Java中的自定义序列化和反序列化
序列化是一种将对象的状态转换为字节流的机制。反序列化是使用字节流在内存中重新创建实际Java对象的逆过程。该机制用于持久化对象。
为什么需要自定义序列化?
在序列化过程中,如果我们使用 'transient' 关键字,可能会丢失数据。 'Transient' 关键字用于我们不想序列化的变量。但有时,需要以与默认序列化不同的方式对其进行序列化(例如在序列化之前加密等),在这种情况下,我们必须使用自定义序列化和反序列化。
下面的程序说明了上述数据丢失的情况:
// Java program to illustrate loss of information
// because of transient keyword.
import java.io.*;
class GfgAccount implements Serializable {
String username = "gfg_admin";
transient String pwd = "geeks";
}
class CustomizedSerializationDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
GfgAccount gfg_g1 = new GfgAccount();
System.out.println("Username : " + gfg_g1.username +
" Password : " + gfg_g1.pwd);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("abc.ser");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
// writeObject() method present in GfgAccount class
// will be automatically called by jvm
oos.writeObject(gfg_g1);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("abc.ser");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
// readObject() method present GfgAccount class
// will be automatically called by jvm
GfgAccount gfg_g2 = (GfgAccount)ois.readObject();
System.out.println("Username : " + gfg_g2.username +
" Password : " + gfg_g2.pwd);
}
}
输出:
Username : gfg_admin Password : geeks
Username : gfg_admin Password : null
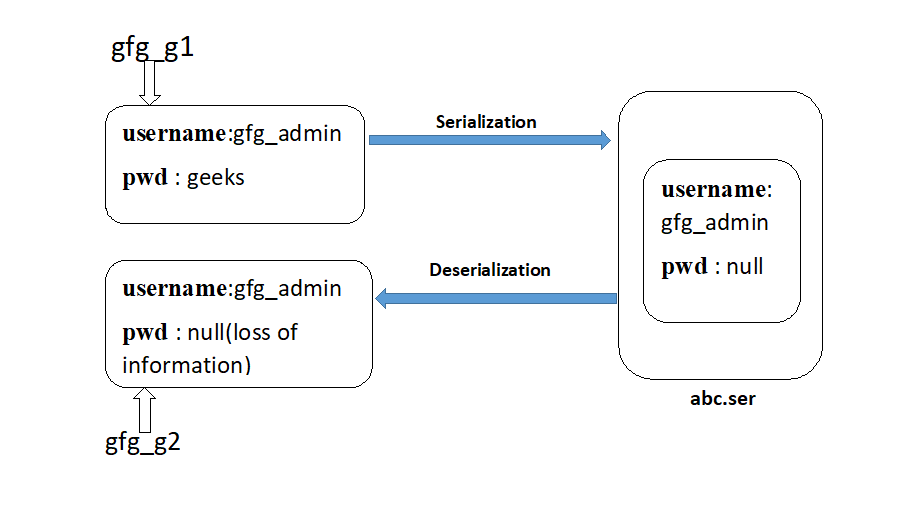
在上图示例中,在序列化之前,Account 对象可以提供正确的用户名和密码,但 Account 对象的反序列化只提供用户名而不提供密码。这是由于将密码变量声明为瞬态。
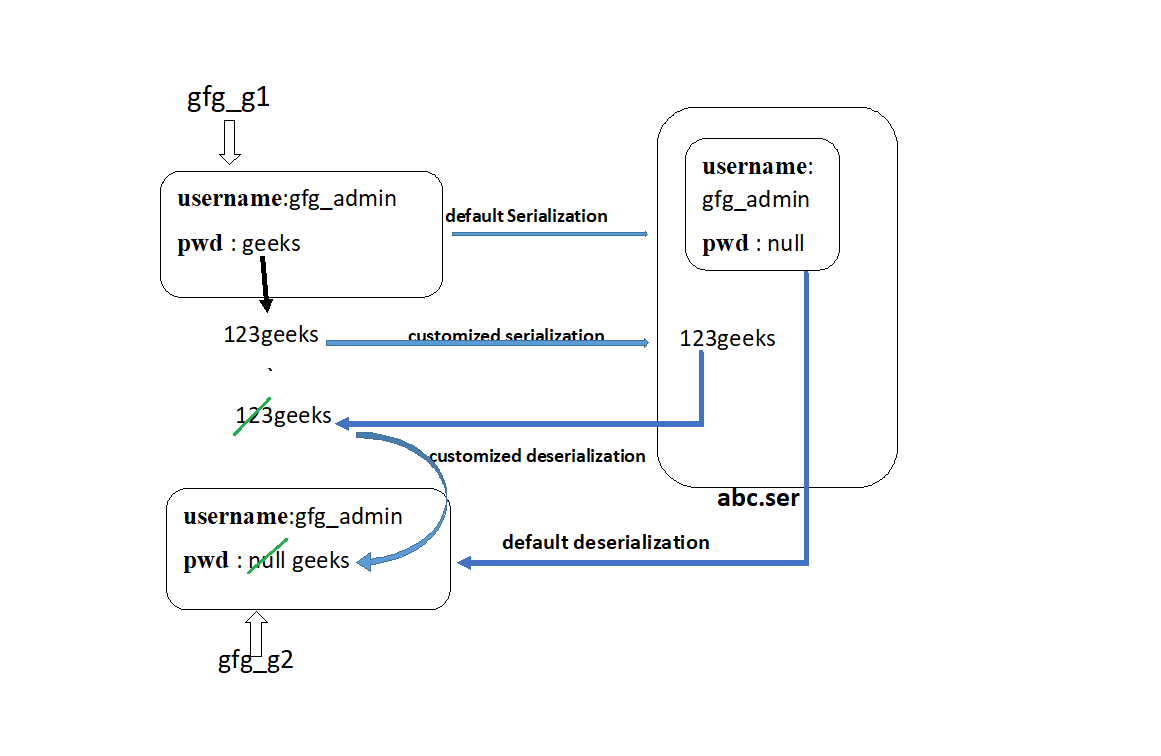
因此,在默认序列化期间,可能会因为瞬态关键字而丢失信息。为了弥补这一损失,我们将不得不使用定制序列化。
可以使用以下两种方法来实现自定义序列化:
- private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream oos) 抛出异常 :这个方法会在序列化的时候被jvm自动执行(也叫回调方法)。因此,要在序列化期间执行任何活动,它必须仅在此方法中定义。
- private void readObject(ObjectInputStream ois) throws Exception: 这个方法在反序列化的时候会被jvm自动执行(也叫回调方法)。因此,要在反序列化期间执行任何活动,它必须仅在此方法中定义。
注意:在执行对象序列化时,我们必须在该类中定义上述两个方法。
// Java program to illustrate customized serialization
