循环单向链表 |插入
我们在以下帖子中讨论了单链表和循环链表:
单链表
循环链表
为什么是圆形?在单向链表中,为了访问链表的任何节点,我们从第一个节点开始遍历。如果我们位于列表中间的任何节点,则无法访问给定节点之前的节点。这个问题可以通过稍微改变单链表的结构来解决。在单向链表中,下一部分(指向下一个节点的指针)为 NULL。如果我们利用这个链接指向第一个节点,那么我们就可以到达前面的节点。有关循环链表的更多优点,请参阅此处。
这样形成的结构是一个循环单链表,如下所示:
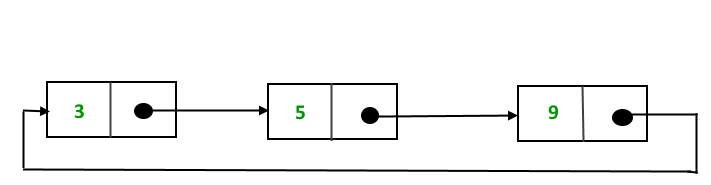
在这篇文章中,解释了使用单向链表在循环链表中实现和插入节点。
执行
为了实现一个循环单向链表,我们使用一个指向链表最后一个节点的外部指针。如果我们有一个指针 last 指向最后一个节点,那么 last -> next 将指向第一个节点。
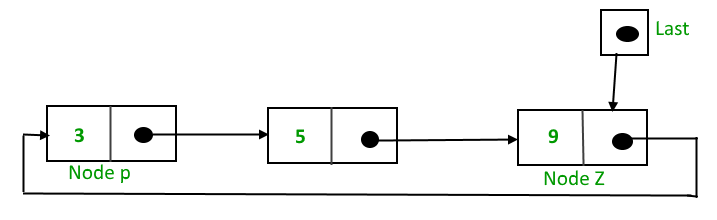
指针last指向节点 Z 并且 last -> next 指向节点 P。
为什么我们采用指向最后一个节点而不是第一个节点的指针?
对于开头插入一个节点,我们需要遍历整个链表。此外,为了在最后插入,必须遍历整个列表。如果我们使用指向最后一个节点的指针而不是开始指针,那么在这两种情况下都不需要遍历整个列表。因此,无论列表的长度如何,在开头或结尾插入都需要恒定的时间。
插入
可以通过三种方式添加节点:
- 插入空列表
- 在列表开头插入
- 在列表末尾插入
- 在节点之间插入
插入空列表
最初,当列表为空时,最后一个指针将为 NULL。

插入节点T后,
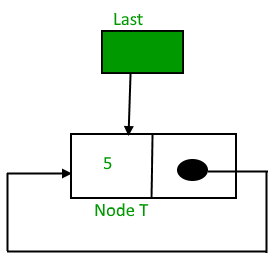
插入后,T是最后一个节点,所以指针last指向节点T。而节点T是第一个也是最后一个节点,所以T指向自己。
将节点插入空列表的函数,
C++
struct Node *addToEmpty(struct Node *last, int data)
{
// This function is only for empty list
if (last != NULL)
return last;
// Creating a node dynamically.
struct Node *temp =
(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Assigning the data.
temp -> data = data;
last = temp;
// Note : list was empty. We link single node
// to itself.
temp -> next = last;
return last;
}Java
static Node addToEmpty(Node last, int data)
{
// This function is only for empty list
if (last != null)
return last;
// Creating a node dynamically.
Node temp = new Node();
// Assigning the data.
temp.data = data;
last = temp;
// Note : list was empty. We link single node
// to itself.
temp.next = last;
return last;
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1C#
static Node addToEmpty(Node last, int data)
{
// This function is only for empty list
if (last != null)
return last;
// Creating a node dynamically.
