使用递归的树的 DFS 遍历
给定一棵二叉树,使用递归的 DFS 遍历它。
与只有一种逻辑遍历它们的线性数据结构(数组、链表、队列、堆栈等)不同,树可以以不同的方式遍历。一般来说,有两种广泛使用的遍历树的方法:
- DFS 或深度优先搜索
- BFS 或广度优先搜索
在本文中,已经讨论了使用 DFS 进行遍历。请参阅此帖子以了解广度优先遍历。
深度优先搜索
DFS(深度优先搜索)是用于遍历树或图的技术。这里回溯用于遍历。在这个遍历中,首先访问最深的节点,然后如果该节点的兄弟节点不存在,则回溯到它的父节点。
图与树的 DFS 遍历
在图中,可能存在循环和断开连接。与图不同,树不包含循环并且始终连接。所以树的DFS相对容易。我们可以简单地从一个节点开始,然后遍历它的相邻(或子节点)而不关心循环。如果我们从单个节点(根)开始,并以这种方式遍历,则可以保证我们遍历整个树,因为没有断开连接,
例子:
Tree:
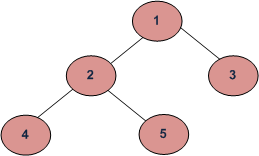
Therefore, the Depth First Traversals of this Tree will be:
(a) Inorder (Left, Root, Right) : 4 2 5 1 3
(b) Preorder (Root, Left, Right) : 1 2 4 5 3
(c) Postorder (Left, Right, Root) : 4 5 2 3 1
下面是使用递归的 DFS 遍历树:
1.中序遍历(练习):
示例:上图的中序遍历是 4 2 5 1 3。
Algorithm Inorder(tree)
1. Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Inorder(left-subtree)
2. Visit the root.
3. Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Inorder(right-subtree)执行:
C++
// C program for different tree traversals
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print the data of node */
cout << node->data << " ";
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
cout << "\nInorder traversal of binary tree is \n";
printInorder(root);
return 0;
} C
// C program for different tree traversals
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print the data of node */
printf("%d ", node->data);
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("\nInorder traversal of binary tree is \n");
printInorder(root);
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for different tree traversals
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node {
int key;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printInorder() { printInorder(root); }
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("\nInorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printInorder();
}
}Python
# Python program to for tree traversals
# A class that represents an individual node in a
# Binary Tree
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.val = key
# A function to do inorder tree traversal
def printInorder(root):
if root:
# First recur on left child
printInorder(root.left)
# then print the data of node
print(root.val),
# now recur on right child
printInorder(root.right)
# Driver code
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print "\nInorder traversal of binary tree is"
printInorder(root)C#
// C# program for different tree traversals
using System;
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node
{
public int key;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printInorder()
{
printInorder(root);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("\nInorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printInorder();
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992Javascript
C++
// C program for different tree traversals
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first print data of node */
cout << node->data << " ";
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node->left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
cout << "\nPreorder traversal of binary tree is \n";
printPreorder(root);
return 0;
} C
// C program for different tree traversals
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first print data of node */
printf("%d ", node->data);
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node->left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("\nPreorder traversal of binary tree is \n");
printPreorder(root);
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for different tree traversals
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node {
int key;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first print data of node */
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node.left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node.right);
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printPreorder() { printPreorder(root); }
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Preorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPreorder();
}
}Python
# Python program to for tree traversals
# A class that represents an individual node in a
# Binary Tree
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.val = key
# A function to do preorder tree traversal
def printPreorder(root):
if root:
# First print the data of node
print(root.val),
# Then recur on left child
printPreorder(root.left)
# Finally recur on right child
printPreorder(root.right)
# Driver code
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print "Preorder traversal of binary tree is"
printPreorder(root)C#
// C# program for different tree traversals
using System;
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
public class Node
{
public int key;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first print data of node */
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node.left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node.right);
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printPreorder() { printPreorder(root); }
// Driver method
public static void Main()
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Preorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPreorder();
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */C++
// C program for different tree traversals
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node->left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node->right);
// now deal with the node
cout << node->data << " ";
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
cout << "\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is \n";
printPostorder(root);
return 0;
} C
// C program for different tree traversals
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node->left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node->right);
// now deal with the node
printf("%d ", node->data);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is \n");
printPostorder(root);
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for different tree traversals
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node {
int key;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// now deal with the node
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printPostorder() { printPostorder(root); }
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPostorder();
}
}Python
# Python program to for tree traversals
# A class that represents an individual node in a
# Binary Tree
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.val = key
# A function to do postorder tree traversal
def printPostorder(root):
if root:
# First recur on left child
printPostorder(root.left)
# the recur on right child
printPostorder(root.right)
# now print the data of node
print(root.val),
# Driver code
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print "\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is"
printPostorder(root)C#
// C# program for different tree traversals
using System;
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
public class Node
{
public int key;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// now deal with the node
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printPostorder() { printPostorder(root); }
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPostorder();
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-JiJavascript
C++
// C program for different tree traversals
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* left, *right;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node->left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node->right);
// now deal with the node
cout << node->data << " ";
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print the data of node */
cout << node->data << " ";
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node->right);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first print data of node */
cout << node->data << " ";
