操作系统中的银行家算法
银行家算法是一种资源分配和死锁避免算法,它通过模拟所有资源的预定最大可能数量的分配来测试安全性,然后进行“s 状态”检查以测试可能的活动,然后再决定是否应该允许分配接着说。
为什么银行家算法如此命名?
银行家算法之所以如此命名是因为它在银行系统中用于检查贷款是否可以批准给一个人。假设一家银行有n个账户持有人,他们的总金额为S。如果有人申请贷款,那么银行首先从银行的总金额中减去贷款金额,如果剩余金额更大比 S 则只批准贷款。这样做是因为如果所有账户持有人都来提取他们的钱,那么银行可以很容易地做到这一点。
换句话说,银行永远不会以无法满足所有客户需求的方式分配资金。银行会尝试始终处于安全状态。
以下数据结构用于实现银行家算法:
让'n'是系统中的进程数, 'm'是资源类型的数量。
可用的 :
- 它是一个大小为“m”的一维数组,表示每种类型的可用资源的数量。
- 可用[ j ] = k 表示有'k'个资源类型R j的实例
最大限度 :
- 它是一个大小为“ n*m”的二维数组,用于定义系统中每个进程的最大需求。
- Max[ i, j ] = k 表示进程P i最多可以请求资源类型R j 的“k”个实例。
分配:
- 它是一个大小为“n*m”的二维数组,它定义了当前分配给每个进程的每种类型的资源数量。
- Allocation[ i, j ] = k 表示进程P i当前分配了'k'个资源类型为R j的实例
需要 :
- 它是一个大小为“n*m”的二维数组,表示每个进程的剩余资源需求。
- Need [ i, j ] = k 表示进程P i当前需要'k'个资源类型为R j的实例
- 需要 [ i, j ] = Max [ i, j ] – 分配 [ i, j ]
分配i指定当前分配给进程 P i的资源,需要i指定进程 P i可能仍请求完成其任务的额外资源。
银行家算法由安全算法和资源请求算法组成
安全算法
判断系统是否处于安全状态的算法可以描述如下:
1) Let Work and Finish be vectors of length ‘m’ and ‘n’ respectively.
Initialize: Work = Available
Finish[i] = false; for i=1, 2, 3, 4….n
2) Find an i such that both
a) Finish[i] = false
b) Needi <= Work
if no such i exists goto step (4)
3) Work = Work + Allocation[i]
Finish[i] = true
goto step (2)
4) if Finish [i] = true for all i
then the system is in a safe state
资源请求算法
让 Request i成为进程 P i的请求数组。请求i [j] = k 意味着进程 P i想要 k 个资源类型 R j 的实例。当进程 P i发出资源请求时,将采取以下操作:
1) If Requesti <= Needi
Goto step (2) ; otherwise, raise an error condition, since the process has exceeded its maximum claim.
2) If Requesti <= Available
Goto step (3); otherwise, Pi must wait, since the resources are not available.
3) Have the system pretend to have allocated the requested resources to process Pi by modifying the state as
follows:
Available = Available – Requesti
Allocationi = Allocationi + Requesti
Needi = Needi– Requesti
例子:
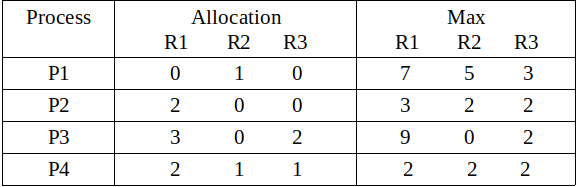
考虑具有五个进程 P 0到 P 4和类型 A、B、C 的三个资源的系统。资源类型 A 有 10 个实例,B 有 5 个实例,类型 C 有 7 个实例。假设在 t 0时刻拍摄了系统快照:

问题1。需求矩阵的内容是什么?
需要 [i, j] = Max [i, j] – 分配 [i, j]
所以,需求矩阵的内容是:
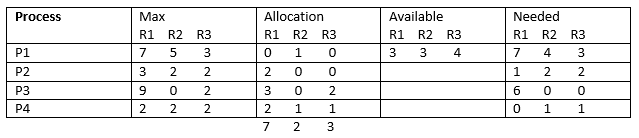
问题2。系统是否处于安全状态?如果是,那么安全顺序是什么?