import java.io.*;
class GfgAccount implements Serializable {
String username = "gfg_admin";
transient String pwd = "geeks";
// Performing customized serialization using the below two methods:
// this method is executed by jvm when writeObject() on
// Account object reference in main method is
// executed by jvm.
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream oos) throws Exception
{
// to perform default serialization of Account object.
oos.defaultWriteObject();
// epwd (encrypted password)
String epwd = "123" + pwd;
// writing encrypted password to the file
oos.writeObject(epwd);
}
// this method is executed by jvm when readObject() on
// Account object reference in main method is executed by jvm.
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream ois) throws Exception
{
// performing default deserialization of Account object
ois.defaultReadObject();
// deserializing the encrypted password from the file
String epwd = (String)ois.readObject();
// decrypting it and saving it to the original password
// string starting from 3rd index till the last index
pwd = epwd.substring(3);
}
}
class CustomizedSerializationDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
GfgAccount gfg_g1 = new GfgAccount();
System.out.println("Username :" + gfg_g1.username +
" Password :" + gfg_g1.pwd);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("abc.ser");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
// writeObject() method on Account class will
// be automatically called by jvm
oos.writeObject(gfg_g1);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("abc.ser");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
GfgAccount gfg_g2 = (GfgAccount)ois.readObject();
System.out.println("Username :" + gfg_g2.username +
" Password :" + gfg_g2.pwd);
}
}
输出:
Username :gfg_admin Password :geeks
Username :gfg_admin Password :geeks