Java中的对象模型
对象模型是一个系统或接口,基本上用于在软件应用程序中根据对象可视化元素。它使用面向对象技术建模,在完成任何编程或开发之前,对象模型用于创建系统模型或体系结构。它定义了系统的面向对象特性,如继承、封装和许多其他面向对象的接口。让我们深入学习一些面向对象的术语:
对象和类
这些构成了Java或任何其他面向对象编程语言中的面向对象范式的基础。它们在这里详细解释:
目的
在面向对象的环境中,对象是物理或概念上的现实世界元素。
特征:
- 独特且有别于系统中的其他对象。
- 指示属于特定对象的某些属性和值的状态。
- 表示其与其他对象或其外部可见活动的交互的行为。
物理对象的示例是狗或人,而概念对象的示例是过程或产品。
班级
一个类是一个对象的蓝图或原型,代表了一组由相同对象创建的对象。对象基本上是这些类的实例。一个类包括 -
- 同一类的对象可以在属性值方面彼此不同。这些属性称为类数据。
- 识别和显示这些对象行为的操作称为函数和方法。
例子:
假设有一个名为 Student 的类。这个类的属性可以是——
- 学生成绩
- 学生就读的部门
- 一学年的学习
- 个人身份,即姓名、卷号、出生日期等。
可以使用以下功能指示要执行的一些操作 -
- averageMarks() – 计算学生的平均分数。
- totalMarks() – 计算学生的总分。
- libraryFine() - 计算学生迟到图书馆需要支付的罚款。
这在下面的代码中得到了证明:
Java
// package whatever
import java.io.*;
public class Student {
public static void main (String[] args) {
// passing parameters to functions
int tot = total_marks(93,99);
double avg = avg_marks(tot, 2);
// printing the output
System.out.println("The total marks is = "+tot+". Th average is = "+avg+".");
}
// function to calculate total
public static int total_marks(int math, int science) {
int total = math + science;
return total;
}
// function to calculate average marks
public static double avg_marks(int total, int num_subs) {
double avg = total/num_subs;
return avg;
}
}Java
// package whatever
import java.io.*;
public class Student {
private int rollNo;
private String name;
private String dep;
// default constructor
public Student() {}
public Student(int rollNo, String name, String dep)
{
this.rollNo = rollNo;
this.name = name;
this.dep = dep;
}
// Methods to get and set the student properties
public int getRollNo() { return rollNo; }
public void setRollNo(int rollNo)
{
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public String getDep() { return dep; }
public void setDep(String dep) { this.dep = dep; }
// function to calculate total
public static int totalMarks(int math, int science)
{
int total = math + science;
return total;
}
// function to calculate average marks
public static double avgMarks(int total, int num_subs)
{
double avg = total / num_subs;
return avg;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// setting student attributes
Student s1 = new Student(23, "Deepthi", "CSE");
// setRollNo(23);
// setName("Deepthi");
// setDep("CSE");
// printing student attributes
System.out.println(
"Roll number of student : " + s1.getRollNo()
+ ". The name of student : " + s1.getName()
+ ". Department of the student : " + s1.getDep() + ".");
// passing parameters to functions
int tot = totalMarks(93, 99);
double avg = avgMarks(tot, 2);
// printing the output
System.out.println("The total marks is = " + tot
+ ". The average is = " + avg
+ ".");
}
}Java
class Vehicle {
String belongsTo = "automobiles";
}
public class Car extends Vehicle {
int wheels = 4;
public static void main(String args[])
{
Car c = new Car();
System.out.println("Car belongs to- "
+ c.belongsTo);
System.out.println("Car has " + c.wheels
+ " wheels.");
}
}输出:
The total marks is = 192. Th average is = 96.0.封装和数据隐藏
为了保护我们的数据不被外部使用访问和利用,我们需要执行封装。这在下面详细解释 -
封装
在一个类中将方法和属性绑定在一起的过程称为封装。如果接口由类提供,则只有封装允许外部访问内部细节或类属性。
数据隐藏
保护对象免受外部方法直接访问的过程称为数据隐藏。
例子:
- setStudentValues() – 为学生的部门、学术和所有个人身份分配值。
- getStudentValues() – 获取存储在各自属性中的这些值。
消息传递
使应用程序具有交互性需要许多对象。消息使用以下功能在对象之间传递 -
- 在消息传递中,可以涉及来自不同进程的对象。
- 类方法需要在消息传递中调用。
- 在两个对象之间,消息传递通常是单向的。
- 在消息传递中启用两个对象之间的交互。
上面的示例在下面的代码中演示 -
Java
// package whatever
import java.io.*;
public class Student {
private int rollNo;
private String name;
private String dep;
// default constructor
public Student() {}
public Student(int rollNo, String name, String dep)
{
this.rollNo = rollNo;
this.name = name;
this.dep = dep;
}
// Methods to get and set the student properties
public int getRollNo() { return rollNo; }
public void setRollNo(int rollNo)
{
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public String getDep() { return dep; }
public void setDep(String dep) { this.dep = dep; }
// function to calculate total
public static int totalMarks(int math, int science)
{
int total = math + science;
return total;
}
// function to calculate average marks
public static double avgMarks(int total, int num_subs)
{
double avg = total / num_subs;
return avg;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// setting student attributes
Student s1 = new Student(23, "Deepthi", "CSE");
// setRollNo(23);
// setName("Deepthi");
// setDep("CSE");
// printing student attributes
System.out.println(
"Roll number of student : " + s1.getRollNo()
+ ". The name of student : " + s1.getName()
+ ". Department of the student : " + s1.getDep() + ".");
// passing parameters to functions
int tot = totalMarks(93, 99);
double avg = avgMarks(tot, 2);
// printing the output
System.out.println("The total marks is = " + tot
+ ". The average is = " + avg
+ ".");
}
}
输出:
Roll number of student : 23. The name of student : Deepthi. Department of the student : CSE.
