检查给定的图是否是树
编写一个函数,如果给定的无向图是树,则返回 true,否则返回 false。例如,下图是一棵树。
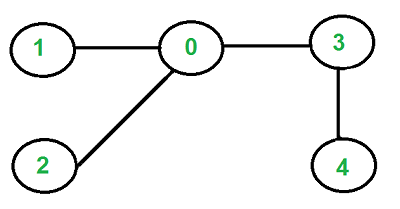
但下图不是一棵树。
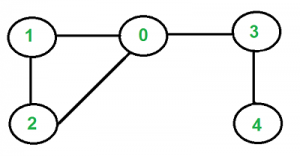
如果无向图具有以下属性,则它是树。
1)没有循环。
2)图是连通的。
对于无向图,我们可以使用 BFS 或 DFS 来检测上述两个属性。
如何检测无向图中的循环?
我们可以使用 BFS 或 DFS。对于每个访问过的顶点'v',如果有一个相邻的'u'使得u已经被访问过并且u不是v的父级,那么图中就有一个循环。如果我们没有为任何顶点找到这样的相邻点,我们就说没有循环(有关详细信息,请参阅在无向图中检测循环)。
如何检查连接性?
由于图是无向的,我们可以从任何顶点开始 BFS 或 DFS 并检查是否所有顶点都可以到达。如果所有顶点都可达,则图是连通的,否则不连通。
C++
// A C++ Program to check whether a graph is tree or not
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Class for an undirected graph
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list *adj; // Pointer to an array for adjacency lists
bool isCyclicUtil(int v, bool visited[], int parent);
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
void addEdge(int v, int w); // to add an edge to graph
bool isTree(); // returns true if graph is tree
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v’s list.
adj[w].push_back(v); // Add v to w’s list.
}
// A recursive function that uses visited[] and parent to
// detect cycle in subgraph reachable from vertex v.
bool Graph::isCyclicUtil(int v, bool visited[], int parent)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
{
// If an adjacent is not visited, then recur for
// that adjacent
if (!visited[*i])
{
if (isCyclicUtil(*i, visited, v))
return true;
}
// If an adjacent is visited and not parent of current
// vertex, then there is a cycle.
else if (*i != parent)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Returns true if the graph is a tree, else false.
bool Graph::isTree()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited and not part of
// recursion stack
bool *visited = new bool[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// The call to isCyclicUtil serves multiple purposes.
// It returns true if graph reachable from vertex 0
// is cyclic. It also marks all vertices reachable
// from 0.
if (isCyclicUtil(0, visited, -1))
return false;
// If we find a vertex which is not reachable from 0
// (not marked by isCyclicUtil(), then we return false
for (int u = 0; u < V; u++)
if (!visited[u])
return false;
return true;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
Graph g1(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
g1.isTree()? cout << "Graph is Tree\n":
cout << "Graph is not Tree\n";
Graph g2(5);
g2.addEdge(1, 0);
g2.addEdge(0, 2);
g2.addEdge(2, 1);
g2.addEdge(0, 3);
g2.addEdge(3, 4);
g2.isTree()? cout << "Graph is Tree\n":
cout << "Graph is not Tree\n";
return 0;
}
Java
// A Java Program to check whether a graph is tree or not
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// This class represents a directed graph using adjacency
// list representation
class Graph
{
private int V; // No. of vertices
private LinkedList adj[]; //Adjacency List
// Constructor
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[V];
for (int i=0; i();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v,int w)
{
adj[v].add(w);
adj[w].add(v);
}
// A recursive function that uses visited[] and parent
// to detect cycle in subgraph reachable from vertex v.
boolean isCyclicUtil(int v, boolean visited[], int parent)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
Integer i;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
Iterator it = adj[v].iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
{
i = it.next();
// If an adjacent is not visited, then recur for
// that adjacent
if (!visited[i])
{
if (isCyclicUtil(i, visited, v))
return true;
}
// If an adjacent is visited and not parent of
// current vertex, then there is a cycle.
else if (i != parent)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Returns true if the graph is a tree, else false.
boolean isTree()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited and not part
// of recursion stack
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// The call to isCyclicUtil serves multiple purposes
// It returns true if graph reachable from vertex 0
// is cyclic. It also marks all vertices reachable
// from 0.
