Java中的ConcurrentNavigableMap接口
ConcurrentNavigableMap接口是Java集合框架的成员。它从 NavigableMap 接口和 ConcurrentMap 接口扩展而来。 ConcurrentNavigableMap 提供对地图元素的线程安全访问以及方便的导航方法。它属于Java.util.concurrent包。
宣言:
public interface ConcurrentNavigableMap extends ConcurrentMap, NavigableMap 这里, K是键对象类型, V是值对象类型。
ConcurrentNavigableMap 的层次结构
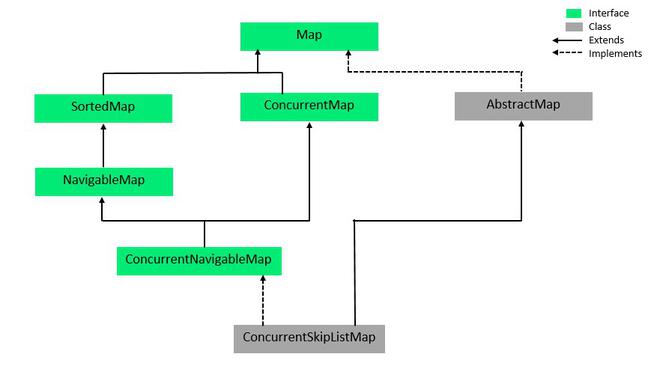
它实现了 ConcurrentMap
例子:
Java
// Java Program to demonstrate the
// ConcurrentNavigableMap Interface
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentNavigableMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListMap;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since ConcurrentNavigableMap
// is an interface so We use
// ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentNavigableMap cnmap
= new ConcurrentSkipListMap();
// Add elements using put() method
cnmap.put(1, "First");
cnmap.put(2, "Second");
cnmap.put(3, "Third");
cnmap.put(4, "Fourth");
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println(
"Mappings of ConcurrentNavigableMap : "
+ cnmap);
System.out.println("HeadMap(3): "
+ cnmap.headMap(3));
System.out.println("TailMap(3): "
+ cnmap.tailMap(3));
System.out.println("SubMap(1, 3): "
+ cnmap.subMap(1, 3));
}
} Java
// Java Program to demonstrate the ConcurrentSkipListMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ConcurrentSkipListMapExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object of
// ConcurrentSkipListMap named cslmap
ConcurrentSkipListMap cslmap
= new ConcurrentSkipListMap();
// Add elements using put()
cslmap.put(1, "Geeks");
cslmap.put(2, "For");
cslmap.put(3, "Geeks");
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println(
"The ConcurrentSkipListMap contains: "
+ cslmap);
// Print the key set using keySet()
System.out.println(
"\nThe ConcurrentSkipListMap key set: "
+ cslmap.keySet());
// Remove elements using remove()
cslmap.remove(3);
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println(
"\nThe ConcurrentSkipListMap contains: "
+ cslmap);
}
} Java
// Java Program for adding elements to a
// ConcurrentNavigableMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class AddingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since ConcurrentNavigableMap is an interface
// We use ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentNavigableMap cnmap
= new ConcurrentSkipListMap();
// Add elements using put()
cnmap.put(8, "Third");
cnmap.put(6, "Second");
cnmap.put(3, "First");
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println(
"Mappings of ConcurrentNavigableMap : "
+ cnmap);
}
} Java
// Java Program for deleting
// elements from ConcurrentNavigableMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class RemovingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since ConcurrentNavigableMap
// is an interface
// We use ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentNavigableMap cnmap
= new ConcurrentSkipListMap();
// Add elements using put()
cnmap.put(8, "Third");
cnmap.put(6, "Second");
cnmap.put(3, "First");
cnmap.put(11, "Fourth");
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println(
"Mappings of ConcurrentNavigableMap : "
+ cnmap);
// Remove elements using remove()
cnmap.remove(6);
cnmap.remove(8);
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println(
"\nConcurrentNavigableMap, after remove operation : "
+ cnmap);
// Clear the entire map using clear()
cnmap.clear();
System.out.println(
"\nConcurrentNavigableMap, after clear operation : "
+ cnmap);
}
} Java
// Java Program for accessing
// elements in a ConcurrentNavigableMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class AccessingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since ConcurrentNavigableMap is an interface
// We use ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentNavigableMap cnmap
= new ConcurrentSkipListMap();
// Add elements using put()
cnmap.put(8, "Third");
cnmap.put(6, "Second");
cnmap.put(3, "First");
cnmap.put(11, "Fourth");
// Accessing the elements using get()
// with key as a parameter
System.out.println(cnmap.get(3));
System.out.println(cnmap.get(6));
System.out.println(cnmap.get(8));
System.out.println(cnmap.get(11));
// Display the set of keys using keySet()
System.out.println(
"\nThe ConcurrentNavigableMap key set: "
+ cnmap.keySet());
}
} Java
// Java Program for traversing a ConcurrentNavigableMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.*;
