从其链表表示构造完整的二叉树
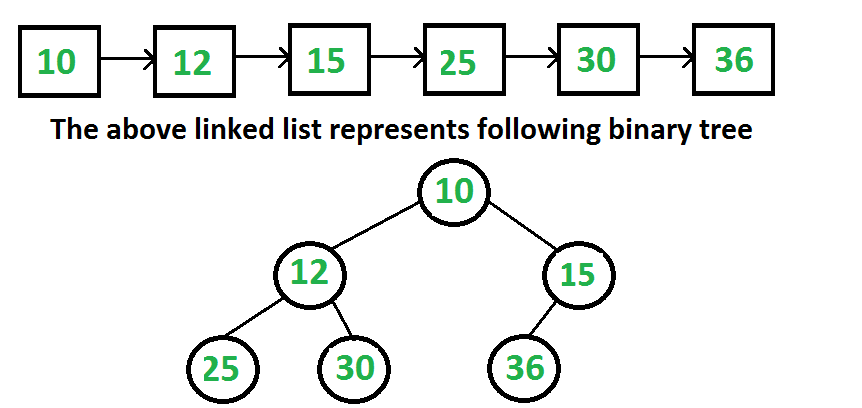
给定完全二叉树的链表表示,构造二叉树。完整的二叉树可以通过以下方法用数组表示。
如果根节点存储在索引 i 处,则其左子节点和右子节点分别存储在索引 2*i+1、2*i+2 处。
假设树以相同的方式由链表表示,我们如何将其转换为每个节点都有数据,左指针和右指针的二叉树的正常链接表示?在链表表示中,我们不能直接访问当前节点的子节点,除非我们遍历链表。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。
我们主要以顺序访问的形式给出层序遍历。我们知道链表的头部总是树的根。我们将第一个节点作为根节点,并且我们也知道接下来的两个节点是根节点的左右子节点。所以我们知道部分二叉树。这个想法是使用队列对部分构建的二叉树进行层序遍历,同时遍历链表。在每一步,我们从队列中取出父节点,将链表的下两个节点作为父节点的子节点,并将接下来的两个节点加入队列。
1.创建一个空队列。
2.将链表的第一个节点设为根节点,并将其入队。
3.直到我们到达列表的末尾,执行以下操作。
…………从队列中取出一个节点。这是当前的父级。
…………遍历列表中的两个节点,将它们添加为当前父节点的子节点。
………… c.将两个节点加入队列。
下面是在 C++ 中实现相同的代码。
C++
// C++ program to create a Complete Binary tree from its Linked List
// Representation
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Linked list node
struct ListNode
{
int data;
ListNode* next;
};
// Binary tree node structure
struct BinaryTreeNode
{
int data;
BinaryTreeNode *left, *right;
};
// Function to insert a node at the beginning of the Linked List
void push(struct ListNode** head_ref, int new_data)
{
// allocate node and assign data
struct ListNode* new_node = new ListNode;
new_node->data = new_data;
// link the old list off the new node
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// move the head to point to the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// method to create a new binary tree node from the given data
BinaryTreeNode* newBinaryTreeNode(int data)
{
BinaryTreeNode *temp = new BinaryTreeNode;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// converts a given linked list representing a complete binary tree into the
// linked representation of binary tree.
void convertList2Binary(ListNode *head, BinaryTreeNode* &root)
{
// queue to store the parent nodes
queue q;
// Base Case
if (head == NULL)
{
root = NULL; // Note that root is passed by reference
return;
}
// 1.) The first node is always the root node, and add it to the queue
root = newBinaryTreeNode(head->data);
q.push(root);
// advance the pointer to the next node
head = head->next;
// until the end of linked list is reached, do the following steps
while (head)
{
// 2.a) take the parent node from the q and remove it from q
BinaryTreeNode* parent = q.front();
q.pop();
// 2.c) take next two nodes from the linked list. We will add
// them as children of the current parent node in step 2.b. Push them
// into the queue so that they will be parents to the future nodes
BinaryTreeNode *leftChild = NULL, *rightChild = NULL;
leftChild = newBinaryTreeNode(head->data);
q.push(leftChild);
head = head->next;
if (head)
{
rightChild = newBinaryTreeNode(head->data);
q.push(rightChild);
head = head->next;
}
// 2.b) assign the left and right children of parent
parent->left = leftChild;
parent->right = rightChild;
}
}
// Utility function to traverse the binary tree after conversion
void inorderTraversal(BinaryTreeNode* root)
{
if (root)
{
inorderTraversal( root->left );
cout << root->data << " ";
inorderTraversal( root->right );
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// create a linked list shown in above diagram
struct ListNode* head = NULL;
push(&head, 36); /* Last node of Linked List */
push(&head, 30);
push(&head, 25);
push(&head, 15);
push(&head, 12);
push(&head, 10); /* First node of Linked List */
BinaryTreeNode *root;
convertList2Binary(head, root);
cout << "Inorder Traversal of the constructed Binary Tree is: \n";
inorderTraversal(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to create complete Binary Tree from its Linked List
// representation
// importing necessary classes
import java.util.*;
// A linked list node
class ListNode
{
int data;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// A binary tree node
class BinaryTreeNode
{
int data;
BinaryTreeNode left, right = null;
BinaryTreeNode(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
ListNode head;
BinaryTreeNode root;
// Function to insert a node at the beginning of
// the Linked List
void push(int new_data)
{
// allocate node and assign data
ListNode new_node = new ListNode(new_data);
// link the old list off the new node
new_node.next = head;
// move the head to point to the new node
head = new_node;
}
// converts a given linked list representing a
// complete binary tree into the linked
// representation of binary tree.
BinaryTreeNode convertList2Binary(BinaryTreeNode node)
{
// queue to store the parent nodes
Queue q =
new LinkedList();
// Base Case
if (head == null)
{
node = null;
return null;
}
// 1.) The first node is always the root node, and
// add it to the queue
node = new BinaryTreeNode(head.data);
q.add(node);
// advance the pointer to the next node
head = head.next;
// until the end of linked list is reached, do the
// following steps
while (head != null)
{
// 2.a) take the parent node from the q and
// remove it from q
BinaryTreeNode parent = q.peek();
BinaryTreeNode pp = q.poll();
// 2.c) take next two nodes from the linked list.
// We will add them as children of the current
// parent node in step 2.b. Push them into the
// queue so that they will be parents to the
// future nodes
BinaryTreeNode leftChild = null, rightChild = null;
leftChild = new BinaryTreeNode(head.data);
q.add(leftChild);
head = head.next;
if (head != null)
{
rightChild = new BinaryTreeNode(head.data);
q.add(rightChild);
head = head.next;
}
// 2.b) assign the left and right children of
// parent
parent.left = leftChild;
parent.right = rightChild;
}
return node;
}
// Utility function to traverse the binary tree
// after conversion
void inorderTraversal(BinaryTreeNode node)
{
if (node != null)
{
inorderTraversal(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
inorderTraversal(node.right);
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.push(36); /* Last node of Linked List */
tree.push(30);
tree.push(25);
tree.push(15);
tree.push(12);
tree.push(10); /* First node of Linked List */
BinaryTreeNode node = tree.convertList2Binary(tree.root);
System.out.println("Inorder Traversal of the"+
" constructed Binary Tree is:");
tree.inorderTraversal(node);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal Python
# Python program to create a Complete Binary Tree from
# its linked list representation
# Linked List node
class ListNode:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# Binary Tree Node structure
class BinaryTreeNode:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Class to convert the linked list to Binary Tree
class Conversion:
# Constructor for storing head of linked list
# and root for the Binary Tree
def __init__(self, data = None):
self.head = None
self.root = None
def push(self, new_data):
# Creating a new linked list node and storing data
new_node = ListNode(new_data)
# Make next of new node as head
new_node.next = self.head
# Move the head to point to new node
self.head = new_node
def convertList2Binary(self):
# Queue to store the parent nodes
q = []
# Base Case
if self.head is None:
self.root = None
return
# 1.) The first node is always the root node,
# and add it to the queue
self.root = BinaryTreeNode(self.head.data)
q.append(self.root)
# Advance the pointer to the next node
self.head = self.head.next
# Until th end of linked list is reached, do:
while(self.head):
# 2.a) Take the parent node from the q and
# and remove it from q
parent = q.pop(0) # Front of queue
# 2.c) Take next two nodes from the linked list.
# We will add them as children of the current
# parent node in step 2.b.
# Push them into the queue so that they will be
# parent to the future node
leftChild= None
rightChild = None
leftChild = BinaryTreeNode(self.head.data)
q.append(leftChild)
self.head = self.head.next
if(self.head):
rightChild = BinaryTreeNode(self.head.data)
q.append(rightChild)
self.head = self.head.next
#2.b) Assign the left and right children of parent
parent.left = leftChild
parent.right = rightChild
def inorderTraversal(self, root):
if(root):
self.inorderTraversal(root.left)
print root.data,
self.inorderTraversal(root.right)
# Driver Program to test above function
# Object of conversion class
conv = Conversion()
conv.push(36)
conv.push(30)
conv.push(25)
conv.push(15)
conv.push(12)
conv.push(10)
conv.convertList2Binary()
print "Inorder Traversal of the contructed Binary Tree is:"
conv.inorderTraversal(conv.root)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// C# program to create complete
// Binary Tree from its Linked List
// representation
// importing necessary classes
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// A linked list node
public class ListNode
{
public int data;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// A binary tree node
public class BinaryTreeNode
{
public int data;
public BinaryTreeNode left, right = null;
public BinaryTreeNode(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
ListNode head;
BinaryTreeNode root;
// Function to insert a node at
// the beginning of the Linked List
void push(int new_data)
{
// allocate node and assign data
ListNode new_node = new ListNode(new_data);
// link the old list off the new node
new_node.next = head;
// move the head to point to the new node
head = new_node;
}
// converts a given linked list representing a
// complete binary tree into the linked
// representation of binary tree.
BinaryTreeNode convertList2Binary(BinaryTreeNode node)
{
// queue to store the parent nodes
Queue q =
new Queue();
// Base Case
if (head == null)
{
node = null;
return null;
}
// 1.) The first node is always the root node, and
// add it to the queue
node = new BinaryTreeNode(head.data);
q.Enqueue(node);
// advance the pointer to the next node
head = head.next;
// until the end of linked list is reached,
// do the following steps
while (head != null)
{
// 2.a) take the parent node from the q and
// remove it from q
BinaryTreeNode parent = q.Peek();
BinaryTreeNode pp = q.Dequeue();
// 2.c) take next two nodes from the linked list.
// We will add them as children of the current
// parent node in step 2.b. Push them into the
// queue so that they will be parents to the
// future nodes
BinaryTreeNode leftChild = null, rightChild = null;
leftChild = new BinaryTreeNode(head.data);
q.Enqueue(leftChild);
head = head.next;
if (head != null)
{
rightChild = new BinaryTreeNode(head.data);
q.Enqueue(rightChild);
head = head.next;
}
// 2.b) assign the left and right children of
// parent
parent.left = leftChild;
parent.right = rightChild;
}
return node;
}
// Utility function to traverse the binary tree
// after conversion
void inorderTraversal(BinaryTreeNode node)
{
if (node != null)
{
inorderTraversal(node.left);
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
inorderTraversal(node.right);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
/* Last node of Linked List */
tree.push(36);
tree.push(30);
tree.push(25);
tree.push(15);
tree.push(12);
/* First node of Linked List */
tree.push(10);
BinaryTreeNode node = tree.convertList2Binary(tree.root);
Console.WriteLine("Inorder Traversal of the"+
" constructed Binary Tree is:");
tree.inorderTraversal(node);
}
}
/* This code is contributed PrinciRaj1992 */ Javascript
输出:
Inorder Traversal of the constructed Binary Tree is:
25 12 30 10 36 15时间复杂度:上述解决方案的时间复杂度为 O(n),其中 n 是节点数。