循环链表的排序插入
难度等级:菜鸟
编写一个 C函数,在已排序的循环链表 (CLL) 中插入一个新值。例如,如果输入 CLL 如下。
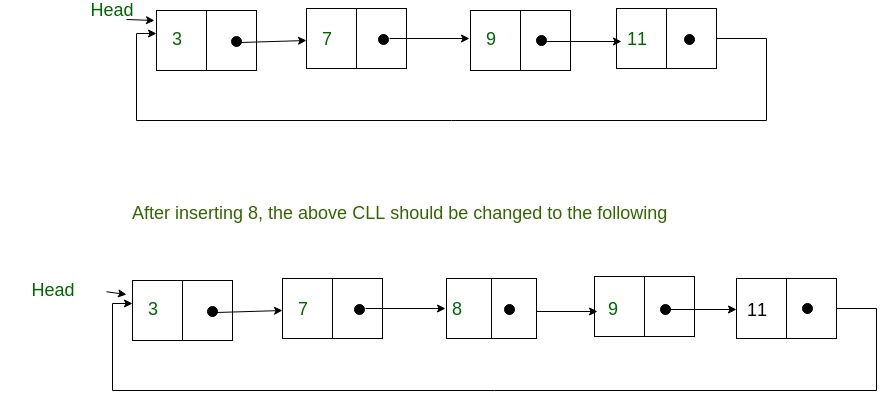
算法:
为新插入的节点分配内存,并将数据放入新分配的节点中。让指向新节点的指针为 new_node。内存分配后,以下是需要处理的三种情况。
1) Linked List is empty:
a) since new_node is the only node in CLL, make a self loop.
new_node->next = new_node;
b) change the head pointer to point to new node.
*head_ref = new_node;
2) New node is to be inserted just before the head node:
(a) Find out the last node using a loop.
while(current->next != *head_ref)
current = current->next;
(b) Change the next of last node.
current->next = new_node;
(c) Change next of new node to point to head.
new_node->next = *head_ref;
(d) change the head pointer to point to new node.
*head_ref = new_node;
3) New node is to be inserted somewhere after the head:
(a) Locate the node after which new node is to be inserted.
while ( current->next!= *head_ref &&
current->next->data data)
{ current = current->next; }
(b) Make next of new_node as next of the located pointer
new_node->next = current->next;
(c) Change the next of the located pointer
current->next = new_node;C++
// C++ program for sorted insert
// in circular linked list
#include
using namespace std;
/* structure for a node */
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
/* function to insert a new_node in a list in sorted way.
Note that this function expects a pointer to head node
as this can modify the head of the input linked list */
void sortedInsert(Node** head_ref, Node* new_node)
{
Node* current = *head_ref;
// Case 1 of the above algo
if (current == NULL)
{
new_node->next = new_node;
*head_ref = new_node;
}
// Case 2 of the above algo
else if (current->data >= new_node->data)
{
/* If value is smaller than head's value then
we need to change next of last node */
while(current->next != *head_ref)
current = current->next;
current->next = new_node;
new_node->next = *head_ref;
*head_ref = new_node;
}
// Case 3 of the above algo
else
{
/* Locate the node before the point of insertion */
while (current->next!= *head_ref &&
current->next->data < new_node->data)
current = current->next;
new_node->next = current->next;
current->next = new_node;
}
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given linked list */
void printList(Node *start)
{
Node *temp;
if(start != NULL)
{
temp = start;
do {
cout<data<<" ";
temp = temp->next;
} while(temp != start);
}
}
/* Driver code */
int main()
{
int arr[] = {12, 56, 2, 11, 1, 90};
int list_size, i;
/* start with empty linked list */
Node *start = NULL;
Node *temp;
/* Create linked list from the array arr[].
Created linked list will be 1->2->11->12->56->90 */
for (i = 0; i< 6; i++)
{
temp = new Node();
temp->data = arr[i];
sortedInsert(&start, temp);
}
printList(start);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra. C
#include
#include
/* structure for a node */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
/* function to insert a new_node in a list in sorted way.
Note that this function expects a pointer to head node
as this can modify the head of the input linked list */
void sortedInsert(struct Node** head_ref, struct Node* new_node)
{
struct Node* current = *head_ref;
// Case 1 of the above algo
if (current == NULL)
{
new_node->next = new_node;
*head_ref = new_node;
}
// Case 2 of the above algo
else if (current->data >= new_node->data)
{
/* If value is smaller than head's value then
we need to change next of last node */
while(current->next != *head_ref)
current = current->next;
current->next = new_node;
new_node->next = *head_ref;
*head_ref = new_node;
}
// Case 3 of the above algo
else
{
/* Locate the node before the point of insertion */
while (current->next!= *head_ref &&
current->next->data < new_node->data)
current = current->next;
new_node->next = current->next;
current->next = new_node;
}
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given linked list */
void printList(struct Node *start)
{
struct Node *temp;
if(start != NULL)
{
temp = start;
printf("\n");
do {
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
} while(temp != start);
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
int arr[] = {12, 56, 2, 11, 1, 90};
int list_size, i;
/* start with empty linked list */
struct Node *start = NULL;
struct Node *temp;
/* Create linked list from the array arr[].
Created linked list will be 1->2->11->12->56->90 */
for (i = 0; i< 6; i++)
{
temp = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = arr[i];
sortedInsert(&start, temp);
}
printList(start);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for sorted insert in circular linked list
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList
{
Node head;
// Constructor
LinkedList() { head = null; }
/* function to insert a new_node in a list in sorted way.