在给定系统上应用安全算法,
问题3。如果进程 P 1请求一个额外的资源类型 A 的实例和两个资源类型 C 的实例会发生什么?
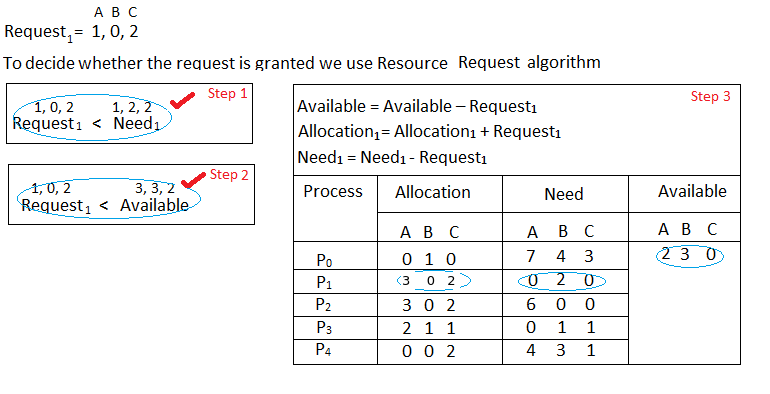
我们必须确定这个新的系统状态是否安全。为此,我们再次对上述数据结构执行安全算法。
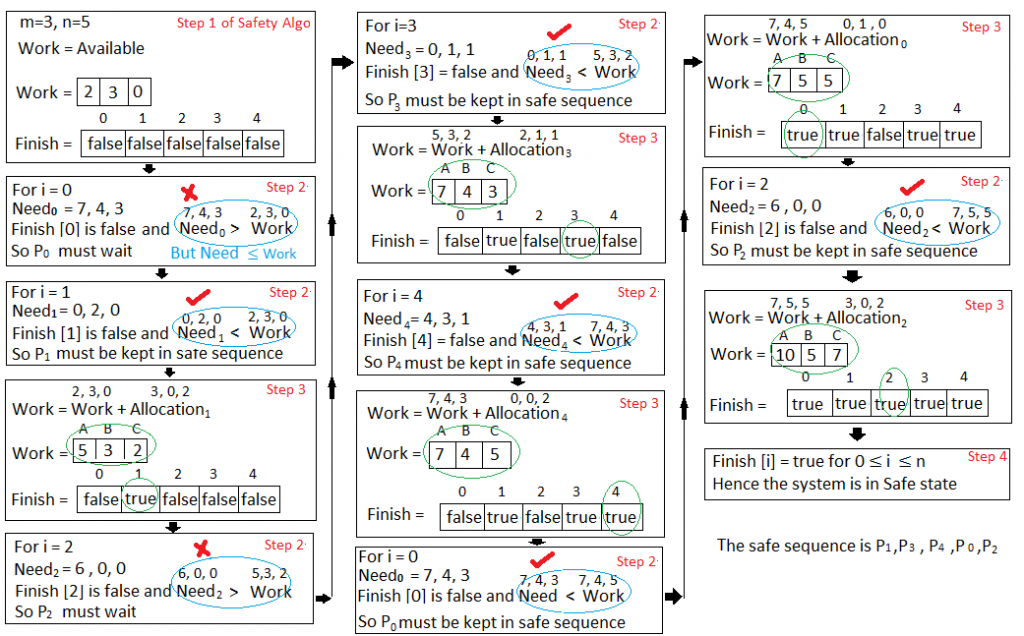
因此新的系统状态是安全的,所以我们可以立即批准进程P 1的请求。
银行家算法代码
C++
// Banker's Algorithm
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// P0, P1, P2, P3, P4 are the Process names here
int n, m, i, j, k;
n = 5; // Number of processes
m = 3; // Number of resources
int alloc[5][3] = { { 0, 1, 0 }, // P0 // Allocation Matrix
{ 2, 0, 0 }, // P1
{ 3, 0, 2 }, // P2
{ 2, 1, 1 }, // P3
{ 0, 0, 2 } }; // P4
int max[5][3] = { { 7, 5, 3 }, // P0 // MAX Matrix
{ 3, 2, 2 }, // P1
{ 9, 0, 2 }, // P2
{ 2, 2, 2 }, // P3
{ 4, 3, 3 } }; // P4
int avail[3] = { 3, 3, 2 }; // Available Resources
int f[n], ans[n], ind = 0;
for (k = 0; k < n; k++) {
f[k] = 0;
}
int need[n][m];
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
need[i][j] = max[i][j] - alloc[i][j];
}
int y = 0;
for (k = 0; k < 5; k++) {
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (f[i] == 0) {
int flag = 0;
for (j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (need[i][j] > avail[j]){
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (flag == 0) {
ans[ind++] = i;
for (y = 0; y < m; y++)
avail[y] += alloc[i][y];
f[i] = 1;
}
}
}
}
cout << "Following is the SAFE Sequence" << endl;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
cout << " P" << ans[i] << " ->";
cout << " P" << ans[n - 1] < C
// Banker's Algorithm
#include
int main()
{
// P0, P1, P2, P3, P4 are the Process names here
int n, m, i, j, k;
n = 5; // Number of processes
m = 3; // Number of resources
int alloc[5][3] = { { 0, 1, 0 }, // P0 // Allocation Matrix
{ 2, 0, 0 }, // P1
{ 3, 0, 2 }, // P2
{ 2, 1, 1 }, // P3
{ 0, 0, 2 } }; // P4
int max[5][3] = { { 7, 5, 3 }, // P0 // MAX Matrix
{ 3, 2, 2 }, // P1
{ 9, 0, 2 }, // P2
{ 2, 2, 2 }, // P3
{ 4, 3, 3 } }; // P4
int avail[3] = { 3, 3, 2 }; // Available Resources
int f[n], ans[n], ind = 0;
for (k = 0; k < n; k++) {
f[k] = 0;
}
int need[n][m];
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
need[i][j] = max[i][j] - alloc[i][j];
}
int y = 0;
for (k = 0; k < 5; k++) {
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (f[i] == 0) {
int flag = 0;
for (j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (need[i][j] > avail[j]){
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (flag == 0) {
ans[ind++] = i;
for (y = 0; y < m; y++)
avail[y] += alloc[i][y];
f[i] = 1;
}
}
}
}
