hash.put(20, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(25, "Welcomes");
identity_hash.put(30, "You");
// Displaying the IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("Initial Mappings are: "
+ identity_hash);
// Getting the value of 25
System.out.println("The Value is: "
+ identity_hash.get(25));
// Getting the value of 10
System.out.println("The Value is: "
+ identity_hash.get(10));
// Using keySet() to get the set view of keys
System.out.println("The set is: " + identity_hash.keySet());
// Using entrySet() to get the set view
System.out.println("The set is: " +
identity_hash.entrySet());
}
}
Initial Mappings are: {10=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You, 20=Geeks, 15=4}
The Value is: Welcomes
The Value is: Geeks
The set is: [10, 25, 30, 20, 15]
The set is: [10=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You, 20=Geeks, 15=4] 4. 遍历
我们可以使用 Iterator 接口来遍历 Collection Framework 的任何结构。由于迭代器使用一种类型的数据,我们使用 Entry< ? , ? > 将两种不同的类型解析为兼容的格式。然后使用 next() 方法我们打印 IdentityHashMap 的元素。
Java
// Java code to illustrate the
// iterating over IdentityHashmap
import java.util.*;
public class IteratingIdentityHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty IdentityHashMap
IdentityHashMap identity_hash
= new IdentityHashMap();
// Mapping string values to int keys
identity_hash.put(10, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(15, "4");
identity_hash.put(20, "Geeks");
identity_hash.put(25, "Welcomes");
identity_hash.put(30, "You");
// Displaying the IdentityHashMap
System.out.println("Initial Mappings are: "
+ identity_hash);
// Create an Iterator over the
// IdentityHashMap
Iterator >
itr = identity_hash.entrySet().iterator();
// The hasNext() method is used to check if there is
// a next element The next() method is used to
// retrieve the next element
while (itr.hasNext()) {
IdentityHashMap.Entry entry
= itr.next();
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey()
+ ", Value = "
+ entry.getValue());
}
}
}
Initial Mappings are: {10=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You, 20=Geeks, 15=4}
Key = 10, Value = Geeks
Key = 25, Value = Welcomes
Key = 30, Value = You
Key = 20, Value = Geeks
Key = 15, Value = 4同步的 IdentityHashMap
如果多个线程同时访问一个身份哈希图,并且至少有一个线程在结构上修改了该图,则必须在外部进行同步。 (结构修改是添加或删除一个或多个映射的任何操作;仅更改与实例已包含的键关联的值不是结构修改。)这通常通过在自然封装映射的某个对象上同步来完成.如果不存在这样的对象,则应使用Collections.synchronizedMap方法“包装”地图。这最好在创建时完成,以防止对地图的意外不同步访问。
Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new IdentityHashMap(…));
IdentityHashMap 的方法
- K - 映射中键的类型。
- V – 映射中映射的值的类型。
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| clear() | Removes all of the mappings from this map. |
| clone() | Returns a shallow copy of this identity hash map: the keys and values themselves are not cloned. |
| containsKey(Object key) | Tests whether the specified object reference is a key in this identity hash map. |
| containsValue(Object value) | Tests whether the specified object reference is a value in this identity hash map. |
| entrySet() | Returns a Set view of the mappings contained in this map. |
| equals(Object o) | Compares the specified object with this map for equality. |
| get(Object key) | Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or null if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this map. |
| isEmpty() | Returns true if this identity hash map contains no key-value mappings. |
| keySet() | Returns an identity-based set view of the keys contained in this map. |
| put(K key, V value) | Associates the specified value with the specified key in this identity hash map. |
| putAll(Map m) | Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this map. |
| remove(Object key) | Removes the mapping for this key from this map if present. |
| size() | Returns the number of key-value mappings in this identity hash map. |
| values() | Returns a Collection view of the values contained in this map. |
在类Java.util.AbstractMap 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| toString() | Returns a string representation of this map. |
在接口Java.util.Map 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| compute(K key, BiFunction remappingFunction) | Attempts to compute a mapping for the specified key and its current mapped value (or null if there is no current mapping). |
| computeIfAbsent(K key, Function mappingFunction) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped to null), attempts to compute its value using the given mapping function and enters it into this map unless null. |
| computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction remappingFunction) | If the value for the specified key is present and non-null, attempts to compute a new mapping given the key and its current mapped value. |
| forEach(BiConsumer action) | Performs the given action for each entry in this map until all entries have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or defaultValue if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
| merge(K key, V value, BiFunction remappingFunction) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value or is associated with null, associates it with the given non-null value. |
| putIfAbsent(K key, V value) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped to null) associates it with the given value and returns null, else returns the current value. |
| remove(Object key, Object value) | Removes the entry for the specified key only if it is currently mapped to the specified value. |
| replace(K key, V value) | Replaces the entry for the specified key only if it is currently mapped to some value. |
| replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) | Replaces the entry for the specified key only if currently mapped to the specified value. |
| replaceAll(BiFunction function) | Replaces each entry’s value with the result of invoking the given function on that entry until all entries have been processed or the function throws an exception. |
IdentityHashMap 与HashMap
- IdentityHashMap 使用相等运算符“==”来比较键和值,而 HashMap 使用 equals 方法来比较 Map 内部的键和值。
- 由于 IdentityHashMap 不使用 equals(),因此对于具有昂贵 equals() 的对象,它比 HashMap 相对快。
- IdentityHashMap 不需要键是不可变的,因为它不依赖于 equals()。
下面的程序说明了 IdentityHashMap 和 HashMap 实现之间的区别。
Java
// Java code to demonstrate IdentityHashMap and
// illustration of how it is different from HashMap
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
public class IdentityHashMapExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating HashMap and IdentityHashMap objects
Map hm = new HashMap<>();
Map ihm = new IdentityHashMap<>();
// Putting key and value in HashMap and IdentityHashMap Object
hm.put("hmkey","hmvalue");
hm.put(new String("hmkey"),"hmvalue1");
ihm.put("ihmkey","ihmvalue");
ihm.put(new String("ihmkey"),"ihmvalue1");
// Print Size of HashMap and WeakHashMap Object
// hm.size() will print 1 since it compares the objects logically
// and both the keys are same
System.out.println("Size of HashMap is : "+hm.size());
// ihm.size() will print 2 since it compares the objects by reference
System.out.println("Size of IdentityHashMap is : "+ihm.size());
}
}
Size of HashMap is : 1
Size of IdentityHashMap is : 2