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node->left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct Node *root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
cout << "\nPreorder traversal of binary tree is \n";
printPreorder(root);
cout << "\nInorder traversal of binary tree is \n";
printInorder(root);
cout << "\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is \n";
printPostorder(root);
return 0;
} C
// C program for different tree traversals
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node->left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node->right);
// now deal with the node
printf("%d ", node->data);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print the data of node */
printf("%d ", node->data);
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node->right);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first print data of node */
printf("%d ", node->data);
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node->left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("\nPreorder traversal of binary tree is \n");
printPreorder(root);
printf("\nInorder traversal of binary tree is \n");
printInorder(root);
printf("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is \n");
printPostorder(root);
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for different tree traversals
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node
{
int key;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// now deal with the node
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first print data of node */
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node.left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node.right);
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printPostorder() { printPostorder(root); }
void printInorder() { printInorder(root); }
void printPreorder() { printPreorder(root); }
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Preorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPreorder();
System.out.println("\nInorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printInorder();
System.out.println("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPostorder();
}
}Python
# Python program to for tree traversals
# A class that represents an individual node in a
# Binary Tree
class Node:
def __init__(self,key):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.val = key
# A function to do inorder tree traversal
def printInorder(root):
if root:
# First recur on left child
printInorder(root.left)
# then print the data of node
print(root.val),
# now recur on right child
printInorder(root.right)
# A function to do postorder tree traversal
def printPostorder(root):
if root:
# First recur on left child
printPostorder(root.left)
# the recur on right child
printPostorder(root.right)
# now print the data of node
print(root.val),
# A function to do preorder tree traversal
def printPreorder(root):
if root:
# First print the data of node
print(root.val),
# Then recur on left child
printPreorder(root.left)
# Finally recur on right child
printPreorder(root.right)
# Driver code
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print "Preorder traversal of binary tree is"
printPreorder(root)
print "\nInorder traversal of binary tree is"
printInorder(root)
print "\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is"
printPostorder(root)C#
// C# program for different Console.Writetree traversals
using System;
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
public class Node
{
public int key;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print
its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// now deal with the node
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first print data of node */
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node.left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node.right);
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printPostorder() { printPostorder(root); }
void printInorder() { printInorder(root); }
void printPreorder() { printPreorder(root); }
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Preorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPreorder();
Console.WriteLine("\nInorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printInorder();
Console.WriteLine("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPostorder();
}
}
// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumarInorder traversal of binary tree is
4 2 5 1 3顺序的用途:
在二叉搜索树 (BST) 的情况下,中序遍历以非递减顺序给出节点。为了以非递增顺序获取 BST 的节点,可以使用 Inorder traversal 的变体,其中 Inorder traversal s reversed。
2. 前序遍历(练习):
示例:上图的前序遍历是 1 2 4 5 3。
Algorithm Preorder(tree)
1. Visit the root.
2. Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Preorder(left-subtree)
3. Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Preorder(right-subtree)执行:
C++
// C program for different tree traversals
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first print data of node */
cout << node->data << " ";
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node->left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
cout << "\nPreorder traversal of binary tree is \n";
printPreorder(root);
return 0;
}
C
// C program for different tree traversals
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first print data of node */
printf("%d ", node->data);
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node->left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("\nPreorder traversal of binary tree is \n");
printPreorder(root);
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for different tree traversals
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node {
int key;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first print data of node */
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node.left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node.right);
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printPreorder() { printPreorder(root); }
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Preorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPreorder();
}
}
Python
# Python program to for tree traversals
# A class that represents an individual node in a
# Binary Tree
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.val = key
# A function to do preorder tree traversal
def printPreorder(root):
if root:
# First print the data of node
print(root.val),
# Then recur on left child
printPreorder(root.left)
# Finally recur on right child
printPreorder(root.right)
# Driver code
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print "Preorder traversal of binary tree is"
printPreorder(root)
C#
// C# program for different tree traversals
using System;
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
public class Node
{
public int key;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first print data of node */
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node.left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node.right);
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printPreorder() { printPreorder(root); }
// Driver method
public static void Main()
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Preorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPreorder();
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
Preorder traversal of binary tree is
1 2 4 5 3预购的用途:
前序遍历用于创建树的副本。前序遍历也用于获取表达式树的前缀表达式。请参阅 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polish_notation 了解前缀表达式为何有用。
3.后序遍历(练习):
示例:上述给定树的后序遍历是 4 5 2 3 1。
Algorithm Postorder(tree)
1. Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Postorder(left-subtree)
2. Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Postorder(right-subtree)
3. Visit the root.执行:
C++
// C program for different tree traversals
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node->left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node->right);
// now deal with the node
cout << node->data << " ";
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
cout << "\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is \n";