printf("Following is the SAFE Sequence\n");
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
printf(" P%d ->", ans[i]);
printf(" P%d", ans[n - 1]);
return (0);
// This code is contributed by Deep Baldha (CandyZack)
} Java
//Java Program for Bankers Algorithm
public class GfGBankers
{
int n = 5; // Number of processes
int m = 3; // Number of resources
int need[][] = new int[n][m];
int [][]max;
int [][]alloc;
int []avail;
int safeSequence[] = new int[n];
void initializeValues()
{
// P0, P1, P2, P3, P4 are the Process names here
// Allocation Matrix
alloc = new int[][] { { 0, 1, 0 }, //P0
{ 2, 0, 0 }, //P1
{ 3, 0, 2 }, //P2
{ 2, 1, 1 }, //P3
{ 0, 0, 2 } }; //P4
// MAX Matrix
max = new int[][] { { 7, 5, 3 }, //P0
{ 3, 2, 2 }, //P1
{ 9, 0, 2 }, //P2
{ 2, 2, 2 }, //P3
{ 4, 3, 3 } }; //P4
// Available Resources
avail = new int[] { 3, 3, 2 };
}
void isSafe()
{
int count=0;
//visited array to find the already allocated process
boolean visited[] = new boolean[n];
for (int i = 0;i < n; i++)
{
visited[i] = false;
}
//work array to store the copy of available resources
int work[] = new int[m];
for (int i = 0;i < m; i++)
{
work[i] = avail[i];
}
while (count work[j])
break;
}
if (j == m)
{
safeSequence[count++]=i;
visited[i]=true;
flag=true;
for (j = 0;j < m; j++)
{
work[j] = work[j]+alloc[i][j];
}
}
}
}
if (flag == false)
{
break;
}
}
if (count < n)
{
System.out.println("The System is UnSafe!");
}
else
{
//System.out.println("The given System is Safe");
System.out.println("Following is the SAFE Sequence");
for (int i = 0;i < n; i++)
{
System.out.print("P" + safeSequence[i]);
if (i != n-1)
System.out.print(" -> ");
}
}
}
void calculateNeed()
{
for (int i = 0;i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0;j < m; j++)
{
need[i][j] = max[i][j]-alloc[i][j];
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int i, j, k;
GfGBankers gfg = new GfGBankers();
gfg.initializeValues();
//Calculate the Need Matrix
gfg.calculateNeed();
// Check whether system is in safe state or not
gfg.isSafe();
}
} Python3
# Banker's Algorithm
# Driver code:
if __name__=="__main__":
# P0, P1, P2, P3, P4 are the Process names here
n = 5 # Number of processes
m = 3 # Number of resources
# Allocation Matrix
alloc = [[0, 1, 0 ],[ 2, 0, 0 ],
[3, 0, 2 ],[2, 1, 1] ,[ 0, 0, 2]]
# MAX Matrix
max = [[7, 5, 3 ],[3, 2, 2 ],
[ 9, 0, 2 ],[2, 2, 2],[4, 3, 3]]
avail = [3, 3, 2] # Available Resources
f = [0]*n
ans = [0]*n
ind = 0
for k in range(n):
f[k] = 0