Node temp =
new Node();
// Assigning the data.
temp.data = data;
last = temp;
// Note : list was empty. We link single node
// to itself.
temp.next = last;
return last;
}
// This code contributed by umadevi9616Javascript
C++
struct Node *addBegin(struct Node *last, int data)
{
if (last == NULL)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
// Creating a node dynamically.
struct Node *temp
= (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Assigning the data.
temp -> data = data;
// Adjusting the links.
temp -> next = last -> next;
last -> next = temp;
return last;
}Java
static Node addBegin(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
// Creating a node dynamically
Node temp = new Node();
// Assigning the data
temp.data = data;
// Adjusting the links
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
return last;
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
static Node addBegin(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
// Creating a node dynamically
Node temp = new Node();
// Assigning the data
temp.data = data;
// Adjusting the links
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
return last;
}
// This code is contributed by Pratham76Javascript
C++
struct Node *addEnd(struct Node *last, int data)
{
if (last == NULL)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
// Creating a node dynamically.
struct Node *temp =
(struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Assigning the data.
temp -> data = data;
// Adjusting the links.
temp -> next = last -> next;
last -> next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}Java
static Node addEnd(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
// Creating a node dynamically.
Node temp = new Node();
// Assigning the data.
temp.data = data;
// Adjusting the links.
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110Python3
def addEnd(self, data):
if (self.last == None):
return self.addToEmpty(data)
# Assigning the data.
temp = Node(data)
# Adjusting the links.
temp.next = self.last.next
self.last.next = temp
self.last = temp
return self.last
# This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110C#
static Node addEnd(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
// Creating a node dynamically.
Node temp = new Node();
// Assigning the data.
temp.data = data;
// Adjusting the links.
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110Javascript
C++
struct Node *addAfter(struct Node *last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == NULL)
return NULL;
struct Node *temp, *p;
p = last -> next;
// Searching the item.
do
{
if (p ->data == item)
{
// Creating a node dynamically.
temp = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Assigning the data.
temp -> data = data;
// Adjusting the links.
temp -> next = p -> next;
// Adding newly allocated node after p.
p -> next = temp;
// Checking for the last node.
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p -> next;
} while (p != last -> next);
cout << item << " not present in the list." << endl;
return last;
}Java
static Node addAfter(Node last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == null)
return null;
Node temp, p;
p = last.next;
do
{
if (p.data == item)
{
temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p.next;
} while(p != last.next);
System.out.println(item + " not present in the list.");
return last;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110C++
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
struct Node *addToEmpty(struct Node *last, int data)
{
// This function is only for empty list
if (last != NULL)
return last;
// Creating a node dynamically.
struct Node *temp =
(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Assigning the data.
temp -> data = data;
last = temp;
// Creating the link.
last -> next = last;
return last;
}
struct Node *addBegin(struct Node *last, int data)
{
if (last == NULL)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
struct Node *temp =
(struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp -> data = data;
temp -> next = last -> next;
last -> next = temp;
return last;
}
struct Node *addEnd(struct Node *last, int data)
{
if (last == NULL)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
struct Node *temp =
(struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp -> data = data;
temp -> next = last -> next;
last -> next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
struct Node *addAfter(struct Node *last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == NULL)
return NULL;
struct Node *temp, *p;
p = last -> next;
do
{
if (p ->data == item)
{
temp = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp -> data = data;
temp -> next = p -> next;
p -> next = temp;
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p -> next;
} while(p != last -> next);
cout << item << " not present in the list." << endl;
return last;
}
void traverse(struct Node *last)
{
struct Node *p;
// If list is empty, return.
if (last == NULL)
{
cout << "List is empty." << endl;
return;
}
// Pointing to first Node of the list.
p = last -> next;
// Traversing the list.
do
{
cout << p -> data << " ";
p = p -> next;
}
while(p != last->next);
}
// Driven Program
int main()
{
struct Node *last = NULL;
last = addToEmpty(last, 6);
last = addBegin(last, 4);
last = addBegin(last, 2);
last = addEnd(last, 8);
last = addEnd(last, 12);
last = addAfter(last, 10, 8);
traverse(last);
return 0;
} Java
class GFG
{
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
};
static Node addToEmpty(Node last, int data)
{
// This function is only for empty list
if (last != null)
return last;
// Creating a node dynamically.