public class TraversalExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since ConcurrentNavigableMap is an interface
// We use ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentNavigableMap cnmap
= new ConcurrentSkipListMap();
// Add elements using put()
cnmap.put(8, "Third");
cnmap.put(6, "Second");
cnmap.put(3, "First");
cnmap.put(11, "Fourth");
// Create an Iterator over the
// ConcurrentNavigableMap
Iterator > itr
= cnmap.entrySet().iterator();
// The hasNext() method is used to check if there is
// a next element The next() method is used to
// retrieve the next element
while (itr.hasNext()) {
ConcurrentNavigableMap
.Entry entry
= itr.next();
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey()
+ ", Value = "
+ entry.getValue());
}
}
}
输出:
Mappings of ConcurrentNavigableMap : {1=First, 2=Second, 3=Third, 4=Fourth}
HeadMap(3): {1=First, 2=Second}
TailMap(3): {3=Third, 4=Fourth}
SubMap(1, 3): {1=First, 2=Second}实现类
ConcurrentNavigableMap 有一个实现类,即ConcurrentSkipListMap 类。 ConcurrentSkipListMap 是 ConcurrentNavigableMap 接口的可扩展实现。 ConcurrentSkipListMap 中的键按自然顺序或在构造对象时使用 Comparator 排序。 ConcurrentSkipListMap 的插入、删除和搜索操作的预期时间成本为log(n) 。它是一个线程安全的类,因此,所有的基本操作都可以同时完成。句法:
ConcurrentSkipListMap< ? , ? > objectName = new ConcurrentSkipListMap< ? , ? >();示例:在下面给出的代码中,我们简单地实例化一个名为 cslmap 的 ConcurrentSkipListMap 类的对象。 put() 方法用于添加元素, remove() 用于删除元素。对于 remove() 方法,语法是objectname.remove(Object key) 。 keySet() 显示映射中的所有键(上面给出的方法表中的描述)。
Java
// Java Program to demonstrate the ConcurrentSkipListMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ConcurrentSkipListMapExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object of
// ConcurrentSkipListMap named cslmap
ConcurrentSkipListMap cslmap
= new ConcurrentSkipListMap();
// Add elements using put()
cslmap.put(1, "Geeks");
cslmap.put(2, "For");
cslmap.put(3, "Geeks");
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println(
"The ConcurrentSkipListMap contains: "
+ cslmap);
// Print the key set using keySet()
System.out.println(
"\nThe ConcurrentSkipListMap key set: "
+ cslmap.keySet());
// Remove elements using remove()
cslmap.remove(3);
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println(
"\nThe ConcurrentSkipListMap contains: "
+ cslmap);
}
}
输出:
The ConcurrentSkipListMap contains: {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
The ConcurrentSkipListMap key set: [1, 2, 3]
The ConcurrentSkipListMap contains: {1=Geeks, 2=For}ConcurrentNavigableMap 的基本操作
1.添加元素
要将元素添加到 ConcurrentNavigableMap 我们可以使用 Map 接口的任何方法。下面的代码展示了如何使用它们。在代码中可以观察到,在构造时没有提供 Comparator 时,遵循自然顺序。
Java
// Java Program for adding elements to a
// ConcurrentNavigableMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class AddingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since ConcurrentNavigableMap is an interface
// We use ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentNavigableMap cnmap
= new ConcurrentSkipListMap();
// Add elements using put()
cnmap.put(8, "Third");
cnmap.put(6, "Second");
cnmap.put(3, "First");
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println(
"Mappings of ConcurrentNavigableMap : "
+ cnmap);
}
}
输出:
Mappings of ConcurrentNavigableMap : {3=First, 6=Second, 8=Third}2. 移除元素
为了删除元素,我们也使用 Map 接口的方法,因为 ConcurrentNavigableMap 是 Map 的后代。
Java
// Java Program for deleting
// elements from ConcurrentNavigableMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class RemovingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since ConcurrentNavigableMap
// is an interface
// We use ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentNavigableMap cnmap
= new ConcurrentSkipListMap();
// Add elements using put()
cnmap.put(8, "Third");
cnmap.put(6, "Second");
cnmap.put(3, "First");
cnmap.put(11, "Fourth");
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println(
"Mappings of ConcurrentNavigableMap : "
+ cnmap);
// Remove elements using remove()
cnmap.remove(6);
cnmap.remove(8);
// Print the contents on the console
System.out.println(
"\nConcurrentNavigableMap, after remove operation : "
+ cnmap);
// Clear the entire map using clear()
cnmap.clear();
System.out.println(
"\nConcurrentNavigableMap, after clear operation : "
+ cnmap);
}
}
输出:
Mappings of ConcurrentNavigableMap : {3=First, 6=Second, 8=Third, 11=Fourth}