printPostorder(root);
return 0;
}
C
// C program for different tree traversals
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node->left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node->right);
// now deal with the node
printf("%d ", node->data);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is \n");
printPostorder(root);
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for different tree traversals
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node {
int key;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// now deal with the node
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printPostorder() { printPostorder(root); }
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPostorder();
}
}
Python
# Python program to for tree traversals
# A class that represents an individual node in a
# Binary Tree
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.val = key
# A function to do postorder tree traversal
def printPostorder(root):
if root:
# First recur on left child
printPostorder(root.left)
# the recur on right child
printPostorder(root.right)
# now print the data of node
print(root.val),
# Driver code
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print "\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is"
printPostorder(root)
C#
// C# program for different tree traversals
using System;
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
public class Node
{
public int key;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// now deal with the node
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printPostorder() { printPostorder(root); }
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPostorder();
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
Postorder traversal of binary tree is
4 5 2 3 1后序的用途:
后序遍历用于删除树。有关详细信息,请参阅删除树的问题。后序遍历对于获取表达式树的后缀表达式也很有用。有关后缀表达式的用法,请参阅 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reverse_Polish_notation。
使用 DFS 实现所有遍历
C++
// C program for different tree traversals
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* left, *right;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node->left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node->right);
// now deal with the node
cout << node->data << " ";
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print the data of node */
cout << node->data << " ";
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node->right);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(struct Node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first print data of node */
cout << node->data << " ";
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node->left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct Node *root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
cout << "\nPreorder traversal of binary tree is \n";
printPreorder(root);
cout << "\nInorder traversal of binary tree is \n";
printInorder(root);
cout << "\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is \n";
printPostorder(root);
return 0;
}
C
// C program for different tree traversals
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node->left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node->right);
// now deal with the node
printf("%d ", node->data);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node->left);
/* then print the data of node */
printf("%d ", node->data);
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node->right);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* first print data of node */
printf("%d ", node->data);
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node->left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
printf("\nPreorder traversal of binary tree is \n");
printPreorder(root);
printf("\nInorder traversal of binary tree is \n");
printInorder(root);
printf("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is \n");
printPostorder(root);
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for different tree traversals
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node
{
int key;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// now deal with the node
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first print data of node */
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node.left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node.right);
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printPostorder() { printPostorder(root); }
void printInorder() { printInorder(root); }
void printPreorder() { printPreorder(root); }
// Driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Preorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPreorder();
System.out.println("\nInorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printInorder();
System.out.println("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPostorder();
}
}
Python
# Python program to for tree traversals
# A class that represents an individual node in a
# Binary Tree
class Node:
def __init__(self,key):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.val = key
# A function to do inorder tree traversal
def printInorder(root):
if root:
# First recur on left child
printInorder(root.left)
# then print the data of node
print(root.val),
# now recur on right child
printInorder(root.right)
# A function to do postorder tree traversal
def printPostorder(root):
if root:
# First recur on left child
printPostorder(root.left)
# the recur on right child
printPostorder(root.right)
# now print the data of node
print(root.val),
# A function to do preorder tree traversal
def printPreorder(root):
if root:
# First print the data of node
print(root.val),
# Then recur on left child
printPreorder(root.left)
# Finally recur on right child
printPreorder(root.right)
# Driver code
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print "Preorder traversal of binary tree is"
printPreorder(root)
print "\nInorder traversal of binary tree is"
printInorder(root)
print "\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is"
printPostorder(root)
C#
// C# program for different Console.Writetree traversals
using System;
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
public class Node
{
public int key;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
// Root of Binary Tree
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root = null;
}
/* Given a binary tree, print
its nodes according to the
"bottom-up" postorder traversal. */
void printPostorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
// first recur on left subtree
printPostorder(node.left);
// then recur on right subtree
printPostorder(node.right);
// now deal with the node
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in inorder*/
void printInorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first recur on left child */
printInorder(node.left);
/* then print the data of node */
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
/* now recur on right child */
printInorder(node.right);
}
/* Given a binary tree, print its nodes in preorder*/
void printPreorder(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* first print data of node */
Console.Write(node.key + " ");
/* then recur on left subtree */
printPreorder(node.left);
/* now recur on right subtree */
printPreorder(node.right);
}
// Wrappers over above recursive functions
void printPostorder() { printPostorder(root); }
void printInorder() { printInorder(root); }
void printPreorder() { printPreorder(root); }
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine("Preorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPreorder();
Console.WriteLine("\nInorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printInorder();
Console.WriteLine("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is ");
tree.printPostorder();
}
}
// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumar
输出:
Preorder traversal of binary tree is
1 2 4 5 3
Inorder traversal of binary tree is
4 2 5 1 3
Postorder traversal of binary tree is
4 5 2 3 1时间复杂度: O(n)
辅助空间:如果我们不考虑函数调用的堆栈大小,则 O(1) 否则 O(n)。