Node temp = new Node();
// Assigning the data.
temp.data = data;
last = temp;
// Creating the link.
last.next = last;
return last;
}
static Node addBegin(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
return last;
}
static Node addEnd(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
static Node addAfter(Node last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == null)
return null;
Node temp, p;
p = last.next;
do
{
if (p.data == item)
{
temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p.next;
} while(p != last.next);
System.out.println(item + " not present in the list.");
return last;
}
static void traverse(Node last)
{
Node p;
// If list is empty, return.
if (last == null)
{
System.out.println("List is empty.");
return;
}
// Pointing to first Node of the list.
p = last.next;
// Traversing the list.
do
{
System.out.print(p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
while(p != last.next);
}
// Driven code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node last = null;
last = addToEmpty(last, 6);
last = addBegin(last, 4);
last = addBegin(last, 2);
last = addEnd(last, 8);
last = addEnd(last, 12);
last = addAfter(last, 10, 8);
traverse(last);
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class CircularLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.last = None
# This function is only for empty list
def addToEmpty(self, data):
if (self.last != None):
return self.last
# Creating the newnode temp
temp = Node(data)
self.last = temp
# Creating the link
self.last.next = self.last
return self.last
def addBegin(self, data):
if (self.last == None):
return self.addToEmpty(data)
temp = Node(data)
temp.next = self.last.next
self.last.next = temp
return self.last
def addEnd(self, data):
if (self.last == None):
return self.addToEmpty(data)
temp = Node(data)
temp.next = self.last.next
self.last.next = temp
self.last = temp
return self.last
def addAfter(self, data, item):
if (self.last == None):
return None
temp = Node(data)
p = self.last.next
while p:
if (p.data == item):
temp.next = p.next
p.next = temp
if (p == self.last):
self.last = temp
return self.last
else:
return self.last
p = p.next
if (p == self.last.next):
print(item, "not present in the list")
break
def traverse(self):
if (self.last == None):
print("List is empty")
return
temp = self.last.next
while temp:
print(temp.data, end = " ")
temp = temp.next
if temp == self.last.next:
break
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
llist = CircularLinkedList()
last = llist.addToEmpty(6)
last = llist.addBegin(4)
last = llist.addBegin(2)
last = llist.addEnd(8)
last = llist.addEnd(12)
last = llist.addAfter(10,8)
llist.traverse()
# This code is contributed by
# Aditya SinghC#
using System;
public class GFG
{
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
};
static Node addToEmpty(Node last, int data)
{
// This function is only for empty list
if (last != null)
return last;
// Creating a node dynamically.
Node temp = new Node();
// Assigning the data.
temp.data = data;
last = temp;
// Creating the link.
last.next = last;
return last;
}
static Node addBegin(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
return last;
}
static Node addEnd(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
static Node addAfter(Node last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == null)
return null;
Node temp, p;
p = last.next;
do
{
if (p.data == item)
{
temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p.next;
} while(p != last.next);
Console.WriteLine(item + " not present in the list.");
return last;
}
static void traverse(Node last)
{
Node p;
// If list is empty, return.
if (last == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("List is empty.");
return;
}
// Pointing to first Node of the list.
p = last.next;
// Traversing the list.