need = [[ 0 for i in range(m)]for i in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
need[i][j] = max[i][j] - alloc[i][j]
y = 0
for k in range(5):
for i in range(n):
if (f[i] == 0):
flag = 0
for j in range(m):
if (need[i][j] > avail[j]):
flag = 1
break
if (flag == 0):
ans[ind] = i
ind += 1
for y in range(m):
avail[y] += alloc[i][y]
f[i] = 1
print("Following is the SAFE Sequence")
for i in range(n - 1):
print(" P", ans[i], " ->", sep="", end="")
print(" P", ans[n - 1], sep="")
# This code is contributed by SHUBHAMSINGH10C#
// C# Program for Bankers Algorithm
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int n = 5; // Number of processes
static int m = 3; // Number of resources
int [,]need = new int[n, m];
int [,]max;
int [,]alloc;
int []avail;
int []safeSequence = new int[n];
void initializeValues()
{
// P0, P1, P2, P3, P4 are the Process
// names here Allocation Matrix
alloc = new int[,] {{ 0, 1, 0 }, //P0
{ 2, 0, 0 }, //P1
{ 3, 0, 2 }, //P2
{ 2, 1, 1 }, //P3
{ 0, 0, 2 }};//P4
// MAX Matrix
max = new int[,] {{ 7, 5, 3 }, //P0
{ 3, 2, 2 }, //P1
{ 9, 0, 2 }, //P2
{ 2, 2, 2 }, //P3
{ 4, 3, 3 }};//P4
// Available Resources
avail = new int[] { 3, 3, 2 };
}
void isSafe()
{
int count = 0;
// visited array to find the
// already allocated process
Boolean []visited = new Boolean[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
visited[i] = false;
}
// work array to store the copy of
// available resources
int []work = new int[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
work[i] = avail[i];
}
while (count work[j])
break;
}
if (j == m)
{
safeSequence[count++] = i;
visited[i] = true;
flag = true;
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
work[j] = work[j] + alloc[i, j];
}
}
}
}
if (flag == false)
{
break;
}
}
if (count < n)
{
Console.WriteLine("The System is UnSafe!");
}
else
{
//System.out.println("The given System is Safe");
Console.WriteLine("Following is the SAFE Sequence");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
Console.Write("P" + safeSequence[i]);
if (i != n - 1)
Console.Write(" -> ");
}
}
}
void calculateNeed()
{
for (int i = 0;i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0;j < m; j++)
{
need[i, j] = max[i, j] - alloc[i, j];
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
GFG gfg = new GFG();
gfg.initializeValues();
// Calculate the Need Matrix
gfg.calculateNeed();
// Check whether system is in
// safe state or not
gfg.isSafe();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Javascript