ConcurrentNavigableMap, after remove operation : {3=First, 11=Fourth}
ConcurrentNavigableMap, after clear operation : {}3. 访问元素
我们可以使用 get() 方法访问 ConcurrentNavigableMap 的元素,下面给出了这个例子。
Java
// Java Program for accessing
// elements in a ConcurrentNavigableMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class AccessingElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since ConcurrentNavigableMap is an interface
// We use ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentNavigableMap cnmap
= new ConcurrentSkipListMap();
// Add elements using put()
cnmap.put(8, "Third");
cnmap.put(6, "Second");
cnmap.put(3, "First");
cnmap.put(11, "Fourth");
// Accessing the elements using get()
// with key as a parameter
System.out.println(cnmap.get(3));
System.out.println(cnmap.get(6));
System.out.println(cnmap.get(8));
System.out.println(cnmap.get(11));
// Display the set of keys using keySet()
System.out.println(
"\nThe ConcurrentNavigableMap key set: "
+ cnmap.keySet());
}
}
输出:
First
Second
Third
Fourth
The ConcurrentNavigableMap key set: [3, 6, 8, 11]4. 遍历
我们可以使用 Iterator 接口来遍历 Collection Framework 的任何结构。由于迭代器使用一种类型的数据,我们使用 .Entry< ? , ? > 将两种不同的类型解析为兼容的格式。然后使用 next() 方法打印 ConcurrentNavigableMap 的元素。
Java
// Java Program for traversing a ConcurrentNavigableMap
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.*;
public class TraversalExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object
// Since ConcurrentNavigableMap is an interface
// We use ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentNavigableMap cnmap
= new ConcurrentSkipListMap();
// Add elements using put()
cnmap.put(8, "Third");
cnmap.put(6, "Second");
cnmap.put(3, "First");
cnmap.put(11, "Fourth");
// Create an Iterator over the
// ConcurrentNavigableMap
Iterator > itr
= cnmap.entrySet().iterator();
// The hasNext() method is used to check if there is
// a next element The next() method is used to
// retrieve the next element
while (itr.hasNext()) {
ConcurrentNavigableMap
.Entry entry
= itr.next();
System.out.println("Key = " + entry.getKey()
+ ", Value = "
+ entry.getValue());
}
}
}
输出:
Key = 3, Value = First
Key = 6, Value = Second
Key = 8, Value = Third
Key = 11, Value = Fourth注意:每次我们说“ConcurrentNavigableMap 的元素”时,必须注意元素实际上存储在 ConcurrentNavigableMap 的实现类的对象中,在这种情况下是 ConcurrentSkipListMap。
ConcurrentNavigableMap 的方法
ConcurrentNavigableMap 继承了 Map 接口、SortedMap 接口、ConcurrentMap 接口、NavigableMap 接口的方法。添加元素、移除元素和遍历的基本方法由父接口给出。 ConcurrentNavigableMap 的方法如下表所示。这里,
- K - 映射中键的类型。
- V – 映射中映射的值的类型。
Method | Description |
|---|---|
| descendingKeySet() | Returns a reverse order NavigableSet view of the keys contained in the map. |
| descendingMap() | Returns a reverse order view of the mappings in the map. |
| headMap(K toKey) | Returns the view of the portion of the map wherein the keys are less than toKey. |
| headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) | Returns the view of the portion of the map wherein the keys are less than toKey, and equal to toKey if inclusive is true. |
| keySet() | Returns a NavigableSet view of the keys contained in this map. |
| navigableKeySet() | Returns a NavigableSet view of the keys contained in this map. |
| subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive) | Returns a view of the portion of the map, keys ranging from fromKey to toKey. |
| subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) | Returns a view of the portion of the map, keys ranging from fromKey, inclusive, to toKey, exclusive. |
| tailMap(K fromKey) | Returns a view of the map wherein the keys are greater than fromKey. |
| tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive) | Returns a view of the map wherein the keys are greater than fromKey, and equal to if inclusive is true. |
在接口Java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
compute(K key, BiFunction ? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) | Attempts to compute a mapping for the specified key and its current mapped value (or null if there is no current mapping). |
computeIfAbsent(K key, Function ? extends V> mappingFunction) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped to null), attempts to compute its value using the given mapping function and enters it into this map unless null. |
computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) | If the value for the specified key is present and non-null, attempts to compute a new mapping given the key and its current mapped value. |