do
{
Console.Write(p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
while(p != last.next);
}
// Driven code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node last = null;
last = addToEmpty(last, 6);
last = addBegin(last, 4);
last = addBegin(last, 2);
last = addEnd(last, 8);
last = addEnd(last, 12);
last = addAfter(last, 10, 8);
traverse(last);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-JiJavascript
在列表开头插入
要在列表的开头插入节点,请执行以下步骤:
1. 创建一个节点,比如 T。
2. 使 T -> next = last -> next。
3. 上一个 -> 下一个 = T。
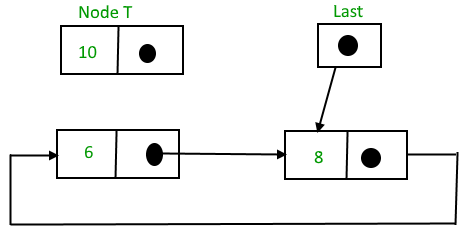
插入后,
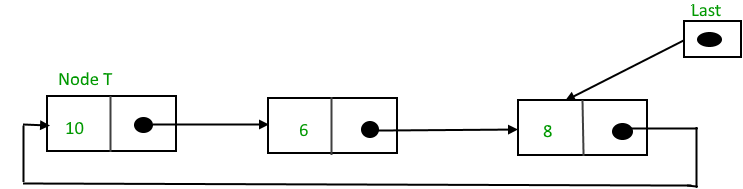
在列表的开头插入节点的函数,
C++
struct Node *addBegin(struct Node *last, int data)
{
if (last == NULL)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
// Creating a node dynamically.
struct Node *temp
= (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Assigning the data.
temp -> data = data;
// Adjusting the links.
temp -> next = last -> next;
last -> next = temp;
return last;
}
Java
static Node addBegin(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
// Creating a node dynamically
Node temp = new Node();
// Assigning the data
temp.data = data;
// Adjusting the links
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
return last;
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C#
static Node addBegin(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
// Creating a node dynamically
Node temp = new Node();
// Assigning the data
temp.data = data;
// Adjusting the links
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
return last;
}
// This code is contributed by Pratham76
Javascript
在列表末尾插入
要在列表末尾插入节点,请执行以下步骤:
1. 创建一个节点,比如 T。
2.使T -> next = last -> next;
3. 上一个 -> 下一个 = T。
4.最后=T。
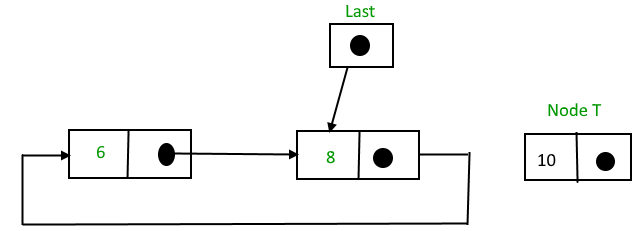
插入后,
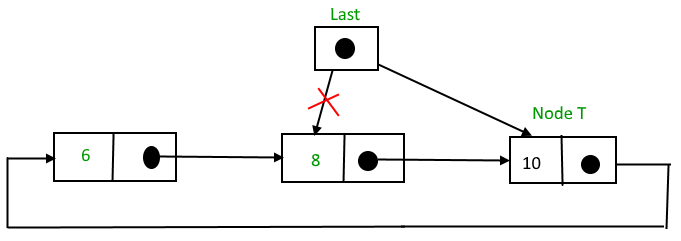
在列表末尾插入节点的函数
C++
struct Node *addEnd(struct Node *last, int data)
{
if (last == NULL)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
// Creating a node dynamically.
struct Node *temp =
(struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Assigning the data.
temp -> data = data;
// Adjusting the links.
temp -> next = last -> next;
last -> next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
Java
static Node addEnd(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
// Creating a node dynamically.
Node temp = new Node();
// Assigning the data.
temp.data = data;
// Adjusting the links.
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
蟒蛇3
def addEnd(self, data):
if (self.last == None):
return self.addToEmpty(data)
# Assigning the data.
temp = Node(data)
# Adjusting the links.
temp.next = self.last.next
self.last.next = temp
self.last = temp
return self.last
# This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
C#
static Node addEnd(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
// Creating a node dynamically.
Node temp = new Node();
// Assigning the data.
temp.data = data;
// Adjusting the links.
