根据给定的行更改和列更改成本,最小化矩阵中从源到目的地的旅行成本
给定一个M*N网格,并给定一个数组startPos[] ,表示起始位置是单元格(startPos[0] , startPos[1]) ,表示其目的地的数组homePos[]位于单元格的(homePos[ 0],homePos[1])。
任何单元格只允许在四个方向上移动:左、右、上、下,并且不能超出边界。给定两个索引为 0 的整数数组:长度为M的rowCosts[]和长度为N的 colCosts[],表示移动的成本。
如果向上或向下移动到具有r行的单元格中,则移动成本为rowCosts[r] 。类似地,如果向左或向右移动到相邻单元格c中,则移动成本为 colCosts 。
返回从源到目的地旅行的最低总成本。
注意:没有与任何移动相关的负成本。
例子:
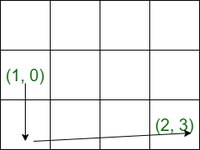
Input: M = 3, N = 4, startPos[] = {1, 0}, homePos[] = {2, 3}, rowCosts[] = {5, 4, 3}, colCosts[] = {8, 2, 6, 7}
Output: 18
Explanation: One ideal path is:
- It starts at (1, 0) and descends to (2, 0). This move costs rowCosts[2] = 3.
- It goes straight to (2, 1). This move costs colCosts[1] = 2.
- It goes straight to (2, 2). This move costs colCosts[2] = 6.
- It goes straight to (2, 3). This move costs colCosts[3] = 7.
- The total cost is 3 + 2 + 6 + 7 = 18.
The movement is shown in the picture below:
Input: M = 3, N = 4, startPos[] = {0, 0}, homePos[] = {0, 0}, rowCosts[] = {5, 4, 3}, colCosts[] = {8, 2, 6, 7}
Output: 0
Explanation: Starting position and destination both are same. So no movement cost.
方法:解决方案依赖于观察:
To reach destination with minimum cost only the rows lying in the range [startPos[0], homePos[0]] and columns lying in the range [startPos[1], homePos[1]] should be crossed.
Reason: Crossing any other row or column will add extra cost as all the movements have positive cost and number of movements increases with extra row and column traversal.
因此,起始位置和起始位置之间的每一行和每一列的成本将只发生一次。计算在homePos[0]和startPos[0]行之间移动的成本。和homePos[1]和startPos[1]列。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 将变量rmin、cmin初始化为开始和结束位置的最小值。
- 将变量rmax、cmax初始化为开始和结束位置的最大值。
- 使用变量i遍历范围[rmin, rmax]并执行以下任务:
- 将值rowCosts[i]添加到变量ans。
- 使用变量i遍历范围[cmin, cmax]并执行以下任务:
- 将值colCosts[i]添加到变量ans。
- 从变量ans 中减去值rowCosts[startPos[0]]、colCosts[startPos[1]] 。
- 执行上述步骤后,打印ans的值作为答案。
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the minimum cost
int minPathCost(vector& startPos,
vector& homePos,
vector& rowCosts,
vector& colCosts)
{
int ans = 0;
int rmin = min(startPos[0], homePos[0]);
int rmax = max(startPos[0], homePos[0]);
int cmin = min(startPos[1], homePos[1]);
int cmax = max(startPos[1], homePos[1]);
// Determine the cost of the rows
// that cross the path.
for (int i = rmin; i <= rmax; i++)
ans += rowCosts[i];
// Determine the cost of the cols
// that cross the path.
for (int i = cmin; i <= cmax; i++)
ans += colCosts[i];
// Starting coordinates need to be
// excluded from the final result
ans -= rowCosts[startPos[0]];
ans -= colCosts[startPos[1]];
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
vector startpos{ 1, 0 };
vector homepos{ 2, 3 };
vector roscost{ 5, 4, 3 };
vector colcst{ 8, 2, 6, 7 };
cout << minPathCost(startpos, homepos,
roscost, colcst);
return 0;
} Java
// Java code to implement the above approach
import java.util.*;
public class GFG
{
// Function to find the minimum cost
static int minPathCost(int []startPos,
int []homePos,
int []rowCosts,
int []colCosts)
{
int ans = 0;
int rmin = Math.min(startPos[0], homePos[0]);
int rmax = Math.max(startPos[0], homePos[0]);
int cmin = Math.min(startPos[1], homePos[1]);
int cmax = Math.max(startPos[1], homePos[1]);
// Determine the cost of the rows
// that cross the path.
for (int i = rmin; i <= rmax; i++)
ans += rowCosts[i];
// Determine the cost of the cols
// that cross the path.
for (int i = cmin; i <= cmax; i++)
ans += colCosts[i];
// Starting coordinates need to be
// excluded from the final result
ans -= rowCosts[startPos[0]];
ans -= colCosts[startPos[1]];
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int []startpos = { 1, 0 };
int []homepos = { 2, 3 };
int []roscost = { 5, 4, 3 };
int []colcst = { 8, 2, 6, 7 };
System.out.println( minPathCost(startpos, homepos,
roscost, colcst));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Samim Hossain Mondal.Python3
# Python code to implement the above approach
# Function to find the minimum cost
def minPathCost(startPos, homePos, rowCosts, colCosts):
ans = 0;
rmin = min(startPos[0], homePos[0]);
rmax = max(startPos[0], homePos[0]);
cmin = min(startPos[1], homePos[1]);
cmax = max(startPos[1], homePos[1]);
# Determine the cost of the rows
# that cross the path.
for i in range(rmin,rmax+1):
ans += rowCosts[i];
# Determine the cost of the cols
# that cross the path.
for i in range(cmin, cmax + 1):
ans += colCosts[i];
# Starting coordinates need to be
# excluded from the final result
ans -= rowCosts[startPos[0]];
ans -= colCosts[startPos[1]];
return ans;
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
startpos = [1, 0];
homepos = [2, 3];
roscost = [5, 4, 3];
colcst = [8, 2, 6, 7];
print(minPathCost(startpos, homepos, roscost, colcst));
# This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarC#
// C# code to implement the above approach
using System;
public class GFG
{
// Function to find the minimum cost
static int minPathCost(int []startPos,
int []homePos,
int []rowCosts,
int []colCosts)
{
int ans = 0;
int rmin = Math.Min(startPos[0], homePos[0]);
int rmax = Math.Max(startPos[0], homePos[0]);
int cmin = Math.Min(startPos[1], homePos[1]);
int cmax = Math.Max(startPos[1], homePos[1]);
// Determine the cost of the rows
// that cross the path.
for (int i = rmin; i <= rmax; i++)
ans += rowCosts[i];
// Determine the cost of the cols
// that cross the path.
for (int i = cmin; i <= cmax; i++)
ans += colCosts[i];
// Starting coordinates need to be
// excluded from the readonly result
ans -= rowCosts[startPos[0]];
ans -= colCosts[startPos[1]];
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int []startpos = { 1, 0 };
int []homepos = { 2, 3 };
int []roscost = { 5, 4, 3 };
int []colcst = { 8, 2, 6, 7 };
Console.WriteLine( minPathCost(startpos, homepos,
roscost, colcst));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarJavascript
18时间复杂度: O(M + N)
辅助空间: O(1)