The total marks is = 192. The average is = 96.0.遗产
通过维护其部分或全部属性从现有类生成新类的过程称为继承。可以生成其他类的原始类是分类父类或超类或基类,而生成的类称为派生类或子类。
例子:
对于 Vehicle 类,派生类可以是 Car、Bike、Bus 等。在此示例中,这些派生类传递其父类 Vehicle 的属性以及它们自己的属性,如车轮数、座位数等。上面的示例在以下代码中演示 -
Java
class Vehicle {
String belongsTo = "automobiles";
}
public class Car extends Vehicle {
int wheels = 4;
public static void main(String args[])
{
Car c = new Car();
System.out.println("Car belongs to- "
+ c.belongsTo);
System.out.println("Car has " + c.wheels
+ " wheels.");
}
}
输出:
Car belongs to- automobiles
Car has 4 wheels.继承类型
- 单一继承——从单一基类生成的一个派生类。
- 多重继承——从两个或多个基类生成的一个派生类。
- 多级继承——一个派生类是从一个基类生成的,该基类也是从另一个基类生成的。
- 层次继承——从基类生成的一组派生类,而基类又可能有自己的派生类。
- 混合继承——由多级和多重继承组合而成的格结构。
多态性
对象可以具有具有不同内部结构的公共外部接口的能力。在实现继承的同时,多态性特别有效。在多态中,函数可以具有相同的名称但可以具有不同的参数列表。
示例: Car 和 Bus 类都可以有 wheel() 方法,但是两者的轮子数量不同,因此由于内部实现不同,因此不会出现冲突。
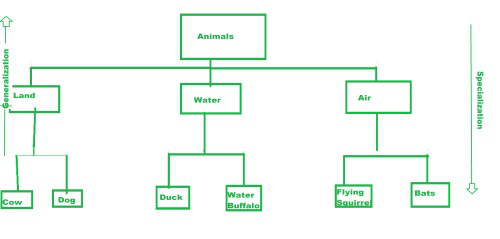
泛化和专业化
派生类从基类生成的不同类层次结构的表示 -
概括
来自派生类的共同特征的组合,以形成一个通用的基类。示例——“牛是陆地动物”。
专业化
对象从现有类到专门组的区别是专门化。这几乎就像泛化的逆过程。
下图展示了泛化与专业化——
链接和关联
链接:对象与其他对象协作的连接表示,即对象之间的关系称为链接。
关联:识别和展示对象之间行为的一组链接称为关联。关联的实例称为链接。
关联度
协会分为三种类型:
- 一元关系:同一类的对象得到连接。
- 二元关系:连接两个类的对象。
- 三元关系:连接三个或更多类的对象。
二元关联的基数
- 一对一:A 类的一个对象与 B 的一个对象相关联。
- 一对多:A 类的一个对象与 B 类的多个对象关联。
- 多对多:A 类的多个对象与 B 类的多个对象相关联。
组合或聚合
一个类通常可以使用其他类和对象的组合来创建。这是类组合或聚合。关系的“有”或“部分”通常是总和。如果一个对象由其他对象组成,则该对象称为聚合对象。
例子:
在学生与书籍的关系中,学生“拥有”书籍,而书籍是学生课程的“一部分”。在这里,学生是完整的对象。一个集合包括——
- 物理遏制——例如,一个袋子由拉链和一个瓶架组成。
- 概念遏制——例如,学生有分数。
对象模型的优点
- 启用 DRY(不要重复自己)编写代码的方式。
- 在集成复杂系统的同时,降低开发风险。
- 实现快速的软件开发。
- 很容易实现升级。
- 使软件更易于维护。