Java和多重继承
多重继承是面向对象概念的一个特征,其中一个类可以继承多个父类的属性。当超类和子类中存在具有相同签名的方法时,就会出现此问题。在调用该方法时,编译器无法确定要调用哪个类方法,甚至在调用哪个类方法时也无法确定优先级。
Note: Java doesn’t support Multiple Inheritance
示例 1:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Unsupportance of
// Multiple Inheritance
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// First Parent class
class Parent1 {
// Method inside first parent class
void fun() {
// Print statement if this method is called
System.out.println("Parent1");
}
}
// Class 2
// Second Parent Class
class Parent2 {
// Method inside first parent class
void fun() {
// Print statement if this method is called
System.out.println("Parent2");
}
}
// Class 3
// Trying to be child of both the classes
class Test extends Parent1, Parent2 {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Creating object of class in main() method
Test t = new Test();
// Trying to call above functions of class where
// Error is thrown as this class is inheriting
// multiple classes
t.fun();
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Unsupportance of
// Multiple Inheritance
// Diamond Problem Similar Scenario
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// A Grand parent class in diamond
class GrandParent {
void fun() {
// Print statement to be executed when this method is called
System.out.println("Grandparent");
}
}
// Class 2
// First Parent class
class Parent1 extends GrandParent {
void fun() {
// Print statement to be executed when this method is called
System.out.println("Parent1");
}
}
// Class 3
// Second Parent Class
class Parent2 extends GrandParent {
void fun() {
// Print statement to be executed when this method is called
System.out.println("Parent2");
}
}
// Class 4
// Inheriting from multiple classes
class Test extends Parent1, Parent2 {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Creating object of this class i main() method
Test t = new Test();
// Now calling fun() method from its parent classes
// which will throw compilation error
t.fun();
}
}Java
// Java program to demonstrate Multiple Inheritance
// through default methods
// Interface 1
interface PI1 {
// Default method
default void show()
{
// Print statement if method is called
// from interface 1
System.out.println("Default PI1");
}
}
// Interface 2
interface PI2 {
// Default method
default void show()
{
// Print statement if method is called
// from interface 2
System.out.println("Default PI2");
}
}
// Main class
// Implementation class code
class TestClass implements PI1, PI2 {
// Overriding default show method
public void show()
{
// Using super keyword to call the show
// method of PI1 interface
PI1.super.show();
// Using super keyword to call the show
// method of PI2 interface
PI2.super.show();
}
// Mai driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating object of this class in main() method
TestClass d = new TestClass();
d.show();
}
}Java
// Java program to demonstrate How Diamond Problem
// Is Handled in case of Default Methods
// Interface 1
interface GPI {
// Default method
default void show()
{
// Print statement
System.out.println("Default GPI");
}
}
// Interface 2
// Extending the above interface
interface PI1 extends GPI {
}
// Interface 3
// Extending the above interface
interface PI2 extends GPI {
}
// Main class
// Implementation class code
class TestClass implements PI1, PI2 {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating object of this class
// in main() method
TestClass d = new TestClass();
// Now calling the function defined in interface 1
// from whom Interface 2and 3 are deriving
d.show();
}
}输出:抛出编译错误
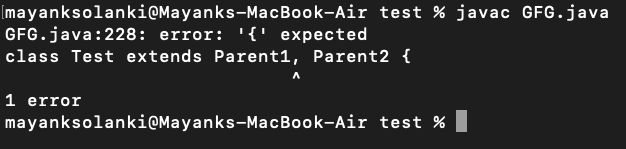
Conclusion: As depicted from code above, on calling the method fun() using Test object will cause complications such as whether to call Parent1’s fun() or Parent2’s fun() method.
示例 2:
GrandParent
/ \
/ \
Parent1 Parent2
\ /
\ /
Test代码如下
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Unsupportance of
// Multiple Inheritance
// Diamond Problem Similar Scenario
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// A Grand parent class in diamond
class GrandParent {
void fun() {
// Print statement to be executed when this method is called
System.out.println("Grandparent");
}
}
// Class 2
// First Parent class
class Parent1 extends GrandParent {
void fun() {
// Print statement to be executed when this method is called
System.out.println("Parent1");
}
}
// Class 3
// Second Parent Class
class Parent2 extends GrandParent {
void fun() {
// Print statement to be executed when this method is called
System.out.println("Parent2");
}
}
// Class 4
// Inheriting from multiple classes
class Test extends Parent1, Parent2 {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Creating object of this class i main() method
Test t = new Test();
// Now calling fun() method from its parent classes
// which will throw compilation error
t.fun();
}
}
输出:

当 run() 方法再次引发编译器错误时,当在其他语言(如 C++)中允许时,多重继承会导致菱形问题。从代码中我们可以看出: 在使用Test对象调用fun()方法时,会出现复杂情况,比如是调用Parent1的fun()还是Child的fun()方法。因此,为了避免这种复杂性, Java不支持类的多重继承。
Java使用类不支持多重继承,处理由于多重继承引起的复杂性非常复杂。它在诸如强制转换、构造函数链接等各种操作期间会产生问题,最重要的原因是我们实际上需要多重继承的场景非常少,因此最好将其省略以使事情简单明了。默认方法和接口的上述问题如何处理?
Java 8 支持默认方法,其中接口可以提供方法的默认实现。并且一个类可以实现两个或多个接口。如果两个实现的接口都包含具有相同方法签名的默认方法,实现类应该明确指定要使用的默认方法,或者它应该覆盖默认方法。
示例 3:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate Multiple Inheritance
// through default methods
// Interface 1
interface PI1 {
// Default method
default void show()
{
// Print statement if method is called
// from interface 1
System.out.println("Default PI1");
}
}
// Interface 2
interface PI2 {
// Default method
default void show()
{
// Print statement if method is called
// from interface 2
System.out.println("Default PI2");
}
}
// Main class
// Implementation class code
class TestClass implements PI1, PI2 {
// Overriding default show method
public void show()
{
// Using super keyword to call the show
// method of PI1 interface
PI1.super.show();
// Using super keyword to call the show
// method of PI2 interface
PI2.super.show();
}
// Mai driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating object of this class in main() method
TestClass d = new TestClass();
d.show();
}
}
Default PI1
Default PI2Note: If we remove the implementation of default method from “TestClass”, we get a compiler error. If there is a diamond through interfaces, then there is no issue if none of the middle interfaces provide implementation of root interface. If they provide implementation, then implementation can be accessed as above using super keyword.
示例 4:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate How Diamond Problem
// Is Handled in case of Default Methods
// Interface 1
interface GPI {
// Default method
default void show()
{
// Print statement
System.out.println("Default GPI");
}
}
// Interface 2
// Extending the above interface
interface PI1 extends GPI {
}
// Interface 3
// Extending the above interface
interface PI2 extends GPI {
}
// Main class
// Implementation class code
class TestClass implements PI1, PI2 {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating object of this class
// in main() method
TestClass d = new TestClass();
// Now calling the function defined in interface 1
// from whom Interface 2and 3 are deriving
d.show();
}
}
Default GPI