| forEach(BiConsumer action) | Performs the given action for each entry in this map until all entries have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or defaultValue if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
merge(K key, V value, BiFunction ,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value or is associated with null, associates it with the given non-null value. |
| putIfAbsent(K key, V value) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value, associates it with the given value. |
| remove(Object key, Object value) | Removes the entry for a key only if currently mapped to a given value. |
| replace(K key, V value) | Replaces the entry for a key only if currently mapped to some value. |
| replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) | Replaces the entry for a key only if currently mapped to a given value. |
replaceAll(BiFunction ,? extends V> function) | Replaces each entry’s value with the result of invoking the given function on that entry until all entries have been processed or the function throws an exception. |
在接口Java.util.Map 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| clear() | Removes all of the mappings from this map (optional operation). |
| containsKey(Object key) | Returns true if this map contains a mapping for the specified key. |
| containsValue(Object value) | Returns true if this map maps one or more keys to the specified value. |
| equals(Object o) | Compares the specified object with this map for equality. |
| get(Object key) | Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or null if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this map. |
| isEmpty() | Returns true if this map contains no key-value mappings. |
| put(K key, V value) | Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map (optional operation). |
| putAll(Map m) | Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this map (optional operation). |
| remove(Object key) | Removes the mapping for a key from this map if it is present (optional operation). |
| size() | Returns the number of key-value mappings in this map. |
在接口Java.util.NavigableMap 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| ceilingEntry(K key) | Returns a key-value mapping associated with the least key greater than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| ceilingKey(K key) | Returns the least key greater than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| firstEntry() | Returns a key-value mapping associated with the least key in this map, or null if the map is empty. |
| floorEntry(K key) | Returns a key-value mapping associated with the greatest key less than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| floorKey(K key) | Returns the greatest key less than or equal to the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| higherEntry(K key) | Returns a key-value mapping associated with the least key strictly greater than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| higherKey(K key) | Returns the least key strictly greater than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| lastEntry() | Returns a key-value mapping associated with the greatest key in this map, or null if the map is empty. |
| lowerEntry(K key) | Returns a key-value mapping associated with the greatest key strictly less than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| lowerKey(K key) | Returns the greatest key strictly less than the given key, or null if there is no such key. |
| pollFirstEntry() | Removes and returns a key-value mapping associated with the least key in this map, or null if the map is empty. |
| pollLastEntry() | Removes and returns a key-value mapping associated with the greatest key in this map, or null if the map is empty. |
在接口Java.util.SortedMap 中声明的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| comparator() | Returns the comparator used to order the keys in this map, or null if this map uses the natural ordering of its keys. |
| entrySet() | Returns a Set view of the mappings contained in this map. |
| firstKey() | Returns the first (lowest) key currently in this map. |
| lastKey() | Returns the last (highest) key currently in this map. |
| values() | Returns a Collection view of the values contained in this map. |