用于从链表末尾打印第 N 个节点的Java程序
给定一个链表和一个数字 n,编写一个函数,返回链表末尾第 n 个节点的值。
例如,如果输入低于列表且 n = 3,则输出为“B”
方法一(使用链表的长度)
1) 计算链表的长度。设长度为 len。
2) 打印链表开头的第 (len – n + 1) 个节点。
双指针概念:第一个指针用来存放变量的地址,第二个指针用来存放第一个指针的地址。如果我们希望通过函数更改变量的值,我们将指针传递给它。如果我们希望改变一个指针的值(即,它应该开始指向别的东西),我们将指针传递给一个指针。
下面是上述方法的实现:
Java
// Simple Java program to find n'th node from end of linked list
class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of the list
/* Linked List node */
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Function to get the nth node from the last of a
linked list */
void printNthFromLast(int n)
{
int len = 0;
Node temp = head;
// 1) count the number of nodes in Linked List
while (temp != null) {
temp = temp.next;
len++;
}
// check if value of n is not more than length of
// the linked list
if (len < n)
return;
temp = head;
// 2) get the (len-n+1)th node from the beginning
for (int i = 1; i < len - n + 1; i++)
temp = temp.next;
System.out.println(temp.data);
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/*Driver program to test above methods */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(20);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(15);
llist.push(35);
llist.printNthFromLast(4);
}
} // This code is contributed by Rajat MishraJava
static void printNthFromLast(Node head, int n)
{
static int i = 0;
if (head == null)
return;
printNthFromLast(head.next, n);
if (++i == n)
System.out.print(head.data);
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56.Java
// Java program to find n'th
// node from end using slow and
// fast pointers
class LinkedList
{
Node head; // head of the list
/* Linked List node */
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Function to get the
nth node from end of list */
void printNthFromLast(int n)
{
Node main_ptr = head;
Node ref_ptr = head;
int count = 0;
if (head != null)
{
while (count < n)
{
if (ref_ptr == null)
{
System.out.println(n
+ " is greater than the no "
+ " of nodes in the list");
return;
}
ref_ptr = ref_ptr.next;
count++;
}
if(ref_ptr == null)
{
if(head != null)
System.out.println("Node no. " + n +
" from last is " +
head.data);
}
else
{
while (ref_ptr != null)
{
main_ptr = main_ptr.next;
ref_ptr = ref_ptr.next;
}
System.out.println("Node no. " + n +
" from last is " +
main_ptr.data);
}
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/*Driver program to test above methods */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(20);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(15);
llist.push(35);
llist.printNthFromLast(4);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra输出
35以下是相同方法的递归 C 代码。感谢 Anuj Bansal 提供以下代码。
Java
static void printNthFromLast(Node head, int n)
{
static int i = 0;
if (head == null)
return;
printNthFromLast(head.next, n);
if (++i == n)
System.out.print(head.data);
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56.