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
Javascript
在节点之间插入
要在两个节点之间插入一个节点,请执行以下步骤:
1. 创建一个节点,比如 T。
2. 搜索后面需要插入T的节点,假设该节点是P。
3.使T -> next = P -> next;
4. P -> 下一个 = T。
假设需要在节点值为10后插入12,
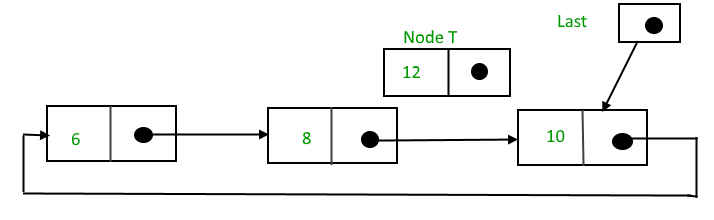
搜索和插入后,
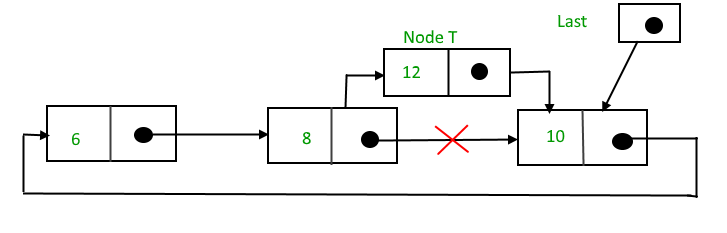
在List末尾插入节点的函数,
C++
struct Node *addAfter(struct Node *last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == NULL)
return NULL;
struct Node *temp, *p;
p = last -> next;
// Searching the item.
do
{
if (p ->data == item)
{
// Creating a node dynamically.
temp = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Assigning the data.
temp -> data = data;
// Adjusting the links.
temp -> next = p -> next;
// Adding newly allocated node after p.
p -> next = temp;
// Checking for the last node.
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p -> next;
} while (p != last -> next);
cout << item << " not present in the list." << endl;
return last;
}
Java
static Node addAfter(Node last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == null)
return null;
Node temp, p;
p = last.next;
do
{
if (p.data == item)
{
temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p.next;
} while(p != last.next);
System.out.println(item + " not present in the list.");
return last;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
下面是一个完整的程序,它使用上述所有方法来创建一个循环单向链表。
C++
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
struct Node *addToEmpty(struct Node *last, int data)
{
// This function is only for empty list
if (last != NULL)
return last;
// Creating a node dynamically.
struct Node *temp =
(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Assigning the data.
temp -> data = data;
last = temp;
// Creating the link.
last -> next = last;
return last;
}
struct Node *addBegin(struct Node *last, int data)
{
if (last == NULL)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
struct Node *temp =
(struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp -> data = data;
temp -> next = last -> next;
last -> next = temp;
return last;
}
struct Node *addEnd(struct Node *last, int data)
{
if (last == NULL)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
struct Node *temp =
(struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp -> data = data;
temp -> next = last -> next;
last -> next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
struct Node *addAfter(struct Node *last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == NULL)
return NULL;
struct Node *temp, *p;
p = last -> next;
do
{
if (p ->data == item)
{
temp = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp -> data = data;
temp -> next = p -> next;
p -> next = temp;
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p -> next;
} while(p != last -> next);
cout << item << " not present in the list." << endl;
return last;
}
void traverse(struct Node *last)
{
struct Node *p;
// If list is empty, return.
if (last == NULL)
{
cout << "List is empty." << endl;
return;
}
// Pointing to first Node of the list.
p = last -> next;
// Traversing the list.
do
{
cout << p -> data << " ";
p = p -> next;
}
while(p != last->next);
}
// Driven Program
int main()
{
struct Node *last = NULL;
last = addToEmpty(last, 6);
last = addBegin(last, 4);
last = addBegin(last, 2);
last = addEnd(last, 8);
last = addEnd(last, 12);
last = addAfter(last, 10, 8);
traverse(last);
return 0;
}
Java
class GFG
{
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
};
static Node addToEmpty(Node last, int data)
{
// This function is only for empty list
if (last != null)
return last;
// Creating a node dynamically.
