使用Python抓取 Google Ngram Viewer
在本文中,我们将学习如何使用Python抓取 Google Ngarm。 Google Ngram/Google Books Ngram Viewer 是一个在线搜索引擎,可以绘制任何一组搜索字符串的频率图表。
什么是 Google Ngram 查看器?
Google Ngram Viewer 是一个搜索引擎,用于确定单词或短语在书中的流行度。 Google ngram 查看器为我们提供了各种过滤器选项,包括选择书籍的语言/类型(也称为语料库)以及书籍出版的年份范围。默认情况下,搜索区分大小写。
Google Ngram 搜索结果是什么样的?
如果我们在 Google Ngram 中搜索“Albert Einstein”,搜索结果会是这样的。
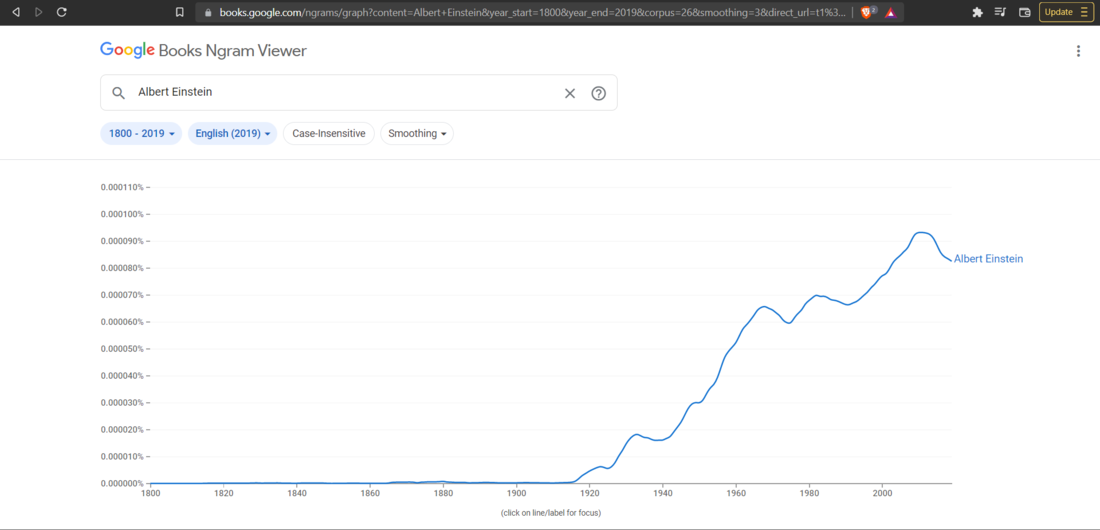
只有一个词的短语(比如“geek”),该短语称为unigram 。类似地,包含两个单词的短语(比如“Isaac Newton”)被称为bigram 。如果你在 google ngram 中搜索一个二元词组,它会告诉你:在书中出现的所有二元词组中,有多少百分比包含你搜索的词组。
我们甚至可以通过用逗号分隔它们来比较同一搜索结果中不同短语的流行度。例如,我们可以比较从 1850 年到 1900 年间“阿尔伯特·爱因斯坦”与“艾萨克·牛顿”在用英语写成的不同书籍中的受欢迎程度。
使用 Google Ngram URL
如果我们在 google ngram 中搜索“Albert Einstein”,年份从 1850 年到 1860 年,语料库是英文,平滑为 0,我们会看到如上图所示的图形。此搜索查询的 URL 将如下所示。
https://books.google.com/ngrams/graph?content=Albert%20Einstein&year_start=1850&year_end=1860&corpus=26&smoothing=0
在上面的 URL 中,如果我们将单词graph替换为单词json,我们将得到我们搜索查询的 JSON 数据而不是 graph。新 URL 将如下所示。
https://books.google.com/ngrams/json?content=Albert%20Einstein&year_start=1850&year_end=1860&corpus=26&smoothing=0
此 URL 的搜索结果将如下所示:

我们可以使用Python提取此 JSON 数据。
如何抓取 Google Ngrams?
为了抓取 google ngram,我们将使用 Python 的requests和urllib库。
现在,我们将创建一个从 google ngram 网站提取数据的函数。仔细阅读与代码一起编写的注释,以便跟进。
Python3
import requests
import urllib
def runQuery(query, start_year=1850,
end_year=1860, corpus=26,
smoothing=0):
# converting a regular string to
# the standard URL format
# eg: "geeks for,geeks" will
# convert to "geeks%20for%2Cgeeks"
query = urllib.parse.quote(query)
# creating the URL
url = 'https://books.google.com/ngrams/json?content=' + query +
'&year_start=' + str(start_year) + '&year_end=' +
str(end_year) + '&corpus=' + str(corpus) + '&smoothing=' +
str(smoothing) + ''
# requesting data from the above url
response = requests.get(url)
# extracting the json data from the response we got
output = response.json()
# creating a list to store the ngram data
return_data = []
if len(output) == 0:
# if no data returned from site,
# print the following statement
return "No data available for this Ngram."
else:
# if data returned from site,
# store the data in return_data list
for num in range(len(output)):
# getting the name
return_data.append((output[num]['ngram'],
# getting ngram data
output[num]['timeseries'])
)
return return_dataPython3
query = "Albert Einstein"
print(runQuery(query))Python3
query = "Albert Einstein,Isaac Newton"
print(runQuery(query))在函数runQuery中,我们将参数字符串查询作为函数的参数,而其余参数是默认参数。默认情况下,年份范围保持在 1850 到 1860 之间,语料库为 26(即英语),平滑保持为 0。我们根据参数字符串创建了 google ngram URL。然后,我们使用这个 URL 从 google ngram 获取数据。返回 JSON 数据后,我们将所需的数据存储在一个列表中,然后返回该列表。
现在,让我们使用runQuery函数找出“Albert Einstein”的流行度。
Python3
query = "Albert Einstein"
print(runQuery(query))
输出:
[(‘Albert Einstein’, [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2.171790969285325e-09,
1.014315520464492e-09, 6.44787723214079e-10, 0.0, 7.01216085197131e-10, 0.0, 0.0])]
我们甚至可以通过用逗号分隔每个短语来在同一个查询中输入多个短语。
Python3
query = "Albert Einstein,Isaac Newton"
print(runQuery(query))
输出:
[(‘Albert Einstein’, [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2.171790969285325e-09,
1.014315520464492e-09, 6.44787723214079e-10, 0.0, 7.01216085197131e-10,
0.0, 0.0]), (‘Isaac Newton’, [1.568728407619346e-06, 1.135979687205690e-06,
1.140318772741011e-06, 1.102130454455618e-06, 1.34806168716750e-06,
2.039112359852879e-06, 1.356955749542976e-06, 1.121004174819972e-06,
1.223622120960499e-06, 1.18965874662535e-06, 1.077695060303085e-06])]