电磁感应
电磁感应,通常称为感应,是一个过程,其中将导体放置在某个位置并且磁场随着导体移动而变化或保持静止。因此,在电导体上产生电压或 EMF(电动势)。 1830 年,迈克尔·法拉第发现了感应定律。让我们仔细看看电磁感应。
电磁感应
假设您在购物时不使用现金,而您的父母使用信用卡。店主总是扫描或刷卡。店主不拍照也不摸卡。但是,他滑动/扫描它。这种刷卡是如何取出钱的?这是由于一种称为“电磁感应”的现象。
移动物体可以产生电流吗?如何判断电和磁之间是否存在联系?想想如果没有电脑、电话或电,生活会是什么样子。法拉第的实验导致了发电机和变压器的发展。
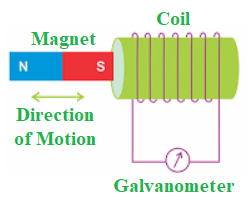
The induction of an electromotive force by the passage of a conductor through a magnetic field or by a change in magnetic flux in a magnetic field is known as electromagnetic induction.
当导体放置在移动磁场中或当它在固定磁场中移动时,就会发生这种情况。
迈克尔法拉第发现了这个电磁感应规则。他架起了一根类似于上图的导线,并将其连接到一个测量电路两端电压的设备上。当条形磁铁穿过设备时测量电路中的电压。这样做的意义在于,它是一种通过使用磁场而不是电池在电路中产生电能的方法。发电机、变压器和电动机等设备使用电磁感应原理。
法拉第电磁感应定律
法拉第给出了两条电磁感应定律:
第一定律:当导体置于变化的磁场中时,会产生感应电动势,如果导体闭合,则会有感应电流流过。
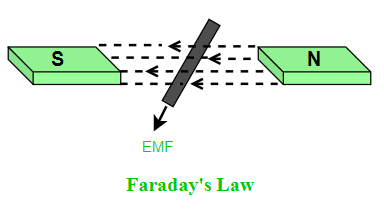
第二定律:感应电动势的大小等于磁通量变化率。
法拉第通过他的实验发现各种元素会影响电压的产生。它们如下:
- 线圈数:感应电压与导线的匝数/线圈数成正比。匝数越多,产生的电压就越多。
- 变化的磁场:感应电压受磁场变化的影响。这可以通过围绕导体旋转磁场或通过在磁场内旋转导体来实现。
Therefore, Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, states that the amount of voltage generated in a coil is proportionate to the changing magnetic field and the number of turns of the coil.
因此,感应电压现在为:
E = N (dϕ ⁄ dt)
where,
- N = number of turns in the coil
- dϕ = change in magnetic flux
- dt = time interval
- E = induced voltage
楞次电磁感应定律
楞次定律指出,当根据法拉第定律感应电动势时,感应电动势的极性(方向)与其产生的原因相反。
According to Lenz’s law,
E = – N (dϕ ⁄ dt)
The negative sign indicates that the induced emf opposes the cause of its production.
电磁感应的应用
- 交流发电机中的电磁感应
- 电力变压器
- 电磁流量计
电力变压器
电力变压器是电磁感应的另一个主要用途。变压器是一种使用磁场将交流电从一个电压电平转换为另一个电压电平的设备。降压变压器的初级电压高于次级电压。升压变压器是一种次级电压具有额外匝数的变压器。为了将电压提高到 100 kV,电力供应商采用了步进变压器,它可以降低电流并减少输电线路中的功率损耗。另一方面,家用电路采用降压变压器将电压降至 120 或 240 V。
交流发电机中的电磁感应
交流电的产生是电磁感应最重要的应用之一。
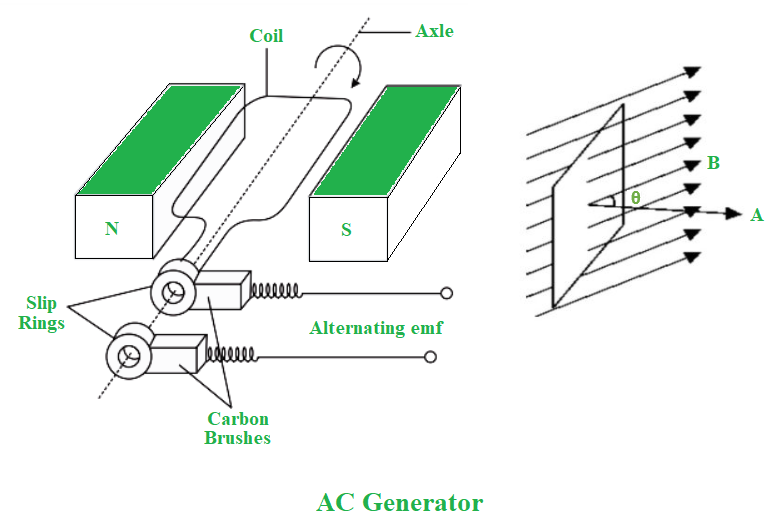
更先进的设备是具有 100 MV 输出容量的交流发电机。当线圈在磁场 B 中旋转时,环路的有效面积等于 A cos θ ,其中θ是 A 和 B 之间的角度。基本交流发电机的工作原理就是这种产生通量变化的方式。旋转线圈的轴线垂直于磁场方向。线圈上的磁通量随着线圈的旋转而变化,从而在线圈中产生感应电动势。
示例问题
问题 1:当磁棒靠近 50 匝的圆形线圈放置时,磁场密度以 0.10 T ⁄ s 的速率变化。求线圈中感应的电动势。
解决方案:
Given:
Number of turns, N = 50 turns
Rate of change of magnetic flux, dϕ ⁄ dt = 0.10 T ⁄ s
E = – N (dϕ ⁄ dt)
= – 50 × 0.10 V
= – 5 V
Hence, the emf induced in the coil is 5 V.
问题2:什么是电磁感应?
解决方案:
Electromagnetic Induction is the induction of an electromotive force by the motion of a conductor through a magnetic field or by a change in magnetic flux in a magnetic field.
问题3:什么是法拉第电磁感应定律?
解决方案:
Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, states that the amount of voltage generated in a coil is proportionate to the number of turns and the changing magnetic field of the coil.
问题4:楞次定律是什么?
解决方案:
According to Lenz’s law, the induced emf opposes the cause of its production,i.e., E = – N (dϕ ⁄ dt). The negative sign indicates that the induced emf opposes the cause of its production.
问题5:提及电磁感应的应用。
解决方案:
Applications of electromagnetic induction:
- Electromagnetic induction in AC generator
- Electrical Transformers
- Magnetic Flow Meter