时间复杂度: O(n),其中 n 是链表的长度。
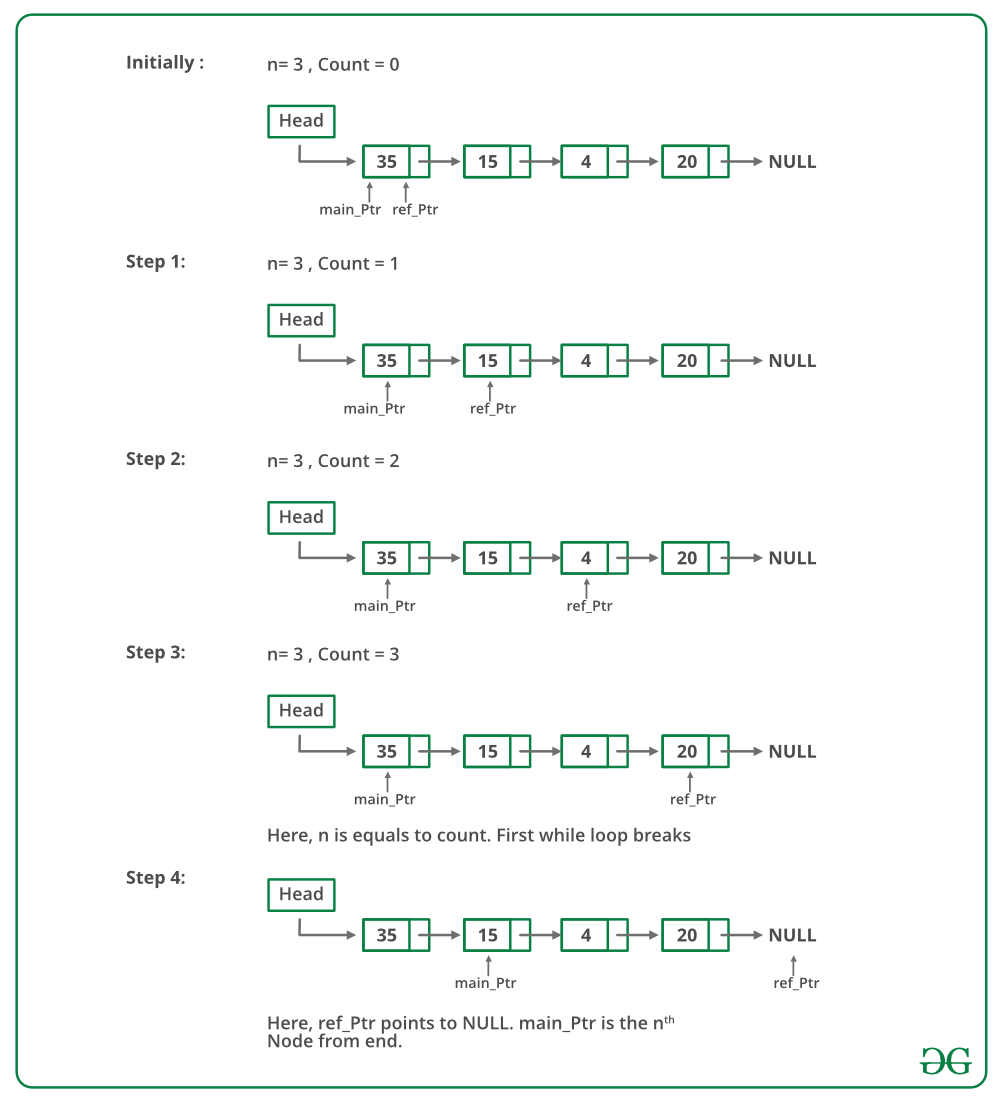
方法2(使用两个指针)
维护两个指针——引用指针和主指针。初始化指向头的引用和主指针。首先,将引用指针从 head 移动到 n 个节点。现在将两个指针一一移动,直到引用指针到达末尾。现在主指针将指向从末尾开始的第 n 个节点。返回主指针。
下图是上述方法的试运行:
下面是上述方法的实现:
Java
// Java program to find n'th
// node from end using slow and
// fast pointers
class LinkedList
{
Node head; // head of the list
/* Linked List node */
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Function to get the
nth node from end of list */
void printNthFromLast(int n)
{
Node main_ptr = head;
Node ref_ptr = head;
int count = 0;
if (head != null)
{
while (count < n)
{
if (ref_ptr == null)
{
System.out.println(n
+ " is greater than the no "
+ " of nodes in the list");
return;
}
ref_ptr = ref_ptr.next;
count++;
}
if(ref_ptr == null)
{
if(head != null)
System.out.println("Node no. " + n +
" from last is " +
head.data);
}
else
{
while (ref_ptr != null)
{
main_ptr = main_ptr.next;
ref_ptr = ref_ptr.next;
}
System.out.println("Node no. " + n +
" from last is " +
main_ptr.data);
}
}
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/*Driver program to test above methods */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(20);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(15);
llist.push(35);
llist.printNthFromLast(4);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra
输出
Node no. 4 from last is 35 时间复杂度: O(n),其中 n 是链表的长度。
有关详细信息,请参阅有关链接列表末尾第 n 个节点的程序的完整文章!