EMF和电位差之间的差异
在现实生活中使用电池和电池时,我们会遇到电池端子之间的两种不同的电位差。这些电位差是由于电池的非理想性质导致的,这会增加电池内部的电阻。电位器用于测量这种差异。这些不同的值称为电动势和电池的电位差。要了解为什么会出现这种现象,我们需要查看电路和电池提供的电阻。让我们详细看看这些概念。
电池的电动势 (EMF)
由电池传递给单位电荷的能量称为电动势 EMF。电池有多种形式和尺寸可供选择。有许多不同类型的发电机由各种来源供电。所有这些设备,无论其能源是什么,都会在其端子之间产生电位差,并且如果将电阻连接到它们,则可以提供电流。众所周知,电位差会产生电场,使电荷移动,进而产生电流。因此,这种电位差有时也称为电动势 (emf)。
与它的名字相反,电动势根本不是一种力量。这是一个潜在的差异。如果准确地说,
E.M.F is a potential difference which is created when no current is flowing in the system.
它的单位被认为是伏特(V)。尽管 EMF 与电压源产生的电位差直接相关,但仍与反映在电池端子上的实际电位差不同。电池周围的端电压通常小于电池的电动势。
电池的电位差
电池的电压输出是通过其端子测量的,这就是为什么它被称为端子电压。在下图中,显示了电池及其内部电阻。电池串联到另一个外部电阻,用 R load表示。电池两端产生的净电压由下面的公式给出,
V = 电动势 – Ir

这里,“I”是在电路中流动的电流,“r”是内部电阻。
如果“I”的流动方向是从电池的负极到正极,则“I”被认为是正极。该等式表明,电流越大,电池的端电压越低。也可以得出,内阻越小,端电压越大。当考虑负载电阻时,电流计算变得有点不同。
The equivalent resistance of the circuit becomes,
R = r + Rload
The current is given by Ohm’s law,
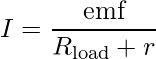
EMF和电位差之间的差异
Electromotive Force (E.M.F) | Potential Difference |
| The difference in the potential of two electrodes of a battery. | Difference of potential between any two points on the circuit. |
| E.M.F is always greater than the potential difference between any points in the circuit. | This is always less than the E.M.F |
| Formula: E = I(R + r) | Formula: V = IR |
| This is caused by the electric, gravitational and magnetic fields. | This difference is only produced by the electric field. |
| The electromotive force is the amount of energy given to each coulomb of charge. | The potential difference is the amount of energy utilized by one coulomb of charge. |
| The electromotive force is independent of the circuit’s internal resistance. | The potential difference is proportional to the circuit’s resistance. |
| The electromotive force is responsible for transferring energy across the circuit. | The potential difference between any two places on the circuit is a measure of energy. |
| When the circuit is unchanged, the magnitude of the electromotive force is always larger than the potential difference. | When the circuit is completely charged, the size of the potential difference is equal to the circuit’s emf. |
| The electromotive force is measured using an emf meter. | The potential difference is measured with a voltmeter. |
示例问题
问题 1:找出将在 2 伏特和 0.02 欧姆内阻的电池内部流动的电流,以防其端子相互连接。
解决方案:
The current in that case will be given by simple application of ohm’s law.
V = 2V
r = 0.02 ohms.
V = IR
Plugging the values in the equation,
I = V/R
I = 2/0.02
= 100 A
问题 2:找出将在 10 伏特和 5 欧姆内阻的电池内部流动的电流,以防其端子相互连接。
解决方案:
The current in that case will be given by simple application of ohm’s law.
V = 10 V
R = 5 ohms.
V = IR
Plugging the values in the equation,
I = V/R
I = 10/5
= 2 A
问题 3:找出将在 10 伏特和 10 欧姆内阻的电池内部流动的电流,以防其端子相互连接。求电池的端电压。
解决方案:
The current in that case will be given by simple application of ohm’s law.
V = 10 V
R= 10 ohms.
V = IR
Plugging the values in the equation,
I = V/R
I = 10/10
= 1 A
The terminal voltage of the battery is given by,
V = emf – Ir
Given , emf = 10 V, I = 1A and r = 10
V = emf – Ir
= 10 – (1)(10)
= 0 V
问题 4:找出将在 10 伏和 5 欧姆内阻和 5 欧姆负载电阻串联的电池内部流动的电流。求电池的端电压。
解决方案:
The current in that case will be given by simple application of ohm’s law.
I = ![]()
emf = 10 V
Rload= 5 ohms.
r = 5
Plugging the values in the equation,
I = ![]()
I = 10 / (5 + 5)
= 1 A
The terminal voltage of the battery is given by,
V = emf – Ir
Given , emf = 10 V, I = 1 A and r = 5
V = emf – Ir
= 10 – (1)(5)
= 10 – 5
= 5 V
问题 5:找出将在 10 伏特和 2 欧姆内阻和 3 欧姆负载电阻串联的电池内部流动的电流。求电池的端电压。
解决方案:
The current in that case will be given by simple application of ohm’s law.
I = ![]()
emf = 10 V
Rload= 3 ohms.
r = 2
plugging the values in the equation,
I = ![]()
⇒ I = ![]()
⇒ I = 2 A
The terminal voltage of the battery is given by,
V = emf – Ir
Given , emf = 10 V, I =2 A and r = 2
V = emf – Ir
= 10 – (2)(2)
= 10 – 6
= 4V