Note that this function expects a pointer to head node
as this can modify the head of the input linked list */
void sortedInsert(Node new_node)
{
Node current = head;
// Case 1 of the above algo
if (current == null)
{
new_node.next = new_node;
head = new_node;
}
// Case 2 of the above algo
else if (current.data >= new_node.data)
{
/* If value is smaller than head's value then
we need to change next of last node */
while (current.next != head)
current = current.next;
current.next = new_node;
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
// Case 3 of the above algo
else
{
/* Locate the node before the point of insertion */
while (current.next != head &&
current.next.data < new_node.data)
current = current.next;
new_node.next = current.next;
current.next = new_node;
}
}
// Utility method to print a linked list
void printList()
{
if (head != null)
{
Node temp = head;
do
{
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != head);
}
}
// Driver code to test above
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
// Creating the linkedlist
int arr[] = new int[] {12, 56, 2, 11, 1, 90};
/* start with empty linked list */
Node temp = null;
/* Create linked list from the array arr[].
Created linked list will be 1->2->11->12->56->90*/
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
temp = new Node(arr[i]);
list.sortedInsert(temp);
}
list.printList();
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank JaiswalPython
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to print the linked LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
print temp.data,
temp = temp.next
while(temp != self.head):
print temp.data,
temp = temp.next
""" function to insert a new_node in a list in sorted way.
Note that this function expects a pointer to head node
as this can modify the head of the input linked list """
def sortedInsert(self, new_node):
current = self.head
# Case 1 of the above algo
if current is None:
new_node.next = new_node
self.head = new_node
# Case 2 of the above algo
elif (current.data >= new_node.data):
# If value is smaller than head's value then we
# need to change next of last node
while current.next != self.head :
current = current.next
current.next = new_node
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Case 3 of the above algo
else:
# Locate the node before the point of insertion
while (current.next != self.head and
current.next.data < new_node.data):
current = current.next
new_node.next = current.next
current.next = new_node
# Driver program to test the above function
#llist = LinkedList()
arr = [12, 56, 2, 11, 1, 90]
list_size = len(arr)
# start with empty linked list
start = LinkedList()
# Create linked list from the array arr[]
# Created linked list will be 1->2->11->12->56->90
for i in range(list_size):
temp = Node(arr[i])
start.sortedInsert(temp)
start.printList()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// C# program for sorted insert
// in circular linked list
using System;
class LinkedList
{
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
Node head;
// Constructor
LinkedList()
{
head = null;
}
/* function to insert a new_node
in a list in sorted way. Note that
this function expects a pointer
to head node as this can modify
the head of the input linked list */
void sortedInsert(Node new_node)
{
Node current = head;
// Case 1 of the above algo
if (current == null)
{
new_node.next = new_node;
head = new_node;
}
// Case 2 of the above algo
else if (current.data >= new_node.data)
{
/* If value is smaller than
head's value then we need
to change next of last node */
while (current.next != head)
current = current.next;
current.next = new_node;
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
// Case 3 of the above algo
else
{
/* Locate the node before
the point of insertion */
while (current.next != head &&
current.next.data < new_node.data)
current = current.next;
new_node.next = current.next;
current.next = new_node;
}
}
// Utility method to print a linked list
void printList()
{
if (head != null)
{
Node temp = head;
do
{
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
while (temp != head);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
// Creating the linkedlist
int []arr = {12, 56, 2, 11, 1, 90};
/* start with empty linked list */
Node temp = null;
/* Create linked list from the
array arr[]. Created linked list
will be 1->2->11->12->56->90*/
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
temp = new Node(arr[i]);
list.sortedInsert(temp);
}
list.printList();
}
}
// This code has been contributed
// by Arnab KunduJavascript
C
// Case 2 of the above algo
else if (current->data >= new_node->data)
{
// swap the data part of head node and new node
// assuming that we have a function swap(int *, int *)
swap(&(current->data), &(new_node->data));
new_node->next = (*head_ref)->next;
(*head_ref)->next = new_node;
}Java
// Case 2 of the above algo
else if (current.data >= new_node.data)
{
// swap the data part of head node and new node
// assuming that we have a function swap(int *, int *)
Node tmp = current.data;
current.data = new_node.data;
new_node.data = tmp;
new_node.next = (head_ref).next;
(head_ref).next = new_node;
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76.C#
// Case 2 of the above algo
else if (current.data >= new_node.data)
{
// swap the data part of head node and new node
// assuming that we have a function swap(int *, int *)
Node tmp = current.data;
current.data = new_node.data;
new_node.data = tmp;
new_node.next = (head_ref).next;
(head_ref).next = new_node;
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56Javascript
输出:
1 2 11 12 56 90时间复杂度: O(n),其中 n 是给定链表中的节点数。
可以优化上述算法/代码的情况2。为了实现建议的更改,我们需要修改案例 2 以遵循。
C
// Case 2 of the above algo
else if (current->data >= new_node->data)
{
// swap the data part of head node and new node
// assuming that we have a function swap(int *, int *)
swap(&(current->data), &(new_node->data));
new_node->next = (*head_ref)->next;
(*head_ref)->next = new_node;
}
Java
// Case 2 of the above algo
else if (current.data >= new_node.data)
{
// swap the data part of head node and new node
// assuming that we have a function swap(int *, int *)
Node tmp = current.data;
current.data = new_node.data;
new_node.data = tmp;
new_node.next = (head_ref).next;
(head_ref).next = new_node;
}
// This code is contributed by pratham76.
C#
// Case 2 of the above algo
else if (current.data >= new_node.data)
{
// swap the data part of head node and new node
// assuming that we have a function swap(int *, int *)
Node tmp = current.data;
current.data = new_node.data;
new_node.data = tmp;
new_node.next = (head_ref).next;
(head_ref).next = new_node;
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56
Javascript
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。