Python系统模块
Python中的sys 模块提供了各种函数和变量,用于操作Python运行时环境的不同部分。它允许在解释器上进行操作,因为它提供对与解释器强烈交互的变量和函数的访问。让我们考虑下面的例子。
例子:
Python3
import sys
print(sys.version)Python3
import sys
for line in sys.stdin:
if 'q' == line.rstrip():
break
print(f'Input : {line}')
print("Exit")Python3
import sys
sys.stdout.write('Geeks')Python3
import sys
def print_to_stderr(*a):
# Here a is the array holding the objects
# passed as the argument of the function
print(*a, file = sys.stderr)
print_to_stderr("Hello World")Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# command line arguments
import sys
# total arguments
n = len(sys.argv)
print("Total arguments passed:", n)
# Arguments passed
print("\nName of Python script:", sys.argv[0])
print("\nArguments passed:", end = " ")
for i in range(1, n):
print(sys.argv[i], end = " ")
# Addition of numbers
Sum = 0
for i in range(1, n):
Sum += int(sys.argv[i])
print("\n\nResult:", Sum)Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# sys.exit()
import sys
age = 17
if age < 18:
# exits the program
sys.exit("Age less than 18")
else:
print("Age is not less than 18")Python3
import sys
print(sys.path)Python3
import sys
# Removing the values
sys.path = []
# importing pandas after removing
# values
import pandasPython3
import sys
print(sys.modules)Python3
import sys
a = 'Geeks'
print(sys.getrefcount(a))输出:
3.6.9 (default, Oct 8 2020, 12:12:24)
[GCC 8.4.0]在上面的示例中,使用sys.version返回一个字符串,其中包含Python解释器的版本和一些附加信息。这显示了 sys 模块如何与解释器交互。让我们深入了解本文以获取有关 sys 模块的更多信息。
使用 sys 输入和输出
sys 模块提供变量以更好地控制输入或输出。我们甚至可以将输入和输出重定向到其他设备。这可以使用三个变量来完成——
- 标准输入
- 标准输出
- 标准错误
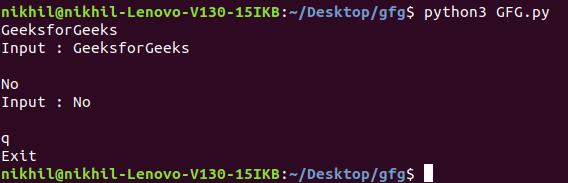
标准输入: 它可用于直接从命令行获取输入。它用于标准输入。它在内部调用 input() 方法。它还会在每个句子后自动添加 '\n'。
例子:
蟒蛇3
import sys
for line in sys.stdin:
if 'q' == line.rstrip():
break
print(f'Input : {line}')
print("Exit")
输出:
标准输出: 类似于Python中解释器的标准输出流的内置文件对象。 stdout 用于将输出直接显示到屏幕控制台。输出可以是任何形式,可以是打印语句,表达式语句,甚至是直接输入的提示。默认情况下,流处于文本模式。事实上,无论在代码中调用打印函数的任何地方,它都会首先写入 sys.stdout,然后最后写入屏幕。
例子:
蟒蛇3
import sys
sys.stdout.write('Geeks')
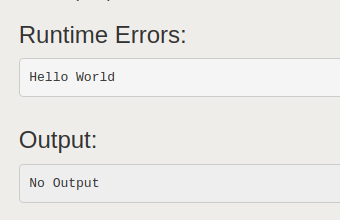
Geeks标准错误: 每当Python中发生异常时,它都会写入 sys.stderr。
例子:
蟒蛇3
import sys
def print_to_stderr(*a):
# Here a is the array holding the objects
# passed as the argument of the function
print(*a, file = sys.stderr)
print_to_stderr("Hello World")
输出:
命令行参数
命令行参数是在程序调用期间与调用语句一起传递的参数。为了使用 sys 模块实现这一点,sys 模块提供了一个名为sys.argv的变量。它的主要目的是:
- 它是一个命令行参数列表。
- len(sys.argv) 提供命令行参数的数量。
- sys.argv[0] 是当前Python脚本的名称。
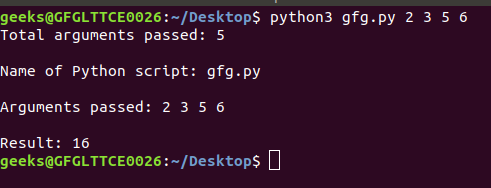
示例:考虑一个用于添加数字的程序,并且数字与调用语句一起传递。
蟒蛇3
# Python program to demonstrate
# command line arguments
import sys
# total arguments
n = len(sys.argv)
print("Total arguments passed:", n)
# Arguments passed
print("\nName of Python script:", sys.argv[0])
print("\nArguments passed:", end = " ")
for i in range(1, n):
print(sys.argv[i], end = " ")
# Addition of numbers
Sum = 0
for i in range(1, n):
Sum += int(sys.argv[i])
print("\n\nResult:", Sum)
输出:
退出程序
sys.exit([arg])可用于退出程序。可选参数 arg 可以是一个整数,给出出口或其他类型的对象。如果是整数,零被认为是“成功终止”。
注意:字符串也可以传递给 sys.exit() 方法。
例子:
蟒蛇3
# Python program to demonstrate
# sys.exit()
import sys
age = 17
if age < 18:
# exits the program
sys.exit("Age less than 18")
else:
print("Age is not less than 18")
输出:
An exception has occurred, use %tb to see the full traceback.
SystemExit: Age less than 18使用模块
系统路径 是 sys 模块中的一个内置变量,它返回解释器将搜索所需模块的目录列表。
在Python文件中导入模块时,解释器首先在其内置模块中搜索指定的模块。如果没有找到,它会查看由sys.path定义的目录列表。
注意: sys.path 是一个普通的列表,可以操作。
示例 1:列出所有路径
蟒蛇3
import sys
print(sys.path)
输出:

示例 2:截断 sys.path 的值
蟒蛇3
import sys
# Removing the values
sys.path = []
# importing pandas after removing
# values
import pandas
输出:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pandas'sys.modules返回当前 shell 已导入的Python模块的名称。
例子:
蟒蛇3
import sys
print(sys.modules)
输出:

引用计数
sys.getrefcount()方法用于获取任何给定对象的引用计数。 Python使用此值,因为当此值变为 0 时,将删除该特定值的内存。
例子:
蟒蛇3
import sys
a = 'Geeks'
print(sys.getrefcount(a))
4Python sys 中的更多功能
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| sys.setrecursionlimit() | sys.setrecursionlimit() method is used to set the maximum depth of the Python interpreter stack to the required limit. |
| sys.getrecursionlimit() method | sys.getrecursionlimit() method is used to find the current recursion limit of the interpreter or to find the maximum depth of the Python interpreter stack. |
| sys.settrace() | It is used for implementing debuggers, profilers and coverage tools. This is thread-specific and must register the trace using threading.settrace(). On a higher level, sys.settrace() registers the traceback to the Python interpreter |
| sys.setswitchinterval() method | sys.setswitchinterval() method is used to set the interpreter’s thread switch interval (in seconds). |
| sys.maxsize() | It fetches the largest value a variable of data type Py_ssize_t can store. |
| sys.maxint | maxint/INT_MAX denotes the highest value that can be represented by an integer. |
| sys.getdefaultencoding() method | sys.getdefaultencoding() method is used to get the current default string encoding used by the Unicode implementation. |