Node temp = new Node();
// Assigning the data.
temp.data = data;
last = temp;
// Creating the link.
last.next = last;
return last;
}
static Node addBegin(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
return last;
}
static Node addEnd(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
static Node addAfter(Node last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == null)
return null;
Node temp, p;
p = last.next;
do
{
if (p.data == item)
{
temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p.next;
} while(p != last.next);
System.out.println(item + " not present in the list.");
return last;
}
static void traverse(Node last)
{
Node p;
// If list is empty, return.
if (last == null)
{
System.out.println("List is empty.");
return;
}
// Pointing to first Node of the list.
p = last.next;
// Traversing the list.
do
{
System.out.print(p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
while(p != last.next);
}
// Driven code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node last = null;
last = addToEmpty(last, 6);
last = addBegin(last, 4);
last = addBegin(last, 2);
last = addEnd(last, 8);
last = addEnd(last, 12);
last = addAfter(last, 10, 8);
traverse(last);
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
蟒蛇3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class CircularLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.last = None
# This function is only for empty list
def addToEmpty(self, data):
if (self.last != None):
return self.last
# Creating the newnode temp
temp = Node(data)
self.last = temp
# Creating the link
self.last.next = self.last
return self.last
def addBegin(self, data):
if (self.last == None):
return self.addToEmpty(data)
temp = Node(data)
temp.next = self.last.next
self.last.next = temp
return self.last
def addEnd(self, data):
if (self.last == None):
return self.addToEmpty(data)
temp = Node(data)
temp.next = self.last.next
self.last.next = temp
self.last = temp
return self.last
def addAfter(self, data, item):
if (self.last == None):
return None
temp = Node(data)
p = self.last.next
while p:
if (p.data == item):
temp.next = p.next
p.next = temp
if (p == self.last):
self.last = temp
return self.last
else:
return self.last
p = p.next
if (p == self.last.next):
print(item, "not present in the list")
break
def traverse(self):
if (self.last == None):
print("List is empty")
return
temp = self.last.next
while temp:
print(temp.data, end = " ")
temp = temp.next
if temp == self.last.next:
break
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
llist = CircularLinkedList()
last = llist.addToEmpty(6)
last = llist.addBegin(4)
last = llist.addBegin(2)
last = llist.addEnd(8)
last = llist.addEnd(12)
last = llist.addAfter(10,8)
llist.traverse()
# This code is contributed by
# Aditya Singh
C#
using System;
public class GFG
{
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
};
static Node addToEmpty(Node last, int data)
{
// This function is only for empty list
if (last != null)
return last;
// Creating a node dynamically.
Node temp = new Node();
// Assigning the data.
temp.data = data;
last = temp;
// Creating the link.
last.next = last;
return last;
}
static Node addBegin(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
return last;
}
static Node addEnd(Node last, int data)
{
if (last == null)
return addToEmpty(last, data);
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = last.next;
last.next = temp;
last = temp;
return last;
}
static Node addAfter(Node last, int data, int item)
{
if (last == null)
return null;
Node temp, p;
p = last.next;
do
{
if (p.data == item)
{
temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.next = p.next;
p.next = temp;
if (p == last)
last = temp;
return last;
}
p = p.next;
} while(p != last.next);
Console.WriteLine(item + " not present in the list.");
return last;
}
static void traverse(Node last)
{
Node p;
// If list is empty, return.
if (last == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("List is empty.");
return;
}
// Pointing to first Node of the list.
p = last.next;
// Traversing the list.
do
{
Console.Write(p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
while(p != last.next);
}
// Driven code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node last = null;
last = addToEmpty(last, 6);
last = addBegin(last, 4);
last = addBegin(last, 2);
last = addEnd(last, 8);
last = addEnd(last, 12);
last = addAfter(last, 10, 8);
traverse(last);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
输出:
2 4 6 8 10 12如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。