将函数应用于 R DataFrame 中的每一行
在本文中,我们将讨论如何在 R 编程语言中对数据框中的每一行应用函数。让我们举一个例子来更好地理解。
例子:
假设我们有一个虚拟数据集,其中 A、B、C 作为列名,一些数值作为行。 A B C 1. 5 6 1 2. 6 4 2 3. 7 3 3 4. 5 4 7 5. 6 2 8 6. 9 6 9
我们想应用一个函数来返回每行值的乘积,那么结果数据框应该是这样的: A B C product 1. 5 6 1 60 2. 6 4 2 48 3. 7 3 3 63 4. 5 4 7 140 5. 6 2 8 96 6. 9 6 9 486
将函数应用于 R 数据框中的每一行:
方法:使用apply函数
apply()用于计算数据框或矩阵上的函数。使用 apply()函数的目的是避免使用循环。 apply()函数将输出作为向量返回。
Syntax: apply(x, margin, func)
Parameters:
x: Array or matrix
margin: dimension on which operation is to be applied
func: operation to be applied
分步实施:
步骤 1:创建一个虚拟数据集。
R
# Apply function to each row in r Dataframe
# Creating dataset
# creating firs column
x <- c(5, 6, 7, 5, 6, 9)
# creating second column
y <- c(6, 4, 3, 4, 2, 6)
# creating third column
z <- c(1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9)
# creating dataframe
df <- data.frame(A = x, B = y, C = z)
display(df)R
# creating function to computer product
product = function(x, output){
# accessing elements from first column
A = x[1]
# accessing elements from second column
B=x[2]
# accessing elements from third column
C= x[3]
# return product
return(A*B*C)
}R
# apply(X,MARGIN,FUN,...)
apply(df,1,product )R
# apply(X,MARGIN,FUN,...)
single <- apply(df,1,product )
# adding product vector to dataframe
cbind(df,product = single)R
# Apply function to each row in r Dataframe
# Creating dataset
# creating firs column
x <- c(5,6,7,5,6,9)
# creating second column
y <- c(6,4,3,4,2,6)
# creating third column
z <- c(1,2,3,7,8,9)
# creating dataframe
df <- data.frame(A=x,B=y,C=z)
# creating function to computer product
product = function(x,output){
# accessing elements from first column
A = x[1]
# accessing elements from second column
B=x[2]
# accessing elements from third column
C= x[3]
# return product
return(A*B*C)
}
# apply(X,MARGIN,FUN,...)
apply(df,1,product )
# apply(X,MARGIN,FUN,...)
single <- apply(df,1,product )
# adding product vector to dataframe
cbind(df,product = single)输出:
A B C
1 5 6 1
2 6 4 2
3 7 3 3
4 5 4 7
5 6 2 8
6 9 6 9第 2 步:创建用于计算产品的自定义函数。
电阻
# creating function to computer product
product = function(x, output){
# accessing elements from first column
A = x[1]
# accessing elements from second column
B=x[2]
# accessing elements from third column
C= x[3]
# return product
return(A*B*C)
}
注意:这里我们只是定义了计算积的函数,没有调用,所以在调用这个函数之前不会有任何输出。
第 3 步:使用 apply函数计算每一行的乘积。
Syntax: (data_frame, 1, function,…)
现在我们正在调用新创建的产品函数并使用 apply函数返回产品。
电阻
# apply(X,MARGIN,FUN,...)
apply(df,1,product )
输出:
[1] 30 48 63 140 96 486注意: apply() 将乘积作为向量列表返回。因此,我们必须使用 cbind(列绑定)将其添加到数据框中。
第 4 步:将产品列表附加到数据框中。
电阻
# apply(X,MARGIN,FUN,...)
single <- apply(df,1,product )
# adding product vector to dataframe
cbind(df,product = single)
输出:
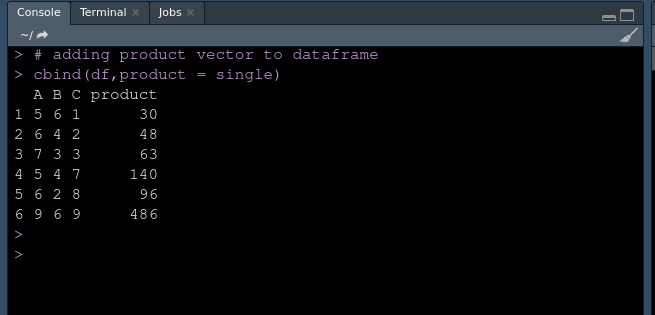
使用 apply()
下面是完整的实现:
电阻
# Apply function to each row in r Dataframe
# Creating dataset
# creating firs column
x <- c(5,6,7,5,6,9)
# creating second column
y <- c(6,4,3,4,2,6)
# creating third column
z <- c(1,2,3,7,8,9)
# creating dataframe
df <- data.frame(A=x,B=y,C=z)
# creating function to computer product
product = function(x,output){
# accessing elements from first column
A = x[1]
# accessing elements from second column
B=x[2]
# accessing elements from third column
C= x[3]
# return product
return(A*B*C)
}
# apply(X,MARGIN,FUN,...)
apply(df,1,product )
# apply(X,MARGIN,FUN,...)
single <- apply(df,1,product )
# adding product vector to dataframe
cbind(df,product = single)
输出:
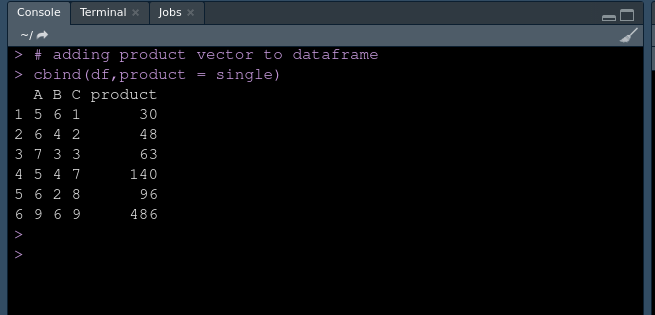
使用 apply()