if (isCyclicUtil(0, visited, -1))
return false;
// If we find a vertex which is not reachable from 0
// (not marked by isCyclicUtil(), then we return false
for (int u = 0; u < V; u++)
if (!visited[u])
return false;
return true;
}
// Driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g1 = new Graph(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
if (g1.isTree())
System.out.println("Graph is Tree");
else
System.out.println("Graph is not Tree");
Graph g2 = new Graph(5);
g2.addEdge(1, 0);
g2.addEdge(0, 2);
g2.addEdge(2, 1);
g2.addEdge(0, 3);
g2.addEdge(3, 4);
if (g2.isTree())
System.out.println("Graph is Tree");
else
System.out.println("Graph is not Tree");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija Python3
# Python Program to check whether
# a graph is tree or not
from collections import defaultdict
class Graph():
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
def addEdge(self, v, w):
# Add w to v ist.
self.graph[v].append(w)
# Add v to w list.
self.graph[w].append(v)
# A recursive function that uses visited[]
# and parent to detect cycle in subgraph
# reachable from vertex v.
def isCyclicUtil(self, v, visited, parent):
# Mark current node as visited
visited[v] = True
# Recur for all the vertices adjacent
# for this vertex
for i in self.graph[v]:
# If an adjacent is not visited,
# then recur for that adjacent
if visited[i] == False:
if self.isCyclicUtil(i, visited, v) == True:
return True
# If an adjacent is visited and not
# parent of current vertex, then there
# is a cycle.
elif i != parent:
return True
return False
# Returns true if the graph is a tree,
# else false.
def isTree(self):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
# and not part of recursion stack
visited = [False] * self.V
# The call to isCyclicUtil serves multiple
# purposes. It returns true if graph reachable
# from vertex 0 is cyclic. It also marks
# all vertices reachable from 0.
if self.isCyclicUtil(0, visited, -1) == True:
return False
# If we find a vertex which is not reachable
# from 0 (not marked by isCyclicUtil(),
# then we return false
for i in range(self.V):
if visited[i] == False:
return False
return True
# Driver program to test above functions
g1 = Graph(5)
g1.addEdge(1, 0)
g1.addEdge(0, 2)
g1.addEdge(0, 3)
g1.addEdge(3, 4)
print ("Graph is a Tree" if g1.isTree() == True \
else "Graph is a not a Tree")
g2 = Graph(5)
g2.addEdge(1, 0)
g2.addEdge(0, 2)
g2.addEdge(2, 1)
g2.addEdge(0, 3)
g2.addEdge(3, 4)
print ("Graph is a Tree" if g2.isTree() == True \
else "Graph is a not a Tree")
# This code is contributed by Divyanshu MehtaC#
// A C# Program to check whether
// a graph is tree or not
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// This class represents a directed graph
// using adjacency list representation
class Graph
{
private int V; // No. of vertices
private List []adj; // Adjacency List
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new List[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new List();
}
// Function to add an edge
// into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].Add(w);
adj[w].Add(v);
}
// A recursive function that uses visited[]
// and parent to detect cycle in subgraph
// reachable from vertex v.
Boolean isCyclicUtil(int v, Boolean []visited,
int parent)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
int i;
// Recur for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
foreach(int it in adj[v])
{
i = it;
// If an adjacent is not visited,
// then recur for that adjacent
if (!visited[i])
{
if (isCyclicUtil(i, visited, v))
return true;
}
// If an adjacent is visited and
// not parent of current vertex,
// then there is a cycle.
else if (i != parent)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Returns true if the graph
// is a tree, else false.
Boolean isTree()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
// and not part of recursion stack
Boolean []visited = new Boolean[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// The call to isCyclicUtil serves
// multiple purposes. It returns true if
// graph reachable from vertex 0 is cyclic.
// It also marks all vertices reachable from 0.
if (isCyclicUtil(0, visited, -1))
return false;
// If we find a vertex which is not reachable
// from 0 (not marked by isCyclicUtil(),
// then we return false
for (int u = 0; u < V; u++)
if (!visited[u])
return false;
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// Create a graph given
// in the above diagram
Graph g1 = new Graph(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
if (g1.isTree())
Console.WriteLine("Graph is Tree");
else
Console.WriteLine("Graph is not Tree");
Graph g2 = new Graph(5);
g2.addEdge(1, 0);
g2.addEdge(0, 2);
g2.addEdge(2, 1);
g2.addEdge(0, 3);
g2.addEdge(3, 4);
if (g2.isTree())
Console.WriteLine("Graph is Tree");
else
Console.WriteLine("Graph is not Tree");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Javascript
输出:
Graph is Tree
Graph is not Tree