Python – JSON 到 XML
JSON文件是以 JavaScript 对象表示法 (JSON) 格式存储简单数据结构和对象的文件,这是一种标准数据交换格式。它主要用于在 Web 应用程序和服务器之间传输数据。JSON对象包含键/值对形式的数据。键是字符串,值是 JSON 类型。键和值用冒号分隔。每个条目(键/值对)由逗号分隔。 JSON 文件是轻量级的、基于文本的、人类可读的,并且可以使用文本编辑器进行编辑。
注意:有关更多信息,请参阅在Python中使用 JSON 数据
XML是一种用于存储数据的标记语言。它区分大小写。 XML 让您可以定义标记元素并生成定制的标记语言。 XML 中的基本单元称为元素。 XML 语言没有预定义的标签。它简化了数据共享、数据传输、平台更改、数据可用性 XML 文件的扩展名为 .xml
注意:有关详细信息,请参阅 XML |基本
JSON 和 XML 文件格式都用于在客户端和服务器之间传输数据。
但是,它们都具有相同的目的,尽管它们的方式不同。
JSON 和 XML 的比较
| JSON | XML |
|---|---|
| JSON object has a type | XML data is typeless |
| JSON types: string, number, array, Boolean | All XML data should be string |
| Data is readily accessible as JSON objects | XML data needs to be parsed |
| JSON is supported by most browsers | Cross-browser XML parsing can be tricky |
| JSON has no display capabilities | XML offers the capability to display data because it is a markup language |
| JSON supports only text and number data type. | XML support various data types such as number, text, images, charts, graphs, etc. It also provides options for transferring the structure or format of the data with actual data. |
| Retrieving value is easy | Retrieving value is difficult |
| Supported by many Ajax toolkit | Not fully supported by Ajax toolkit |
| A fully automated way of deserializing/serializing JavaScript | Developers have to write JavaScript code to serialize/de-serialize from XML |
| Native support for object | The object has to be express by conventions – mostly missed use of attributes and elements. |
| It supports only UTF-8 encoding. | It supports various encoding |
| It doesn’t support comments. | It supports comments. |
| JSON files are easy to read as compared to XML. | XML documents are relatively more difficult to read and interpret. |
| It does not provide any support for namespaces | It supports namespaces. |
| It is less secured. | It is more secure than JSON. |
在Python 3 中处理 JSON
为了处理 JSON 文件格式, Python提供了一个名为json的模块。
第一步:导入json模块
import json as JS第 2 步:导入 xml.etree.ElementTree 模块
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET第 3 步:读取 json 文件
这里, “data”是我们加载 JSON 数据的变量。
with open("quiz.json", "r") as json_file:
data = JS.load(json_file);
第 4 步:构建根元素
每个 xml 文件必须只有一个根元素
root = ET.Element("quiz")第 5 步:构建根的子元素
SubElement 有两个参数:
- root - 它是存储根元素的变量的名称。
- subelement_name:它是子元素的名称。示例:
Maths = ET.SubElement(root, "maths")STEP 6:构建xml文档树
tree = ET.ElementTree(root)第 7 步:将 xml 写入 quiz.xml 文件
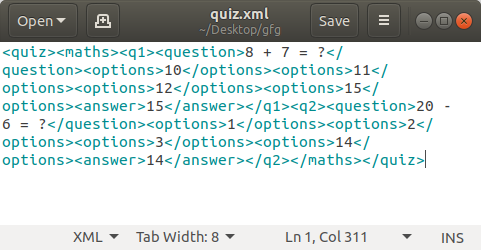
tree.write("quiz.xml")注意: XML 元素不支持整数值,因此我们需要将它们转换为字符串。
例子:
JSON文件:
# Program to read JSON file
# and generate its XML file
# Importing json module and xml
# module provided by python
import json as JS
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# Opening JSON file in read mode
with open("myfile3.json", "r") as json_file:
# loading json file data
# to variable data
data = JS.load(json_file);
# Building the root element
# of the xml file
root = ET.Element("quiz")
# Building the sub root elements
# We don't add text since the value
# associated with subelement is a
# python dictionary
Maths = ET.SubElement(root, "maths")
# Building subelement of maths as q1
Q1 = ET.SubElement(Maths, "q1")
ET.SubElement(Q1, "question").
text = data["quiz"]["maths"]["q1"]["question"]
# Building multiple subelements with name options to hold different values
# Xml elements cannot hold integer values so we need to
# convert them to string
ET.SubElement(Q1, "options").text = str(data["quiz"]
["maths"]["q1"]
["options"][0])
ET.SubElement(Q1, "options").text = str(data["quiz"]
["maths"]["q1"]
["options"][1])
ET.SubElement(Q1, "options").text = str(data["quiz"]
["maths"]["q1"]
["options"][2])
ET.SubElement(Q1, "options").text = str(data["quiz"]
["maths"]["q1"]
["options"][3])
ET.SubElement(Q1, "answer").text = str(data["quiz"]
["maths"]["q1"]
["answer"])
# Building subelement of maths as q2
Q2 = ET.SubElement(Maths, "q2")
ET.SubElement(Q2, "question").text = data["quiz"]
["maths"]["q2"]["question"]
# Building multiple subelements
# with name options to hold
# different values
ET.SubElement(Q2, "options").text = str(data["quiz"]
["maths"]
["q2"]
["options"][0])
ET.SubElement(Q2, "options").text = str(data["quiz"]
["maths"]
["q2"]
["options"][1])
ET.SubElement(Q2, "options").text = str(data["quiz"]
["maths"]["q2"]
["options"][2])
ET.SubElement(Q2, "options").text = str(data["quiz"]
["maths"]["q2"]
["options"][3])
ET.SubElement(Q2, "answer").text = str(data["quiz"]
["maths"]["q2"]
["answer"])
# Building the tree of the xml
# elements using the root element
tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
# Writing the xml to output file
tree.write("quiz.xml")
输出: