计算完整二叉树中的节点数
给定由N个节点组成的完全二叉树的根,任务是找出给定二叉树中的节点总数。
例子:
Input:
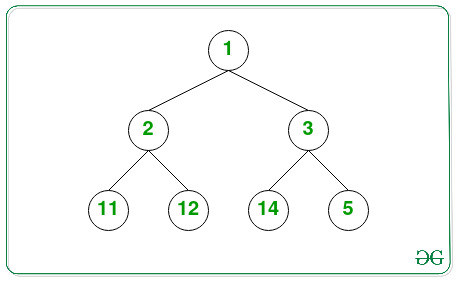
Output: 7
Input:
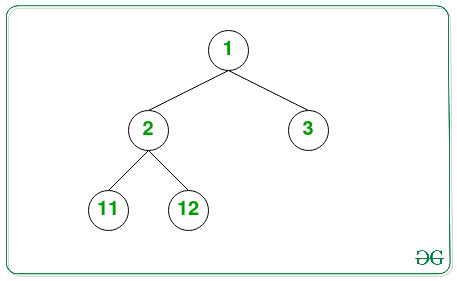
Output: 5
朴素方法:解决给定树的简单方法是对给定树执行 DFS 遍历并计算其中的节点数。遍历后,打印获得的节点总数。
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(1)
有效的方法:上述方法也可以通过以下事实进行优化:
A complete binary tree has (2h – 1) nodes in total.
按照这个逻辑,在第一种情况下,比较左子树的高度和右子树的高度。如果它们相等,则它是一棵完整的树,那么答案将是2^height – 1 。否则,如果不相等,则递归调用左子树和右子树计算节点数。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 定义一个函数left_height(root)并通过遍历根的左方向找到给定 Tree 的左高度,并将其存储在一个变量中,比如leftHeight 。
- 定义一个函数right_height(root)并通过遍历根的正确方向找到给定 Tree 的正确高度,并将其存储在变量中,比如rightHeight 。
- 为当前根值找到给定树的左右高度,如果相等,则返回(2 height – 1)的值作为节点的结果计数。
- 否则,递归调用左右子树的函数并返回它们的总和 + 1作为节点的结果计数。
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a Tree Node
class node {
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
node* newNode(int data);
// Function to get the left height of
// the binary tree
int left_height(node* node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node) {
ht++;
node = node->left;
}
// Return the left height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the right height
// of the binary tree
int right_height(node* node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node) {
ht++;
node = node->right;
}
// Return the right height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the count of nodes
// in complete binary tree
int TotalNodes(node* root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Find the left height and the
// right heights
int lh = left_height(root);
int rh = right_height(root);
// If left and right heights are
// equal return 2^height(1<left)
+ TotalNodes(root->right);
}
// Helper function to allocate a new node
// with the given data
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return (Node);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(9);
root->right->right = newNode(8);
root->left->left->left = newNode(6);
root->left->left->right = newNode(7);
cout << TotalNodes(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by aditya kumar (adityakumar129) C
// C program for the above approach
#include
#include
// Structure of a Tree Node
typedef struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
}node;
// Helper function to allocate a new node
// with the given data
node* newNode(int data)
{
node * Node = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return (Node);
}
// Function to get the left height of
// the binary tree
int left_height(node* node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node) {
ht++;
node = node->left;
}
// Return the left height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the right height
// of the binary tree
int right_height(node* node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node) {
ht++;
node = node->right;
}
// Return the right height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the count of nodes
// in complete binary tree
int TotalNodes(node* root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Find the left height and the
// right heights
int lh = left_height(root);
int rh = right_height(root);
// If left and right heights are
// equal return 2^height(1<left) + TotalNodes(root->right);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(9);
root->right->right = newNode(8);
root->left->left->left = newNode(6);
root->left->left->right = newNode(7);
printf("%d",TotalNodes(root));
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by aditya kumar (adityakumar129) Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Structure of a Tree Node
static class node {
int data;
node left;
node right;
};
// Function to get the left height of
// the binary tree
static int left_height(node node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node!=null) {
ht++;
node = node.left;
}
// Return the left height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the right height
// of the binary tree
static int right_height(node node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node!=null) {
ht++;
node = node.right;
}
// Return the right height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the count of nodes
// in complete binary tree
static int TotalNodes(node root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Find the left height and the
// right heights
int lh = left_height(root);
int rh = right_height(root);
// If left and right heights are
// equal return 2^height(1<Python3
# Python program for the above approach
# Structure of a Tree Node
class node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.val = key
# Function to get the left height of
# the binary tree
def left_height(node):
ht = 0
while(node):
ht += 1
node = node.left
# Return the left height obtained
return ht
# Function to get the right height
# of the binary tree
def right_height(node):
ht = 0
while(node):
ht += 1
node = node.right
# Return the right height obtained
return ht
# Function to get the count of nodes
# in complete binary tree
def TotalNodes(root):
# Base case
if(root == None):
return 0
# Find the left height and the
# right heights
lh = left_height(root)
rh = right_height(root)
# If left and right heights are
# equal return 2^height(1<C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
public class GFG{
// Structure of a Tree Node
class node {
public int data;
public node left;
public node right;
};
// Function to get the left height of
// the binary tree
static int left_height(node node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node != null) {
ht++;
node = node.left;
}
// Return the left height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the right height
// of the binary tree
static int right_height(node node)
{
int ht = 0;
while (node != null) {
ht++;
node = node.right;
}
// Return the right height obtained
return ht;
}
// Function to get the count of nodes
// in complete binary tree
static int TotalNodes(node root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Find the left height and the
// right heights
int lh = left_height(root);
int rh = right_height(root);
// If left and right heights are
// equal return 2^height(1<Javascript
输出:
9时间复杂度: O((log N) 2 )
辅助空间: O(log N) 因为递归堆栈空间